Water supply system of an apartment building diagram. Open and closed hot water supply system - diagrams and calculation example
Hot water supply networks have much in common with cold water supply networks. The hot water supply network comes with a lower and top wiring. The hot water supply network can be dead-end and looped, but, unlike cold water supply networks, looping the network is necessary to maintain a high water temperature.
Simple (dead-end) hot water networks are used in small low-rise buildings, in domestic premises of industrial buildings and in buildings with stable hot water consumption (baths, laundries).
Schemes of hot water supply networks with a circulation pipeline should be used in residential buildings, hotels, dormitories, medical institutions, sanatoriums and rest homes, in preschool institutions, as well as in all cases where uneven and short-term water withdrawal is possible.
Typically, a hot water supply network consists of horizontal supply lines and vertical distribution pipelines-risers, from which apartment distribution lines are arranged. Hot water supply risers are laid as close to the appliances as possible.
In addition, hot water supply networks are divided into two-pipe (with looped risers) and single-pipe (with dead-end risers).
Let's consider some of the large number of possible hot water supply network schemes.
When the lines are routed from the top (Fig. 14), the collection circulation pipeline is closed in the form of a ring. The circulation of water in the pipeline ring in the absence of water intake is carried out under the influence of gravitational pressure that arises in the system due to the difference in the density of cooled and hot water. The water cooled in the risers falls down into the water heater and displaces water with a higher temperature from it. Thus, continuous water exchange occurs in the system.
Rice. 10 Dead-end hot water supply circuit:
1 - water heater; 2 - distribution risers.
R 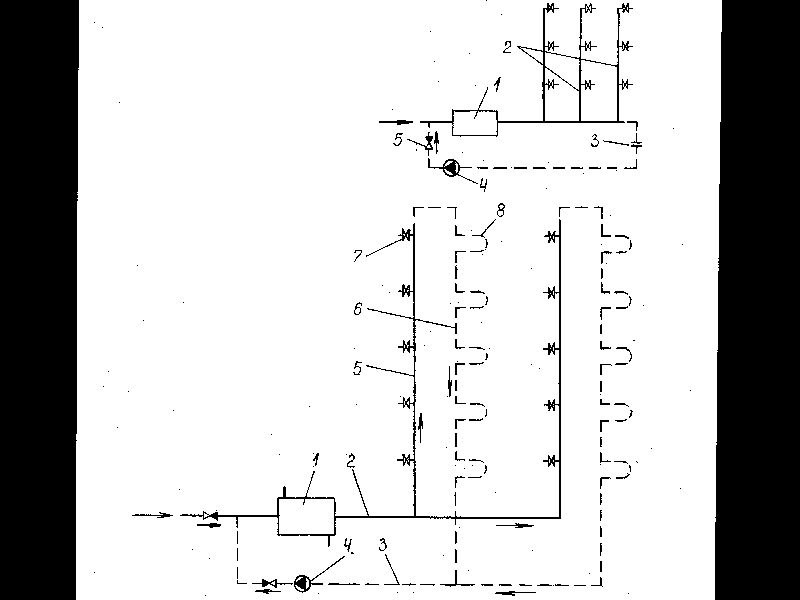 is. 9 Scheme with upper distribution of the supply line:
is. 9 Scheme with upper distribution of the supply line:
1 - water heater; 2 - supply riser; 3 - distribution risers; 4 - circulation network.
Rice. 11 Scheme with looped main pipelines:
1 - water heater; 2 - distribution risers; 3 - diaphragm (additional hydraulic resistance); 4 - circulation pump; 5 - check valve.
Rice. 12 Two-pipe scheme hot water supply:
1 - water heater; 2 - supply line; 3 - circulation line; 4 - circulation pump; 5 - supply riser; 6 - circulation riser; 7 - water intake; 8 - heated towel rails.

Rice. 13 Scheme with one unifying circulation riser:
1 - water heater; 2 - supply line; 3 - circulation line; 4 - circulation pump; 5 - water risers; 6 - circulation riser; 7 - check valve.

Rice. 14 Sectional single-pipe hot water supply circuit:
1 - supply line; 2 - circulation line; 3 - idle supply riser; 4 - water riser; 5 - ring jumper; 6 - shut-off valves; 7 - heated towel rail.
The dead-end network diagram (Fig. 15) has the lowest metal consumption, but due to significant cooling and irrational discharge of cooled water, it is used in residential buildings up to 4 floors high, if the risers do not have a heated towel rail and length main pipes small If the length of the main pipes is large and the height of the risers is limited, a scheme with looped supply and circulation lines is used and a circulation pump is installed on them (Fig. 16).
The most widespread is the two-pipe scheme (Fig. 17), in which circulation through the risers and mains is carried out using a pump that takes water from the return line and supplies it to the water heater. A system with one-sided connection of water points to the supply riser and installation of heated towel rails on the return riser is the most common version of such a scheme. The two-pipe scheme turned out to be reliable in operation and convenient for consumers, but it is characterized by high metal consumption.
To reduce metal consumption in last years began to use a scheme in which several supply risers are combined by a jumper with one circulation riser (Fig. 18).
Recently, diagrams of a single-pipe hot water supply system with one idle supply riser per group of water risers have appeared (Fig. 19). The idle riser is isolated and installed in pairs with one water riser or in a sectional unit consisting of 2-3 looped water risers. The main purpose of the idle riser is to transport hot water from the main to the upper lintel and then to the water risers. In each riser, independent additional circulation occurs due to the gravitational pressure that arises in the circuit of the sectional unit due to the cooling of water in the water risers. The idle riser helps the correct distribution of flows within the sectional unit.
Water supply installation apartment building represents a whole range of works aimed at improving the building and ensuring comfortable living. The main task when creating the distribution is to provide all apartments with a stable water flow and normalize the pressure. It should also be taken into account that in order to ensure a comfortable stay, it is necessary to organize not only a stable supply of cold, but also hot water, as well as sewerage.
In order to implement the project, numerous computational and research papers. In particular, we are talking about the hydraulic calculation of hot and cold water, annular diameter and water loss, etc. Moreover, when constructing a residential apartment building, it is necessary to take into account the organization of a fire water supply system, which will allow the fire area to be quickly localized in the event of a fire.
Be that as it may, the initial task is to determine the location of water intake, that is, the source. When it comes to apartment buildings within the city or in the immediate vicinity of a populated area, the issue is resolved without variation, the source is selected central water supply. Decentralized water supply is carried out only when the construction of a new residential area is carried out in a place where pipes are laid centralized water supply impossible.
Types of work performed in an apartment building
As already noted, unlike the private sector, organizing water supply in an apartment building represents a whole range of work. It includes the following provisions:
- Studying the object and taking measurements;
- Creating a project;
- The installation itself;
- Testing.
At first glance, it may seem that everything is quite standard and simple, but in fact, in a multi-story building you need to devote much more time to developing a project than in a private house. After all, in order for the pressure in apartments to be stable and sufficient for comfortable living, it is necessary to clearly calculate the number of floors and water pressure in the central pipeline. The stability of the pressure in the connected pipes to each apartment depends on the correctness of the calculations. After all, it is necessary to take into account the dependence: the higher the floor, the lower the pressure, which is why special pressure regulators are installed in high-rise buildings.
Installation is carried out on special supports or fittings and attached to the walls of the building. Considering that the load on the structure when installing pipes is quite high, this stage also requires clear calculations.
Stages of water supply installation
Installation of water supply in an apartment building is divided into the following stages:
- Digging a trench to connect the water supply to the central pipe;
- Installation of a supporting structure that will hold the risers;
- Installation of risers and connection to the main line;
- Pipeline layout in apartments;
- Sewage installation;
- Commissioning works.
After test runs, a pipe suitable for the centralized main is buried to a depth below the freezing depth of the soil.
Terms of cooperation
Please note that we only employ professionals. high level with solid work experience. All brigades are equipped necessary equipment and special equipment. Our company has the appropriate permit and license to carry out work on connecting and organizing water supply in apartment buildings.
When placing an order for work, we enter into an agreement with the customer, in accordance with which the following are discussed and approved:
- Deadlines;
- Materials (their quantity and type);
- Price.
Please note that the final cost does not change and is announced only after final calculations.
In order for any residential building to function normally, it is necessary to install a water supply system. Her competent device will ensure timely supply and sufficient water pressure. This article will discuss in detail the hot water supply scheme, types of connection and its features in an apartment building.
Water supply and sanitation scheme - Photo 01
What is special about the water supply of an apartment building?
It is very difficult to provide water to a building with a large number of storeys. After all, the house consists of many apartments with separate bathrooms and plumbing fixtures. In other words, water supply schemes in apartment buildings are a kind of complex with separate pipe distributions, pressure regulators, filters and metering equipment.
Most often, residents of high-rise buildings use water from the central water supply. With the help of a water supply, it is supplied to individual plumbing fixtures under a certain pressure. Often water is purified using chlorination.
Composition of the central water supply system
Centralized water supply schemes in multi-storey buildings consist of a distribution network, water intake structures and treatment plants. Before getting into the apartment, water travels a long way from the pumping station to the reservoir. Only after purification and disinfection is water sent to the distribution network. With the help of the latter, water is supplied to appliances and equipment. Pipes of the central hot water supply circuit multi-storey building can be made of copper, metal-plastic and steel.

Schematic diagram centralized system water supply – Photo 02
The latter type of material is practically not used in modern buildings.
Types of water supply schemes
There are three types of water supply system:
- collector;
- sequential;
- combined (mixed).
IN Lately when in apartments it is increasingly common a large number of plumbing equipment, use a collector wiring diagram. It is the best option for the normal functioning of all devices. The collector-type hot water supply scheme eliminates pressure drops at different connection points. This is the main advantage of this system.
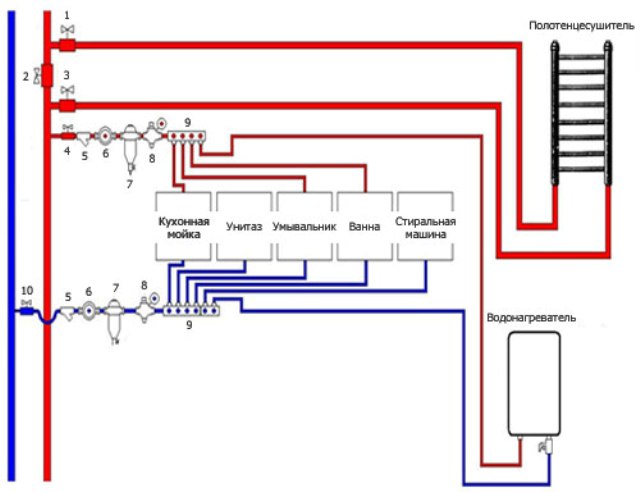
Scheme collector wiring pipes – Photo 03
If we consider the diagram in more detail, we can conclude that there will be no problems with using the plumbing equipment for its intended purpose at the same time. The essence of the connection is that each individual water consumer is connected to the cold and hot water supply riser collectors separately. The pipes do not have many branches, so the likelihood of leakage is very low. Such water supply schemes in multi-storey buildings are easy to maintain, but the cost of the equipment is quite high.
According to experts, the collector hot water supply system requires the installation of a more complex installation of plumbing fixtures. However, these negative aspects are not so critical, especially considering the fact that collector circuit There are many advantages, for example - hidden installation pipes and metering individual characteristics equipment.
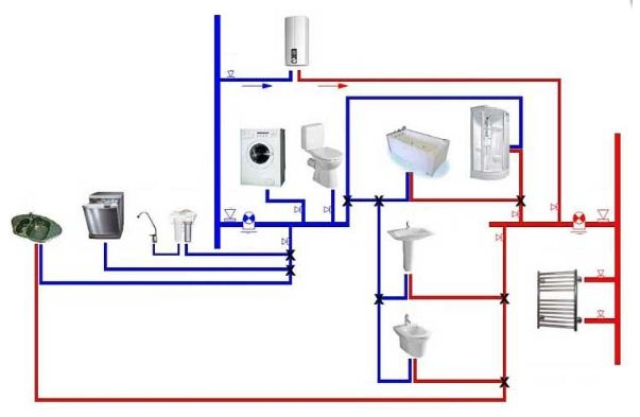
Sequential layout of water supply pipes in an apartment - Photo 04
A sequential hot water supply circuit for a multi-storey building is the simplest wiring method. This system is time-tested; it was put into operation during the Soviet era. The essence of its device is that the cold and hot water supply pipelines are parallel to each other. Engineers advise using this system in apartments with one bathroom and a small amount of plumbing equipment.
Popularly, such a hot water supply scheme for a multi-storey building is called a tee scheme. That is, from the main highways there are branches that are connected to each other by tees. Despite the ease of installation and savings consumables, this scheme has several main disadvantages:
- In the event of a leak, it is difficult to look for damaged areas.
- Inability to supply water to a separate plumbing fixture.
- Difficulty in accessing pipes in case of breakdown.
Hot water supply for an apartment building. Scheme
Pipe connections are divided into two types: to the hot and cold water supply riser. Briefly they are called cold water and hot water. The hot water supply system of an apartment building deserves special attention. The DHW network diagram consists of two types of wiring - lower and upper. To save high temperature Looped wires are often used in pipelines. The gravitational pressure forces the water to circulate in the ring, despite the absence of water intake. In the riser it cools and enters the heater. Water with a higher temperature is supplied to the pipes. This is how continuous circulation of the coolant occurs.
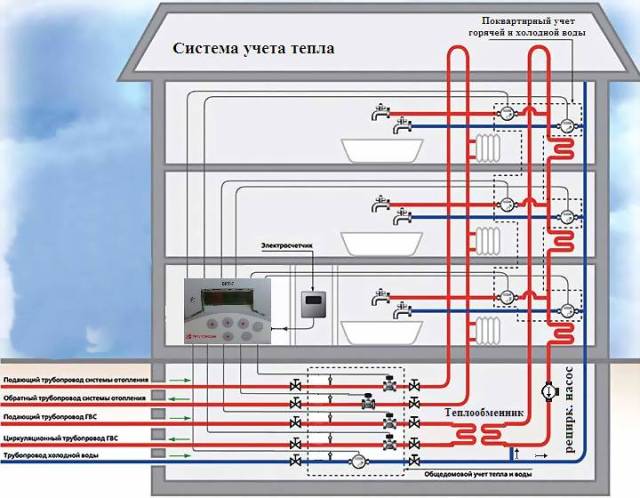
Hot water supply device at home - Photo 05
Dead-end highways are also not uncommon, but most often they can be found in utility rooms of industrial facilities and in small residential buildings with low storeys. If water selection is planned intermittently, then a circulation pipeline is used. Engineers advise using hot water supply in apartment buildings (the diagram was discussed above) with a number of floors of no more than 4. A pipeline with a dead-end riser is also found in dormitories, sanatoriums and hotels. Dead-end network pipes have a lower metal consumption and therefore cool faster.
DHW networks include a horizontal main pipeline and distribution risers. The latter provide pipe distribution to individual objects - apartments. DHW is installed as close as possible to plumbing equipment.
For buildings with a large length of main pipes, schemes with circulation and looped supply pipelines are used. A prerequisite is the installation of a pump to maintain circulation and constant water exchange.
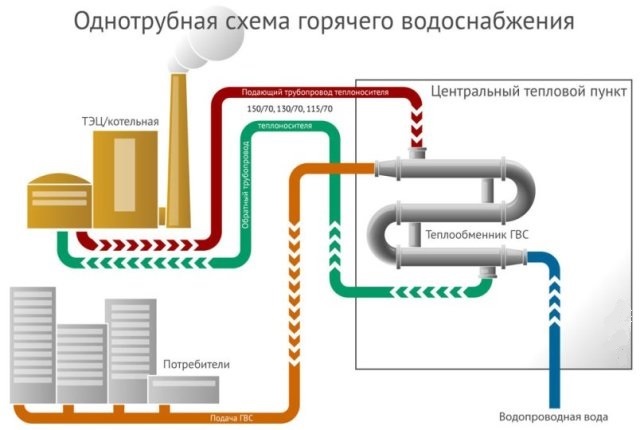
Single-pipe DHW diagram— Photo 06

Two-pipe DHW circuit - Photo 07
Modern builders and engineers are increasingly resorting to the use of two-pipe DHW systems. The principle of operation is that the pump takes water from the return line and supplies it to the heater. This pipeline has a higher metal consumption and is considered the most reliable for consumers.
Perhaps everyone knows that the huge boiler-cooling towers and striped chimneys emitting smoke, which are visible from anywhere in the city, belong to the thermal power plant. Moreover, many people know that these colossuses provide our homes with light, heating and hot water. But what exactly is the process of heat generation and how cooling tower columns are involved in it is a rather confusing question.
Consumables
The entire process of CHP operation begins with water preparation. Since it is used here as the main coolant, it requires preliminary cleaning before entering the steam boiler, where the main metamorphoses will occur with it. To prevent scale on the walls of boilers, the water is first softened - its hardness sometimes needs to be reduced by 4000 times, and it also needs to be removed from various impurities and suspended matter.
As a rule, gas, coal or peat are used as fuel for heating water boilers at various power plants. The combustion of these materials releases thermal energy, which is used at the station to operate the entire power unit. Coal is ground before use, and the incoming gas is purified from mechanical impurities, hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide.
Steam production
The huge steam boiler in the turbine hall - the height of a 9-story building is not the limit - can be called the heart of the thermal power plant. It is powered by prepared fuel, releasing a huge amount of energy. Under its force, the water in the boiler turns into steam with an outlet temperature of almost 600 degrees. Under the pressure of this steam, the generator blades rotate, resulting in the creation of electricity.
The thermal power plant also produces thermal energy intended for heating and hot water supply to the region and city. For this purpose, there are selections on the turbine that remove part of the heated steam before it reaches the condenser. The exhausted steam is transferred to a network heater, which acts as a heat exchanger.
Heating network
Once in the tubes of network heaters, the water is heated and transmitted through underground pipelines further into heating network due to pumps driving water through pipes. Heating networks, as a rule, carry water at 70-150 degrees - it all depends on the temperature outside: the lower the degree outside, the hotter the coolant.
It becomes a transfer point for coolant. It serves an entire system of buildings, an enterprise or a microdistrict at once. This is a kind of intermediary between the object that creates heat and the direct consumer. If water in a boiler room is heated due to fuel combustion, then the central heating station works with an already heated coolant.
 Hot water recipe
Hot water recipe
The supply of coolant ends at the entrance to the central heating substation or ITP (individual heating substation) - so, the coolant is transferred to further actions in the hands of the HOA or other management company. It is at the heating point that the hot water, with which we are accustomed to dealing - the water coming here from the thermal power plant heats clean cold water from the water intakes and turns it into the very hot water that flows in our taps.
After heating the building and room, this water gradually cools, its temperature drops to 40-70 degrees. Part like this water is coming for mixing with the coolant and supplied to our taps with hot water. The road to the other part is back to the station, here the cooled water will be warmed by network heat exchangers.
What are cooling towers for?
The majestic and massive towers, called cooling towers, are not the reactors and centers of action in a thermal power plant and actually play a supporting role. Surprisingly, they are used in heating plants to cool water. But why let water that is constantly heated cool?
Cooling towers use the second part of the “return”, which has gone through a heating-cooling cycle. But its temperature is still quite high: 50 degrees is too high for further use. The water that has been in cooling towers is used to cool the condensers of steam turbines. This is necessary so that the steam that has passed through the steam turbine can enter the condenser and condense on the cold pipes inside it. These pipes are precisely cooled by the water that has passed through the cooling tower, the temperature of which is now about 20 degrees. If they are not cooled, then there will be no steam flow through the turbine, and then it will not be able to work. The condenser will again turn the steam into water, which will be recirculated.
Description:
Water supply networks are accepted as ring ones. The material of pipelines has a great influence on reliability; overgrowth or corrosion of which leads to deterioration of hydraulic characteristics, accidents and interruptions in the supply of water to consumers. Right choice pipeline material, use of copper and plastic pipes, little susceptible to corrosion and overgrowth, significantly increases the reliability and durability of systems.
Water supply and sanitation in high-rise buildings
Towards the publication of the book ""
Today, when in major cities The construction of high-rise buildings is actively developing in Russia; specialists are in dire need of regulatory documents and practical literature more than ever. Existing standards and the design rules for multifunctional high-rise buildings in Moscow (MGSN 4.19–2005) are temporary. In this regard, NP "ABOK" decided to summarize the existing experience in the design and operation of high-rise buildings and publish the book Engineering Equipment of High-Rise Buildings. Considerable attention is paid to the issues of water supply and sanitation of high-rise buildings.
Increasing the hydraulic reliability of domestic and drinking water supply systems is ensured by zoning them according to the height of the building. remote control. It is advisable to integrate these systems into automated system building management.
Water supply networks are accepted as ring ones. The material of pipelines has a great influence on reliability; overgrowth or corrosion of which leads to deterioration of hydraulic characteristics, accidents and interruptions in the supply of water to consumers. The correct choice of pipeline material, the use of copper and plastic pipes, which are less susceptible to corrosion and overgrowth, significantly increases the reliability and durability of the systems.
Water tanks, providing temporary backup, create a regulating and emergency supply of water in the building and stabilize the water pressure in the system.
To reduce the hydraulic instability of internal networks, when the water temperature changes sharply when the neighbors' faucets are turned on or in a nearby room, it is advisable to use manifold apartment wiring, when each faucet is connected by a separate pipeline to a common manifold connected to the riser.
Based on these considerations, in elite and commercial high-rise buildings, the risers of the water supply system are laid in the niche of the staircase and elevator hall, from where hot and cold water pipelines are introduced into the apartment. The system is equipped with hot and cold water meters, which, together with filters and pressure regulators, are installed in distribution cabinets in the staircase and elevator hall. Payment for actually consumed resources is carried out according to meter readings. This solution allows, if necessary, to cut off one of the consumers, check the pressure, and adjust the consumers. Localization of the damaged area allows minimizing the damage from the accident, while the water supply to neighboring apartments does not stop. Wiring to apartments and in the apartment is carried out, as for the heating system, from PEX pipes, usually placed behind a false ceiling (or in the floor). Since the wiring from the shut-off valve to the water supply fittings is carried out without breaks, in “one pipe,” this circuit is highly reliable and resistant to leaks. In turn, the smooth inner surface of the cross-linked polyethylene pipe allows you to avoid overgrowing of the pipe even when using very hard water. The water supply system is also divided into zones by height, and in the systems described, the risers of the systems are laid parallel in the niches of the staircase-elevator assembly and have easy access for maintenance and repair. By analogy with heating systems, all hot water supply risers are equipped with compensators and fixed supports.
The calculated circulation is set using control and balancing valves. The use of modern regulators allows the use of one group of hot water supply heat exchangers for 2–3 zones in an individual heating point. When constructing a building, fire water supply must be installed first. Let this system be in a “dry” mode, but it must be possible to supply water into it at any time and extinguish, for example, a fire household waste on any floor.
Temporary water supply to facilities under construction must ensure fire-fighting water flow. A temporary fire-fighting booster pump can be installed on such a water supply system, which can be turned on manually and, in the event of a fire, extinguish the fire. Currently, cast iron socketless pipes are widely used in all new buildings. Such pipes do not burn, unlike PVC pipes, which burn during a fire, transmit fire to adjacent floors and release toxic substances. Besides, cast iron pipes soundproofed, which is important for luxury buildings. One of the main advantages of this system is the ability to quickly dismantle individual sections of sunbeds on the technical floor in order to remove cement-sand and paint-adhesive deposits, which cover up to 3/4 of the section of sunbeds in two weeks.
For high-quality cleaning of sun loungers with the Cobra machine with simultaneous washing, a system with a cleaning device made of two half-outlets is used so that the open socket is located above the main pipe.
Special attention should be given to high-rise building releases. Since buildings have significant subsidence, outlets in the outer walls are not sealed tightly, but a special damping device is used to prevent the outlet pipe from breaking. This also applies to all other networks. Another problem is water drainage in case of fire.
If sprinkling of apartments is provided, the requirement for 100% waterproofing of apartments (and not just the bathroom area) must be met, since leaks to the lower floors will lead to the need for compensation for damage. For inter-apartment halls, it is necessary to make floor slopes towards the intake openings (the ladder is not suitable in this case, since it has a small throughput) and bring out the pipes at the floor level of the inter-apartment hall (with discharge into the drainage network).
The sixth chapter of the book “Engineering equipment of high-rise buildings” is entirely devoted to issues of water supply and sanitation. The following took part in its creation: A. Ya. Dobromyslov, V. N. Isaev, A. N. Kolubkov, M. G. Mkhitaryan, S. A. Nikonov. The following is an abbreviated version of one of the articles in the chapter.
6.4. FEATURES OF DESIGN AND OPERATION OF WATER SUPPLY AND SEWERAGE SYSTEMS OF HIGH-RISE RESIDENTIAL BUILDINGS
Modern high-rise buildings are either infill development or a developed stylobate with several towers. High-rise buildings are zoned vertically - divided into zones of a certain height, separated by technical floors. On the technical floors, water supply networks are laid out and prefabricated sewerage networks are laid. Availability of technical floors - best option for exploitation, but, as a rule, investors try to do without them. The height of the zone is determined by the value of the permissible hydrostatic pressure in the lower devices or other elements of the systems, as well as the possibility of placing equipment and communications on technical floors. The engineering equipment area, as a rule, coincides with the boundaries of the fire compartment in height.
6.4.1. Water supply
Depending on the architectural and planning solutions, the following options for installing water supply systems are used:
– installation of an ITP with booster pumping stations and hot water supply heat exchangers for each high-rise zone (fire compartment) for a single building;
– installation of an ITP with one group of hot water supply heat exchangers and booster pumping stations for cold and hot water supply under each or a group of buildings for each high-rise zone (fire compartment) in the case of a developed complex with a stylobate part. This scheme was successfully implemented at the facilities " Scarlet Sails", "Sparrow Hills" and "Triumph Palace". In these horizontally and vertically developed complexes, the laying of pipelines from ITP to buildings is provided in dedicated technical corridors, together with other pipelines (Fig. 6.4, 6.5).
As a rule, capacitive electric boilers are also installed in ITPs or under buildings, providing uninterrupted hot water supply during planned outages in the heating network. The capacity of the boilers is selected based on ensuring a 1.5-hour maximum hourly flow of hot water supply with an 8-hour period of water heating (Fig. 6.6). There are two fundamentally different approaches
Abroad, especially in Asia, the vertical supply of water to building zones is carried out by sequentially supplying water to tanks installed on technical floors. In this case, the lower pump supplies water to the tank on the middle technical floor, from this tank another pump supplies water to the tank on the next floor, etc. From the tanks, water flows downwards by gravity, providing water to the underlying floors. Tanks are usually two-section. When it is necessary to disinfect and clean a section of the tank, water supply carried out from the second section. Closed systems were organized for each zone, especially since modern pumping equipment for water supply (not special pumps) allows maintaining pressure up to 400 m of water. Art.
At the same time, pumping stations are located in the ITP and at lower levels based on ease of operation. The traditional scheme for Asian countries with water pumping on technical floors is shown in Fig. 6.7a. Based on the results of trips to a number of countries, initiated by the Moscow Government, to exchange experience in high-rise construction, the main constructive solution
of these systems with the location of intermediate tanks and transfer pumps on technical floors. This decision complies with the provisions of the regulations adopted in these countries on the construction of so-called safety zones every 12–15 floors, where people can wait out the fire in specially designated areas. Hence the location of water supply equipment on the same floors. All tanks are made of two sections, to allow cleaning and repair without stopping the water supply. The main disadvantages of using this scheme in high-rise housing construction
For comparison, using the example of the same building, the water supply diagram used in the design of high-rise residential complexes in Moscow is shown (Fig. 6.7b). It is easy to see that when installing frequency-controlled pumps, this scheme is simpler and more economical. Installing pumps in the same room with equipment for heating, ventilation and hot water supply systems is much more convenient during operation. In elite and commercial high-rise buildings, the risers of the water supply system are laid in the niche of the staircase and elevator hall, from where hot and cold water pipelines are introduced into the apartment (Fig. 6.8). This arrangement of risers is due to the fact that in high-rise residential complexes, apartments, as a rule, belong to the elite class, therefore, in the event of an accident due to the fault of the maintenance service, the amount of damages can reach 80–120 thousand US dollars. In case of use vertical systems hot water supply in case of emergency separate apartment the entire zone must be shut down. In municipal housing, to eliminate an accident, you can open the apartment in the presence of police officers, but in housing belonging to the elite class, this is often impossible. In the practice of the maintenance service, there was a case when, in the summer, the owners of the apartment in which the accident occurred were on vacation, there was no access to the apartment, which did not allow eliminating the consequences of the accident. As a result, the water supply to the entire zone was turned off, and for two months the maintenance service carried water to the apartments manually.
The water supply system is equipped with hot and cold water meters, which, together with filters, pressure regulators and check valves, are installed in the same niche on each floor of the building. Ensuring the calculated water flow through the circulation risers is ensured using regulators. One of the possible hot water supply schemes for the building area is shown in Fig. 6.9.
Entry into the apartments is carried out in the space of the false ceiling using pipelines made of cross-linked polyethylene, which do not have any fittings throughout the entire length before entering the apartment. Considering temperature regime pipelines, pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene PEX-a, PEX-b, PEX-c, as well as PE-RT, which have the appropriate certificate for use in water supply systems, can be used without restrictions.
The consumer's water supply system must have an excess pressure of at least 7 m of water. Art., but according to technical specifications equipment that is now installed in most luxury apartments, the required (available) pressure at the entrance to the apartment must be at least 25 m of water. Art. Based on these considerations and based on the geometric height of the zones, booster pumping units are selected. To ensure that the pressure does not exceed the design pressure, it is planned to install limiting pressure regulators for devices on each floor per group of apartments at 40 m of water. Art. These same pressure regulators make it possible to ensure the normal functioning of thermo-mixing units (mixers with temperature controllers), which can operate normally with a pressure difference between hot and cold water no more than 6 m of water. Art. Check valves were installed at the entrance of the cold and hot water supply systems to the apartment, since the maintenance service was faced with the problem of water flow from the cold to the hot mains. This is due to the installation of equipment in apartments, which, if used incorrectly, mixes water throughout the entire area. For example, electronically controlled showers have two shutdown modes - “stop” and “off”. There are two in these cabins solenoid valves on the mixer and one valve on the flow. If a person presses the “stop” button, all three valves close, if the “off” button, only one collapsible mixer closes, and water is mixed through the shower cabins throughout the entire zone. Similar problems arise when using some bidet models.
The cleanliness of the apartment halls of the complexes in question is equal to office premises, and washing them requires a fairly large water consumption - 2.8 l/m 2. In such high-rise buildings, it is very difficult to manually deliver such an amount of water to all floors. Therefore, faucets and drains are installed in the rooms in front of the garbage chute, allowing you to collect water for washing the floor and drain it after use.
For promotions pumping stations such buildings as, for example, “Scarlet Sails”, “Sparrow Hills” and “Triumph Palace”, pumping units are successfully used, which provide for frequency regulation of each pump in the station, which, according to a certain cycle, becomes the station’s control controller, which significantly increases its reliability.
