Laying power cable lines - cable laying. Laying power cables and cable lines Overhead installation methods
Connecting electrical power is our main task!
We are pleased to welcome you to the website of the ELEZAR Company - one of the leaders in the electrification market in the Moscow region. For more than five years now, the ELEZAR Company has been successfully implementing electricity connection to the facilities of Moscow and the Moscow region from the power grids of the Moscow United Electric Grid Company (MOESK). Our goal - professional help in power connection with minimal costs on the part of consumers.
Today the ELEZAR Company offers connection of private households and small, medium and large businesses to networks MOESK. The experienced and well-coordinated team of the Company will professionally and in a short time solve all problems related to energy supply your home, cottage, garden plot, garden non-profit partnership (SNT), dacha non-profit partnership (DNP), enterprise, logistics complex, office and any other individual and commercial property.
Electrical Installation Company "ELEZAR" is a modern and dynamically developing enterprise. In 2009, a branch of the Company was opened in Novosibirsk. The Company's branch produces turnkey electrical connection for business and private customers of Novosibirsk and the Novosibirsk region.
Our specialization
The ELEZAR company provides comprehensive support electrical installation work in Moscow and the Moscow region. Our profile is: increase, consolidation (change of owner), restoration of expired specifications, connection of power and everything connected with this:
- technological feasibility analysis,
- development action plan,
- individual preparation of a package of documents,
- ensuring control over the application,
- obtaining an agreement on accession and technical specifications,
- development of a power supply project (detailed topographic survey),
- coordination project documentation,
- electrical installation component,
- commissioning works,
- commissioning of the electrical installation,
- issuance of an electricity supply contract,
- customer instructions (optional).
What are the benefits of working with an electrical installation company?
In the process of connecting objects to electrical networks, many departments and regulatory bodies are involved: electrical networks MOESK, Energosbyt, Energonadzor, Mosoblgaz, city or rural district administration, expert laboratories, regulatory authorities... And in each of these authorities, the consumer needs to receive, sign and certify a number of necessary documents. If at least one of the many links in this chain fails, the consumer finds himself in a dead end situation. How to protect yourself from wasting time chasing employees network organizations, effort, exorbitant costs, finally who will come up with a creative solution?
The most correct thing in this case is to contact an intermediary company that will take on the responsibility of connecting your home or business to the power grid, but you need to choose it correctly. We offer cooperation with ELEZAR, where they will help you obtain all the documents necessary for the energy supply of the facility - in short time and by optimal price. In some cases, independent paperwork takes from one to two years; ELEZAR Company specialists will be able to hand you an ab/book of a ready-made subscriber package within three or four months after you contact the Company.
The main stages of our work
The main thing for any consumer is receiving reasonable technical specifications for connecting electricity to power grids of MOESK. To do this, we submit an application to the electrical networks whose service area includes your locality, and deal with it at all stages of production. Within ten days you will know all the necessary information on your energy receiving facility - an on-call service.
You need to bring a set of documents to the ELEZAR Company for expert analysis. We adjust and supplement the basic package. The general package for the Service for Technological Connections of MOESK branches on the part of our organization is ready, we are drawing up an agreement for the stages of cooperation and starting to work.
The timing of consideration of submitted applications depends on the prevailing technical circumstances, location of the facility, size requested electrical power and, as a rule, do not exceed 45 calendar days. The ELEZAR Company has flexible prices, which include, among other things, an express procedure for processing applications .
So, technical specifications (permits) have been received, and the first stage of the contract has been completed. After this, we propose a second stage II, related to the direct connecting electricity. No less important moments are project , estimate, coordination, network construction, commissioning of the electrical installation, switching on- and they should be trusted to specialists with many years of professional experience.
Our partners
Connecting electricity is not only a labor-intensive process, but also quite lengthy. What to do when you need light not in a few months, but now? In this case, generators and power plants provided by the DIEN-Systems Company, a recognized leader in the field of autonomous power supply, will help you.
How to lay electrical cables, we recommend reading the second section of PUE 6. “Outdated” version. The provisions listed in the document are advisory in nature. Those who comply with the requirements for laying electrical cables will certainly avoid violations. The information is presented within one document, all you have to do is read it. Let's see how to lay power electrical cables.
How and where to lay the cable
First examine the end of PUE 6, dispelling doubts. The endless list of approvals will convince readers: a real document appeared before their eyes, having seen the hands of many builders and officials. New requirements may appear, but later. PUE 6 electrical lines classifies:
- The first part examines types of electrical wiring, choice, typical conditions: premises, street, attic.
- Lines with voltage below 35 kW (separately before/after 1 kV).
- Lines with voltage below 220 kV (including cables up to 35 kV).
- Overhead cable lines (up to/above 1 kV).
The first to discuss the scope of application is PUE 6 (section 2). The requirements below must be met for cables with a cross-section of phase conductors up to 16 square millimeters. Unfortunately, it is omitted whether to use copper or aluminum. We conclude: it is always good until proven otherwise. Let's first consider the classification of electrical wiring:
- By nature of occurrence:
- Open. It can be stationary, portable, mobile. Lays on outdoors along the surfaces of structures, between supports. Along the way, insulators, rollers, pipes, boxes, sleeves, baseboards, and posts are used.
- Closed. It is laid inside the walls: hidden by plaster, grooves, inside concrete (walls, floor, ceiling) as a monolith, using cavities.
- External electrical wiring is laid along external walls. The suspended length is no more than 100 meters (four spans of 25 meters each). Other concerns air lines, underground routes.
Gasket allowed electric cable in the bathroom floor. Another question concerns the protection measures provided (grounded grid). The matter is limited to trifles.

Laying wires inside buildings
Among general requirements the inadmissibility of laying nearby circuits with voltages up to/above 42 volts is indicated, with rare exceptions (see clause 2.1.16). Relevant to today's reality, when I wanted to illuminate the bathroom without restrictions with a constant 12 volts. Fortunately, the DIN rail adapter sells for 800 rubles. It turns out that it is forbidden to merge into one branch. Wire your home from 12 volts. Safe, allows the use of a minimum wiring cross-section.
PUE 6 gives the answer here: use fireproof partitions between the wires. Much more interesting would be the requirement for the phase and neutral (return) wires to be connected together (it is prohibited to use adjacent pipes). Village residents should know: cables are not laid in combustible cavities or niches wooden walls. Ceramic insulating rollers are used (distance to the plane is more than 10 mm, or by placing fireproof material).
When laid open, the distance from the floor is at least 2.5 meters. We believe that in private houses the villagers do not comply with the requirement. Only for high-risk areas. There is no obligation to reduce the voltage, placing the upper limit at 42 volts, the electric cable for internal gasket placing at a height of two meters. But it can be done. Remember the 12 volt adapter, placed in the distribution board. It will definitely be enough to provide lighting for a village house. As for sockets, protected installation (cable ducts) should be used. When the protection level of the box is IP20 and higher, the height is not standardized. Connections are allowed in the form:
- crimping;
- terminal blocks;
- welding;
- rations.

By the way, bare twists are prohibited even for grounding circuits. The insulation of joints is no worse than linear sections. Next come the obvious requirements: absence of tension, accessibility of components and connections (to service specialists). A combustion-protected cable must be laid under the cladding: many installers have forgotten. YouTube will give you any number of stories: the cladding of PVC panels hides traditional PVC for several cores. The mentioned part of the PUE is inactive, the installation process itself does not become less dangerous. The conclusions are clear: we do it for ourselves (so that we are guaranteed nothing will happen).
Thus, laying the electrical cable in wooden house handles with subtle art. Aluminum corrugation is useful. It is clear that plastic is not always suitable for reasons of lack of fire resistance. Take comfort: aluminum corrugation is easy to ground, certainly improves the electromagnetic environment of the house, simplifies the replacement of wiring, and protects against fire. Like other metal parts of the building, hoses, pipes, cable channels are zeroed. Can serve as a screen. Read more about the standards for laying electrical cables in the table. 2.1.3 PUE 6, regarding the peculiarities of installation in various climatic conditions (heat, dampness), many rules are prescribed in section 2.1.
Increased attention is paid to places where they intersect with pipelines. The electrical cable is laid leaving a gap of at least 5 cm. If there is hot water or something flammable (read gas) in the pipeline, the distance doubles. Moreover, 25 cm of protection against mechanical damage should be provided on each side of the intersection. On a parallel pipeline or cable, the distance is taken to be 10 or 40 cm minimum depending on the contents (gas, kerosene, hot water, steam).

External building wiring
Rules for laying external electrical wiring
Finally, it will be a wonder color coding electrical cable for external gasket from the substation:
- Yellow – phase A.
- Green – phase B.
- Red – phase C.
- Blue – neutral working wire.
- With yellow and green stripes - neutral protective wire.
- The reserve tire is marked with transverse stripes to the main ones.
The color differs (slightly) from PVS cables, which are not intended to carry three-phase lines. Laying an electrical cable in the ground at the dacha is carried out by other types. The marking of pipes is in accordance with GOST R IEC 61386.24, examples of cables will be provided by GOST 16442. The latter document will indicate which brand of electrical cable is unsuitable for laying in the ground. Installation details are indicated in PUE 6, starting in paragraph 2.3.83. It is said that the cable line lies no closer than 0.7 meters to the surface. The bottom is filled with bedding (sand, crushed stone), and the top is covered lightly with soil, freed from various types of debris.
Selecting the wiring cross-section (cable cores)
According to PUE 6, the cable is divided into two categories by core cross-sectional sizes:
- Within 6 square millimeters for copper, 10 for aluminum is selected from tables 1.3.4 and 1.3.5 directly. As for long-term operation.
- Otherwise, when the core thickness is higher, you need to multiply the tabulated current by a correction factor of 0.875 / √ TPV. Where TPV is the relative duration of equipment activity in the operating cycle. Simply put, the equipment works less over a period of time, the core is thinner.
Please note that the figures indicated in the table are widely quoted in the literature without indicating the source. PUE 6 says: the maximum long-term current of the core is determined by the type of cable (the number of conductors in the insulation), the laying method discussed above. By grouping the data, readers will easily select an electrical cable for laying over the air or underground. It’s nice that the parameters are graded according to the type of insulation and voltage. There is not enough space to call the information exhaustive, some of which current legislation withdrawn from official circulation.
It has become difficult to find requirements for the cross-section of the cable neutral conductor three-phase network. PUE 6 directly says: it must be at least 50% of the phase phase, sometimes it increases to 100%. Correction factors for selecting the current limit depending on temperature may be useful. environment. You will see that depending on the conditions, the cable cross-section can be reduced, or, conversely, it will have to be increased. Correction factors are introduced for soil type. It is important for those who want to lay the route correctly.
Readers will like Table 2.1.1, indicating the smallest cross-sections of conductors for copper and aluminum. For stationary cable laying on rollers indoors, the value is at least 1 square millimeter of copper. The current can reach 17 A (PVC cords with PVC insulation), approximately 3.7 kW of power. I wanted LED bulbs connecting with a thinner section is not possible. Let’s assume that PUE 6 was released long before home-based sources appeared in our area. Surely engineers will have to reconsider the measurements and make adjustments to the type of light bulbs.
Cable blocks
The permissible current of cable units depending on the structure is widely discussed. The laying process is described in section 2.3 (now removed). It is said that cast iron, concrete, and asbestos-cement pipes are suitable for the cable block. Calculation of the number of channels and structuring is carried out in accordance with clause 1.3.20, with 15% (at least 1 piece) set aside as a reserve (in case it is necessary to lay an additional line).
The depth of the cable blocks is selected in accordance with clause 2.3.84. In most cases it is 0.7 - 1 meter. There are allowances for reducing the distance to half a meter over a section length of no more than 5 meters. It will allow you to correctly lay channels, which should have a slope of 0.2% towards the wells (the depth increases). When laying, take into account: minimum distance between the lines is determined by the voltage and increases with increasing voltage.
The definition of cable units is hushed up, so readers probably have a mountain-sized question. Meanwhile, the structures are formed by channels of various kinds connecting the wells. Thanks to the structure underground laying electrical cable is carried out without involving construction equipment. The main thing is that there is no need to open expensive coatings. We bet they're using some kind of cable ducts underneath the Piazza.
Similar technology helps lay cables under river beds. A special unit drills an arched tunnel in the ground that goes out to the opposite bank. The cable is laid inside. If necessary, the walls are, of course, reinforced. Makes it possible in the future to freely repair a section of the route, change certain cores (add, replace, remove). It is clear that underwater types of cable laying are not available to most private owners; you need to know in case you need to go through a difficult section.
Conclusion
We remind you that the specified PUE 6 is “outdated”. It is still acceptable to be guided when carrying out work. Similarly, the installation of electrical cables in the apartment is carried out in accordance with documents certified by professionals.
Alsera company performs all types of work related to the laying of power cables:
- pad power cable in trenches (including punctures under roads)
- laying power cables on cable racks and in cable ducts
- installation of power structures on the facades of buildings and structures
- air device cable lines
Having extensive experience in this field and the availability of our own material and technical base, we guarantee the Customer high-quality performance of work within the time frame clearly specified in the Contract. Work in progress qualified specialists under the constant supervision of the responsible site foreman. Our employees have all the permits and permits necessary to carry out the work.
We provide a comprehensive supply of cable and wire products and all materials necessary for the execution of work. Our own transport department will ensure prompt delivery of materials to the site.
When contacting our company, we guarantee a prompt solution to the assigned tasks, from drawing up an estimate to a laboratory report. To prepare a commercial offer for professional installation power cable, you can send technical task, project, or diagrams to us by mail [email protected], or call an engineer to the site.
Our engineer’s visit to the site (within the Moscow Ring Road) is free!
Cost of laying power cable
| Job title | Unit. | We're standing. unit (rub.) |
|---|---|---|
| Installation of the end coupling | PC. | from 950 |
| Installation of coupling | PC. | from 1500 |
| Pipes protective gasket (HDPE 50-150 mm) | m.p. | from 50 |
| Laying power cable 5x10 - 5x25 | m.p. | 150 |
| Laying power cable 5x35 - 5x70 | m.p. | 250 |
| Laying power cable 5x95 - 5x150 | m.p. | 400 |
| Laying power cable > 5x150 | m.p. | from 450 |
| Excavation (trench) | m3 | from 650 |
| Construction of a protective base (brick, block) | m.p. | from 70 |
| Protective base device (signal tape) | m.p. | from 15 |
| Sand cushion device | m.p. | from 90 |
Photos of works:

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
|

|

|
Contact us by phone listed in the “Contacts” section and you will receive a durable and reliable power cable that will provide you with uninterrupted energy transfer to any point!
Very often, when we change places, we are faced with the need to build a power supply chain and SCS for new or simply workplaces or company employees, or household consumers. Or are they forced to face a complete replacement? electrical networks. Often a radical modernization of wiring, Internet or telecommunications is needed. Basically, cable chains are laid in trenches, special trays, boxes, on overpasses, open type on the walls, hidden by the floor or in the ceiling. To select a laying location and perform it correctly for different types wires, you need to take into account many nuances.
- Securing the drum
- Raising it with a jack
- Opening the drum housing
- Rolling out by gradual rotation of the drum and pulling into the gasket specified in the project.
Laying power cables is most economical if done in trenches. For this purpose, wires armored with steel strips and covered with cable yarn insulation are used. For one trench the norm is up to 6 wires. The gaps between them should be from 100 to 250 mm. If from different groups of service provision, then the space increases to 50 cm.
They are laid at least 0.7 m deep, but when crossing the route - 1 m. If it is not possible to make a gap, then they are placed in pipes. When crossing an engineering structure, mechanical protection is installed. Simply place the cable into the pipe. If there is a cable located in a given area before the building stands, then lay empty pipes next to it for future communications.
There is another option - to lay the wires in blocks. This is, of course, not the most economical way, but the blocks consist of asbestos cement, ceramic pipes or reinforced concrete frames, which doubly protects the wire.
A line that has more than six wires must be laid in channels. You need to place slabs on top. If the laying is outside buildings, then it is covered with sand. In the deepest channels or tunnels, the cable is carried through cable structures. Automatic fire extinguishing devices and messages in the presence of smoke are installed in the tunnels. To prevent moisture from entering the tunnel, mechanical drainage machines are installed.
Tunnels, in which there are many communications, are considered to be collectors. It is allowed to use unarmored wires in tunnels, collectors, and channels. IN distribution structures wires with armored coating on top are used. To reduce spontaneous destruction of metals and active heat transfer, the armor is painted black. Wires that cross bodies of water are placed in pipes buried in the ground. Ground wiring of up to 20 pieces is done on wooden trestles. In particular harsh environment, placed on the sides of the heat communication network boxes.
For more detailed information about power cable routing, see the video on the next tab.
Laying low-current cables
The rules for installing low-current networks include:
- The minimum space between adjacent low-current and high-current flows should be 0.5 m, but when overlapping, an angle of 90º is required
- It is forbidden to bring threads of low-current networks into the riser where electrical wires are located.
- It is forbidden to combine wires. Use only whole coils of wire
- The distribution box must be fixed to the wall, but not under or above the openings
- Be sure to ground the bus or any copper conductor
- All boxes and blocks are filled to a maximum of half
Low-current networks include telephone, computer, and television networks.

To build such networks, different wires are needed depending on the purpose. For example, a computer network requires the use of copper cables; a telephone circuit requires category 3 wiring.
Where to lay such networks:

When drawing wire lines, the possibility of risky mechanical overloads occurring in the working procedure is eliminated. They are laid in case of ground movements or deformation under the influence of temperatures or lighting, with an average spatial margin. Indoors this is done using the wave method in trays using cable slacks.
It is PROHIBITED to lay the spare length of wiring in rings, remember about induction.
The cable, which is laid on walls or other flat surfaces horizontally, is secured at the end points, at the bends of the cable. Fixed with couplings and rubber strips for unarmored types.

Installation consists of two phases:
- Attach cable retaining structures
- Lay and connect to electrical equipment outlets
After removing the drum body, inspect its outer turns. If they are damaged, they are cut out and the insulating shell is checked with a voltage load. Paper insulation is examined for dryness. After such a check, sealed caps are placed on the ends.

Laying power and low-current cables
Any cables are laid in the following installation options:
- Hidden
- In brick and concrete;
- In plasterboard objects;
- Under false flooring
- Open
- In plastic cable ducts
- Electrical installation made of plastic;
- Do not lay in one groove without partitions;
- Use shielded wool or mechanical pipes;
- If possible, lay cables on opposite walls.
- When crossing, form an angle of 90º
- The distribution equipment should be located far from the low-current cable.
In the PUE, on the parallel installation of low-current and electrical cables for 1985, in section 2, chapter 2.1.2.1.16, there is a complete ban on the joint installation of distribution cables. But if the trays and boxes have a continuous partition bordering them, then the gasket may be allowed.
According to others regulatory documents There are clearly defined cases in which gasketing is completely prohibited. And this:
- If the influence of one cable on another exceeds the norms;
- If there is a possibility of damage by current to the consumer;
- If there is a possibility of acoustic shock;
- If there is a risk of false guidance signals;
Let's take a closer look at the wiring options, both hidden and open. So, hidden wiring in the walls eliminates the possibility of further improvement or, for example, change electrical wiring without destroying the wall structure, the only positive aspect is the duration of use and general form such wiring in the wall. Hidden wiring in partitions made of plasterboard is low-cost and easy to implement, but plasterboard is not so reliable material, like concrete, over time it crumbles and deforms, which will lead to damage to the network.

Raised floors are used only with the use of floor hatches, these are small holes in the floor for control. But the use of these hatches has a list of disadvantages:
- High price for a short period of work;
- Inconveniences of use
- Binding to tables;
- The option to access networks is below it.
In general, the use of a raised floor convenient solution for offices, a huge minus is the price.
Let's move on to open wiring. Wiring in small plastic channels is more suitable for moving the workplace than for creating new wiring. This is the most a budget option, but it will also look accordingly. The following is an open routing of wires in plastic channels.
This is the most best option, do not destroy partitions, floors and other coverings, and do not depend in any way on construction processes, which take place in this moment. Another advantage is the speed of channel fixation. It is also worth noting that any renovation work in such a channel are carried out easily and without causing great inconvenience.
The power supply to any room or separate electrical installation begins with an input or power wire. There is no strict definition in the Electrical Installation Rules; the document only regulates the testing and installation of power cables. In principle, this type of electrical wiring can include any conductor that connects the supply substation to the input device.
This category also includes wires running from the input device to distribution panels or cabinets. That is, the cable in the entrance to the input machine of your apartment, and the wire connecting the machine to your meter (electricity meter) refers to the power one. If the meter is installed outside the distribution panel, it is also connected to the machines using a power cable.
How to choose the right power cable
We are not interested in overhead networks that supply power using electrical poles. The maximum you will have to deal with is the power wire from the nearest pole to your private home.
Important! Do not confuse the diameter and cross-section of the conductor. A section is an area!
This parameter is not a dogma. For example, the same 4 mm² wire is designed for a continuous load of 38 amperes. With a single-phase connection of 220 volts, this is already more than 8 kW of load. Having installed input protection 32 amps (with appropriate specifications), you are approaching the maximum wiring capabilities. It makes sense to use a power cable cross-section of 6 mm².
The numbers discussed refer specifically to the power wire. Subscriber wiring to sockets and lighting devices is carried out with 1.5 mm² residential wire. The exception is the power group of sockets for a boiler, electric oven, washing machine. By the way, such wiring can also be classified as power, but not by purpose, but by load.

A separate topic is color marking. The electrical installation rules require the use of the following colors:

- The working zero is blue along the entire length of the conductor.
- Protective grounding is yellow-green insulation, the colors are located along the wire.
- Phase - There are no color coding requirements for single-phase connections.
Let's consider the third point in more detail. With a three-phase connection, each phase has its own color. This is important, since mixing up the phases means damaging the electrical installation. Therefore, the PUE prescribes the following designations:
- A. “yellow” phase
- B. green phase
- C. “red” phase
For a single-phase connection (after a three-phase input), it does not matter between which phase and zero 220 volts are formed.
For reference: European color marking of phases differs from the requirements of the PUE.

In the vast majority of cases, you will have to install a single-phase power cable. Therefore, the complex marking of three-phase inputs should not confuse you.
Correct routing of the power cable
If the cable is laid separately from the electrical station (switchgear) to the consumer input, only mechanical requirements must be met.
Along the walls or load-bearing structures, the wiring is attached to mounting clips. If the strength of the attachment points is in doubt, you can run the power cable along a guide: a steel bandage strip or a supporting cable.
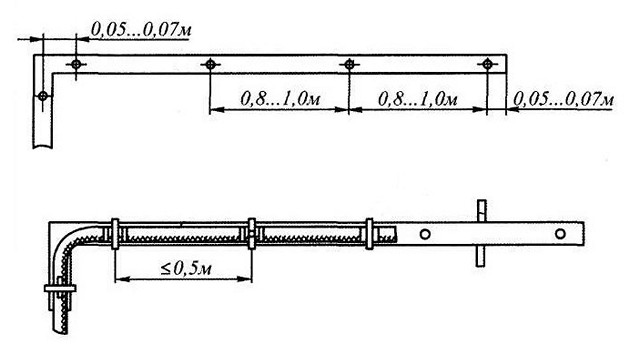
Aerial laying (the cable hangs freely from one attachment point to another) requires either a strong supporting sheath or a suspension system. The most commonly used is steel cable.

If the wire is self-supporting, special tension clamps are used. The cable at the point of approach to the wall or other structure is fixed in the device, and its free end is directed to the entry point.

Laying power cables in trays is widespread. No equipment is required; the wire is placed in a box and covered with a lid. There are only a few restrictions. The joint installation of power and low-current cables is regulated. Rules for electrical installations. There are no strict prohibitions, with the exception of redundant power lines. They are laid separately.

The thing is that power cables (unless they are in steel armor connected to protective grounding), form quite strong interference. It is difficult to neutralize them using filters: when the load changes, the nature of the interference also changes. And the power cable is rarely under a stable load.
Therefore, power, signal (communication, computer networks, television), and the control lines must be spaced. At least according to to different parties boxes, or better yet, in separate trays.
Regardless of the installation method, the external cable is introduced into the room using a curved pipe that prevents moisture from penetrating into the room. The cable must enter it from the bottom up, otherwise moisture may get through the sheath into the input shield.

Power Wiring Splicing
Connecting power cables affects more than just safety. Although a broken live wire will cause enough trouble. A poor-quality splice can cause sparking under load, a progressive increase in resistance, and rapid heating. Despite non-combustible insulation, it may cause a fire.
In addition, poor contact at the splice leads to loss of cable power, and the current strength may decrease.
It would seem, why use pieces of wire if you can stretch an unbroken chain. However, in reality, breaks occur (it is necessary to make an emergency splice), and the cable may simply not be enough. Therefore, the question is: “how to connect the power cable?” worries many.
There are a few simple rules:

Video on the topic
