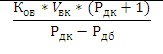Expansion membrane tank for heating: design features and operating principle. Membrane tank for a heating system: operating principle and its functions.
Offline heating system There must be an expansion tank for heating, or a compensator. Its function is to compensate for the excess pressure that occurs in the system when the coolant expands due to heating. At rapid rise temperature coolant liquid expands and a pressure surge occurs, the so-called water hammer. It can destroy pipeline elements and connecting fittings. Other names expansion device: hydraulic accumulator, expansomat.
Design and principle of operation of expansion tanks for heating
Heating systems can be open or closed. Accordingly, heating expansion tanks exist open type and closed.
Open type tanks
An open expansion tank for heating is a parallelepiped-shaped container made of stainless steel. This tank is placed at the highest point of an open heating system, usually in the attic.
Pipes connected to the tank:
- mainline;
- circulation;
- alarm, with locking device.
In this type of heating system, the coolant (water) circulates naturally, without pumps. Despite the comparative cheapness and simplicity of such heating, it is gradually becoming a thing of the past due to numerous shortcomings.
- IN open tank The coolant constantly evaporates, so you need to monitor the water level and add as necessary. For the same reason, it is problematic to use another coolant, such as antifreeze - it evaporates even faster.
- It is possible for water to overflow from the tank, so it is necessary to ensure its drainage into the sewer or drainage system.
- An open expansion tank requires good thermal insulation so that the water does not freeze in severe frosts.
- Installation in the attic will require additional pipes and connecting elements.
- Air entering the system from the expansion device provokes corrosion of the pipeline and radiators, and also leads to the appearance of air jams.
The open compensator system is suitable for heating small one-story houses. Larger houses are heated with closed systems.
Closed tanks
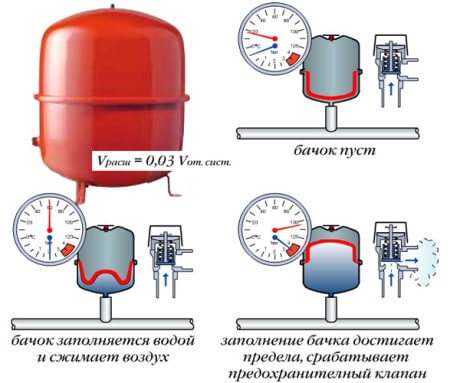
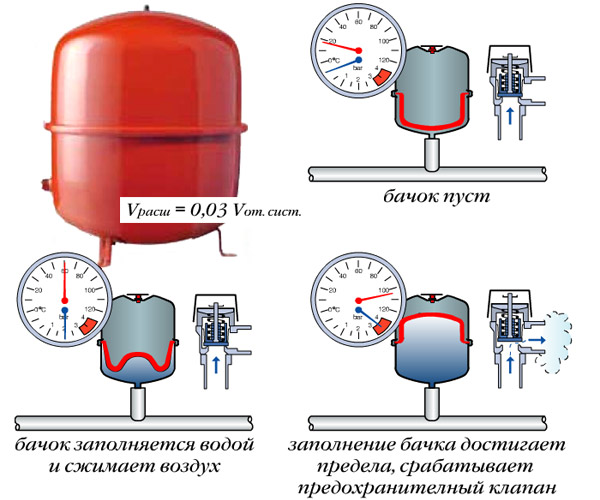
A closed, or membrane expansion tank of a heating system contains an elastic membrane inside, which divides the internal volume of the compensator tank into two compartments, gas and liquid. The gas part contains air under pressure (in some models - nitrogen or inert gas), and the liquid part receives excess coolant when heated.

Tank closed type(membrane)
The higher the temperature, the more the liquid part of the accumulator is filled. At the same time, the gas part contracts and the pressure in it increases. When the threshold value is reached, it triggers safety valve, excess pressure is released. And when the heating system cools down, the reverse process occurs and the coolant returns from the tank to the pipeline.
Operating principle of a membrane expansion tank
There are two types of membrane compensators.
- With a diaphragm type membrane. These are small sized tanks. The diaphragm membrane in them is non-removable and cannot be replaced: if it breaks, you will have to completely replace the device.
- With a balloon (pear-shaped) membrane. It can be changed when worn out; it is used in large thousand-liter tanks.
The volume of expansion tanks for heating can vary widely from two to several thousand liters. The shape of the closed hydraulic accumulator is flat or cylindrical. In a flat expansion tank, the membrane-diaphragm is located vertically, in a cylindrical tank it is horizontal.
It is worth paying attention: a membrane compensator is sometimes mistakenly called a vacuum expansion tank for heating. However, this device does not use a vacuum. The heating system may have a vacuum deaerator to remove air microbubbles from the water.
Installing a membrane expansion tank
Unlike open membrane accumulator For ease of maintenance, you can install it directly in the heating point, next to the boiler. Usually it is placed on straight section before circulation pump, it is desirable that water (or other coolant) enters the compensator from above. It must be equipped with a pressure gauge, a safety valve and connected to the return line.
Hydraulic accumulators with a volume of up to 30 liters are mounted on the wall, larger ones are installed on the floor. When mounting on a wall, the tank should be securely fastened, since its weight increases sharply when filled with water.

Several membrane tanks in a heating point
Important performance characteristics and compensator volume calculation
When selecting an expansion tank, take into account the maximum operating temperature and pressure. For example, the coolant can heat up to +120° C, and the peak pressure in the heating expansion tank can reach 6-10 bar (the usual average value is 2-4 bar). Therefore, the characteristics of the membrane, its durability, heat resistance, compliance sanitary standards.
The volume of the compensator depends on the volume of coolant as a whole in the system. It is not necessary to calculate the volume mathematically accurately; a simplified method is often used: select a tank with a capacity equal to 10% of the total volume of the coolant. And if this volume is unknown, then they proceed from the power of the boiler and the type of heating devices. The ratios are as follows: for heating radiators they take – 11 l/kW, for heated floors – 17.5 l/kW, for wall-floor heaters – 7.5 l/kW.
If the capacity of the selected compensator is insufficient, the safety valve will release pressure too often. In this case, it is enough to purchase and connect in parallel another expansion tank.
It is quite difficult to take into account all the nuances, especially since in each house the heating system necessarily has its own characteristics. In order not to make a mistake when choosing and installing a device, it is better to contact a specialized company.
Video: installation of an expansion tank
When arranging a heating system, it is necessary to pay attention to absolutely all aspects, from the design of the heating unit to its configuration. Among all the diversity functional elements The vacuum expansion tank for heating plays an important role in creating high-quality heating equipment. Thanks to this device, the volume of coolant is adjusted, which makes it possible to prevent rupture of the heating main, radiators and shut-off valves.
Operating principle and types of compensatory devices
If you are going to install a heating unit in country house, then the expansion tank for heating (expanzomat) must necessarily appear in it.
The operation scheme of a compensation tank for heating is simple: as the temperature of the coolant increases, its volume (we are talking about water, since it is what is most often used for piping heating units) increases. Due to the fact that the circuit is closed, the liquid does not evaporate or burn, which, in turn, provokes an increase in pressure in the line, which must be reduced to avoid an emergency. This stabilization of pressure in the heating system is called compensation, and it is for these purposes that an expansion tank for heating is used.
Types of expansion machines
Until recently, heating units were widely used that operated through gravitational circulation of the coolant, that is, without centrifugal pumps. Open type expansion tanks were installed for them. But at the same time, such devices had a lot of disadvantages, so today they are practically not used for piping thermal blocks.

The whole point is that air got into the open expansion chambers, which provoked the development of corrosion on the internal surfaces of the heat exchangers. In addition, the liquid from the system regularly evaporated, which required constant monitoring of its quantity, since this could lead to a decrease in the efficiency of the entire heating unit. And besides, such tanks must be located at the highest point of the system, which is not always convenient and practical.
Modern heating blocks are characterized by the use pumping units and closed expansion tanks. In this case, the advantage is that the thermal circuit is completely sealed.
The operating diagram of the membrane compensatory tank of the heating system is based on the following principle: inside it there is a membrane that divides the expansion chamber into two parts. One half contains air or gas, which is pumped into it under pressure. While the other part directly regulates the amount of liquid. Membrane for expansion tank It is made of elastic material, which causes the air chamber to contract when water gets inside it, the pressure in it increases, thereby compensating for the increased pressure in the thermal circuit. When the coolant cools, the reverse process occurs.
Closed-type expansion chambers can be flanged (with a replaceable membrane block) and solid (with a non-replaceable membrane). The second option is the most preferable due to its favorable cost. But at the same time, flanged expansion joints operational characteristics much better, since if the membrane ruptures, it can be easily replaced with a new one.
Selecting an expansion tank
Choosing a heating system compensator is quite an important matter, so you need to take it seriously. An important aspect of choosing a compensator is:
- type - closed or open;
- standard size;
- membrane properties:
- resistance to diffusion processes;
- working temperature;
- service life.
You can find out all this data directly in the store where you will purchase the expanzomat.
How to calculate the volume of the compensator?
First, let's determine the relationship between the required cubic capacity and the parameters that influence it. When calculating, it is necessary to take into account the fact that the larger the volume of the thermal circuit and the higher the maximum permissible temperature regime will be in it, the larger the size of the compensatory tank should be.
So, to determine the volume of the expansion tank, you can use the following formula:
|
|
- Kov is a coefficient that shows the size of the increase in the cubic capacity of the coolant when it is heated.
According to research data, for every 10°C increase in the temperature of the water in the main, it becomes 0.3% more. In simplified calculations, a figure of 5% is used. If antifreeze (antifreeze) circulates through the thermal circuit, then this value will be from 8 to 10% depending on the type of antifreeze liquid.
- Vvk is the volume of water in the main.
These data are taken from project calculations that were performed at the stage of drawing up the heating unit diagram. If you do not have such data, you will have to determine the cubic capacity of the coolant yourself. This can be done by draining the liquid from the pipeline. The amount of water is measured by buckets or a flow meter that is installed on the stream.
- R dk - maximum permissible pressure the boiler and the entire circuit as a whole. This value is taken from the heating element’s rating data.
- R db is the pressure indicator in the air compartment of the regulator, which is indicated by the manufacturer in the technical data sheet of the unit.
Based on the calculation results, you will receive the exact value.
Installation of the expansion tank of the heating system is carried out in accordance with all the rules for installing such equipment, which are regulated by the project and the instructions of the equipment manufacturer. The installation of an open type compensator is carried out at the highest point of the heating main. Whereas closed tanks are placed anywhere, but not directly after the pumping unit.
When installing compensating tanks, it is necessary to pay attention Special attention its fasteners, since its mass together with the liquid is quite large.
As a rule, such equipment is equipped with all the necessary fastening elements, however, according to user reviews, they are not always able to ensure reliable fixation of the tank.
In addition, when installing this functional device, it is worth thinking about the fact that it should be convenient for you to use it.
Features of maintenance of the compensating tank
- regular checks for corrosion, dents and smudges - at least once every 6 months;
- checking the initial pressure of the gas space for compliance with the calculated indicator - at least once every 6 months;
- checking the membrane for deformations and damage - at least once every 6 months;
- The unused tank is stored in a dry place.
Here, in fact, are all the subtleties of the design of this functional equipment. We hope this publication will help you equip your home with an efficient heating system.
VIDEO: Review of expansion tanks with a volume of 2-12500 liters with fixed and replaceable membranes and automatic expansion systems, controlled by compressors
A membrane expansion tank is an essential component of the heating system, without which it is impossible to fully heat the room during the cold season. With the help of this device, critical differences in water volumes that result from its heating are compensated.
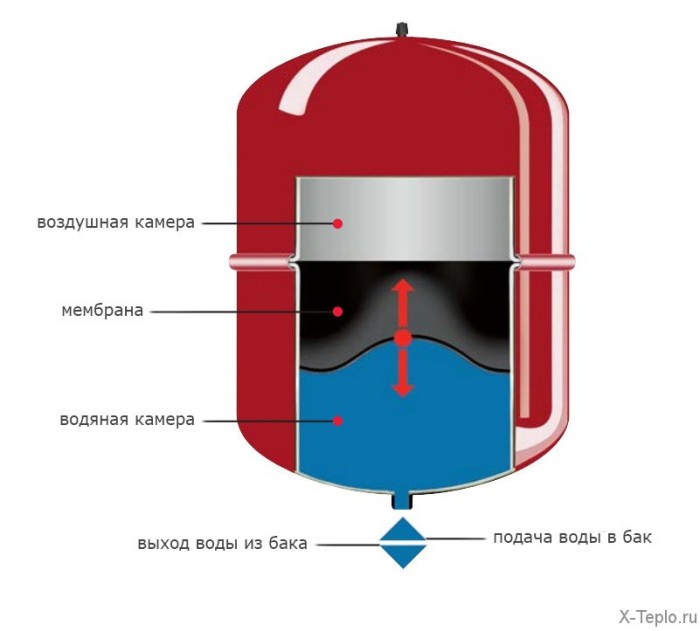
Tank structure
If the heating system does not include an additional device into which excess liquid can flow, it may fail. The role of the spare capacity is precisely fulfilled by membrane tank, which is necessary for uninterrupted operation.
Membrane
The tank body has an elastic membrane that divides its inner chamber into two parts. One part contains coolant, and the second is filled with air. Nitrogen can be used instead.
Depending on the model, the device may include a replaceable or non-replaceable membrane. In the first case, the coolant is placed in an elastic cavity and does not come into contact with metal internal surfaces.
Installation (or removal) of the membrane is carried out through a flange, which is secured with bolts. Such manipulations are performed when Maintenance equipment.
If the device has a non-replaceable membrane, then it is equipped with an internal cavity of two sections. In this case, dismantling is not provided.
To protect the system from overpressure, membrane tanks are equipped with safety valves.
Operating principle
The operating principle of the device is based on changes in the volume of liquid when heated and cooled.
In a closed circuit, water, when heated, expands, and the pressure in the entire network increases. The excess volume of liquid enters the expansion tank, where it reduces the amount of air, stretching the membrane between the chambers. 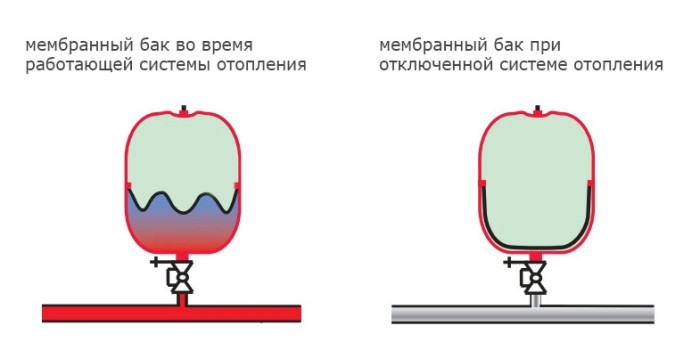
As the temperature drops, the pressure in the system drops and air displaces water from the container. Water will flow from the tank until the pressure is equalized.
Application area
Membrane tanks are widely used. They are built into systems such as:
- heat supply with an autonomous heat source;
- heating system connected to the central heating main line according to an independent circuit;
- heating powered by solar collectors and thermal channels;
- any systems with a closed loop and variable temperature of the working environment.
Advantages
The invention of a closed expansion tank with a membrane made it possible to increase the working life of the entire heating system. The device has the following advantages:
- allows you to use water of any composition, incl. hypercalcified;
- a membrane made of butyl and natural rubber allows the use of equipment for drinking water;
- the operating principle and membrane design of the device can ensure the reception of a significant amount of displaced liquid;
- easy installation;
- minimal losses from evaporation;
- low operating costs.
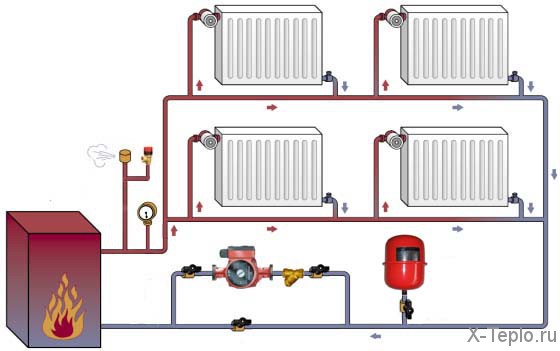
Diagram of use in a heating system.
The compact dimensions of the flat membrane tank allow for economical use of room space, so it is best suited for oversized rooms.
Expansion tank prevents the occurrence of increased loads in the heating system and is effective means preventing emergency situations.
Equipment selection
First of all, the volume of coolant for the heating system is taken into account. If the selection is made incorrectly and the volume is not enough, then cracks and water leaks will appear at the joints.
In addition, the pressure may drop below the safe minimum. This will lead to airing of the internal cavity of the tank, then it will be necessary urgent repairs. Therefore, it is better to select a model based on the characteristics contained in the accompanying instructions.
The initial pressure in the expansion tank connected to the cold heating network must match the static pressure of the system. The permissible discrepancy between indicators can be + 30–50 kPa.
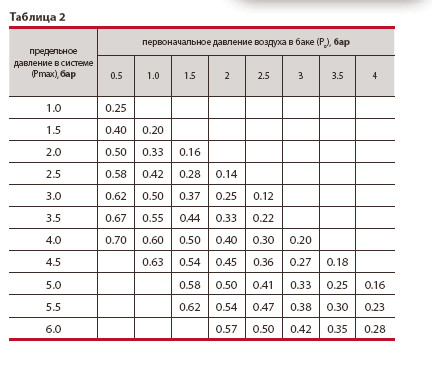
This table will help you calculate the required tank volume.
The tank must have a volume of at least 10-12% of the total volume of the heating network in which it is used. This will exclude possible way out failure of both the tank itself and the entire heating network as a whole during a pressure surge.
When choosing suitable model The maximum permissible pressure at which the device can operate must also be taken into account.
Membrane tanks protect the heating system from excessive temperature increases and regulate the pressure level in it. Therefore, such devices are equipped with independent temperature and pressure sensors.
Device installation
The installation is carried out in such a way that subsequent maintenance can be carried out without hindrance.
A new tank, as a rule, has an excess initial gas pressure, which spreads throughout the entire volume. Before installing the expansion tank, it is necessary to pump it up to a pre-calculated pressure.
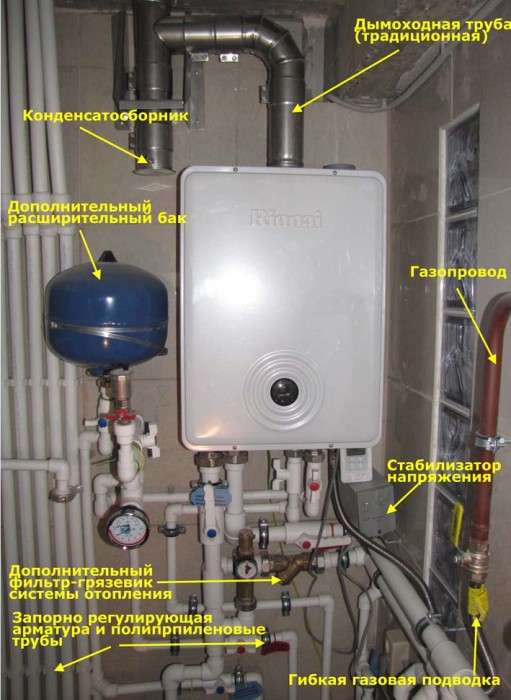

The membrane tank should be installed before the water supply branch. It is necessary to ensure that water is drained and the system is recharged. The room must maintain a positive temperature.
Additional loads on the tank are not allowed! If the container has a volume from 8 to 30 liters, then wall mounting is allowed. For large volumes, equipment is placed on legs.
Grounding should be done to prevent electrolytic corrosion.
Device setup
In order not to wonder how to check the pressure, it is advisable to install a pressure gauge at the outlet. To remove excess air, it is rational to supplement the equipment with an automatic valve.

The required pressure is set in strict sequence. First, the pressure is released through the nipple or using a compressor. Then connect the device to the heating system and fill it with water. The process is not stopped until the pressure in the system and the tank becomes the same.
Expansion membrane tank - element closed system heating, designed to compensate for the thermal expansion of the coolant and maintain the required pressure.
Note! In addition to being used in heating systems, membrane tanks are also used in water supply systems. They “soften” the water hammer that occurs when turning on/off pumping stations, and also maintain constant pressure in the system.
Membrane tank design
The expansion membrane tank for heating is a sealed cylindrical steel body coated in red epoxy varnish(there are also tanks coated with blue varnish, but these are intended for cold water). The housing contains 2 chambers: gas and water, which are separated from each other by a movable gas-tight membrane (diaphragm) made of butyl rubber. Thanks to this material, the membrane is able to function stably at various temperatures (from -10 to +100°C) and perform up to 100,000 cycles.
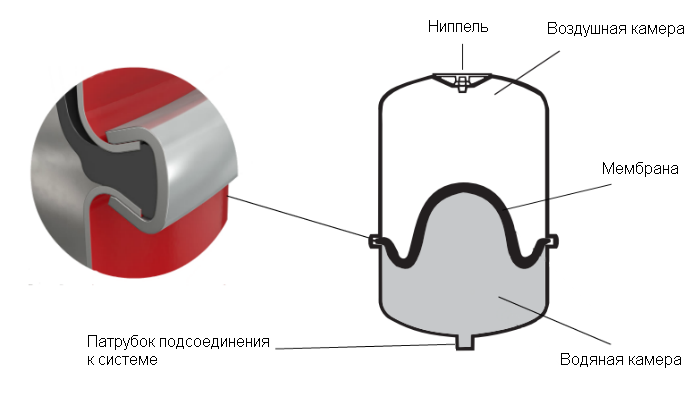
The membrane almost completely eliminates the interaction of coolant and gas. The absence of such interaction allows pre-pressure to be maintained longer in gas chamber, which has a positive effect on the service life of the tank.
Note! Modern high-quality membranes do not simply stretch under the pressure of the expanding coolant, but seem to “stick” to the walls of the tank. This operating principle allows you to increase the service life of the membrane.
Both chambers have the same pressure, which allows you to maintain the tightness of this section of the heating system. The air chamber is filled with a nitrogen-containing mixture. As the coolant expands, nitrogen is compressed, allowing the coolant to “enter” water chamber.
Most modern membrane heating tanks have a nipple built into the body (similar to a regular car nipple), with which you can “pump up” the air chamber, increasing the pressure in it. You can do this yourself at home using a pump or compressor. However, it should be remembered that it is recommended to pump in nitrogen, not air. The fact is that the oxygen contained in the air will cause accelerated corrosion of the walls of the tank body, which will inevitably shorten the service life of the device. Nitrogen is neutral and does not contribute to corrosion.
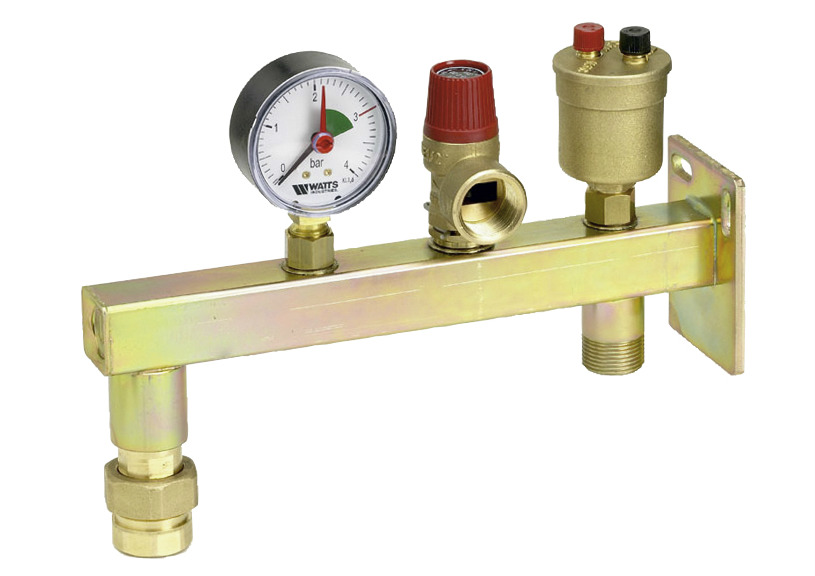

The tank body has an outlet with an external threaded connection, which simplifies the installation process. Depending on the model, the thread may be:
- At the tanks low pressure(from 0.5 to 1.5 bar) – 3/4″ or 1″;
- For medium pressure tanks (1.5 bar) – 1″;
- At the tanks high pressure(from 3 bar and above) – from 1″ to flange connection DN 100;
Operating principle of a membrane tank
When the heating system starts, the coolant heats up and increases in volume. This excess volume moves into the water chamber of the expansion tank. After the coolant cools, the pressure in the air chamber squeezes out the membrane, thereby displacing the coolant from the water chamber back into the heating circuit.
In addition, as noted above, the membrane tank maintains the required pressure in the entire heating system. For example, if an insignificant coolant leak occurs somewhere, then the pressure in the entire system should drop, but this does not happen, because the pressure in the air chamber will push the membrane, and with it the coolant, back into the system, thereby creating limited recharge.
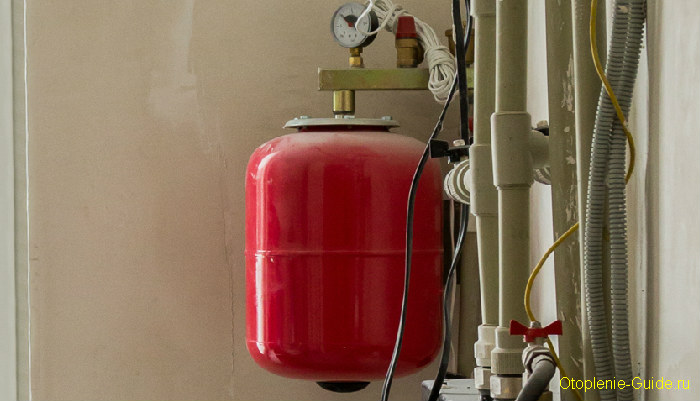

Diaphragm tank with safety group.
The membrane can be damaged as a result of improper use:
- There is a possibility of membrane rupture if, when filling the water chamber with coolant, no required pressure in the air chamber;
- Before releasing gas from the air chamber, it is necessary to shut off and drain the coolant from the water chamber.
Tank calculation
Heating for every 10°C increases the volume of coolant by an average of 0.3-0.4%. Based on these data, the required tank volume is calculated.
The percentage of expansion of the coolant (water) depending on the heating temperature:
Important! Any membrane heating tank is equipped with a ball valve with a drain, which allows you to shut off the flow of coolant to the tank. This is necessary for quick, convenient replacement of the tank in case of failure.
Open type expansion tank
At the moment, this type of expansion tank is practically not used, because has the following disadvantages:
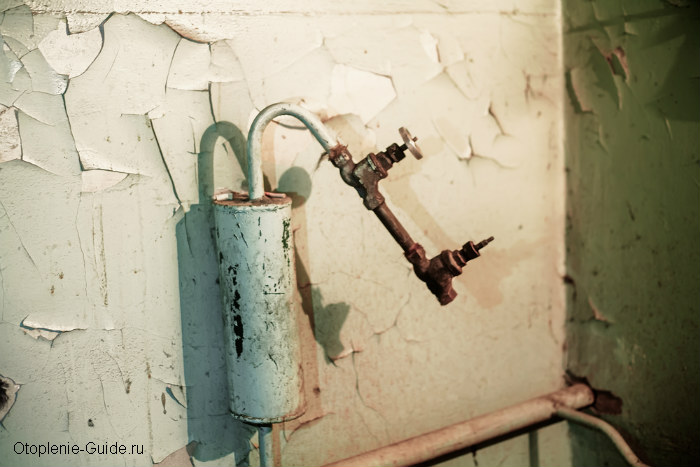

Open expansion tank.
- The coolant is in constant contact with air, which leads to airing of the system and the appearance of air pockets. Therefore, it is necessary to remove air regularly or required. Otherwise, the air can lead to corrosion of individual elements of the heating system, as well as a decrease in the heat transfer of heating devices;
- Due to the constant presence of the coolant in contact with air, it evaporates. You have to regularly add coolant to the system;
- Air microbubbles circulating through the heating system create unpleasant noise in pipes and radiators, and also lead to premature wear of parts. In addition, microbubbles “reduce the performance” of the circulation pump;
- Unlike a membrane tank, which can be installed at any point in the system (next to the boiler, in the basement,...), an open type expansion tank is installed only at the highest point. This leads to an increase in the cost of the system, because It is necessary to use additional pipes and fittings to mount the tank at the highest point.
A membrane expansion tank is a device that allows you to smooth out pressure surges in water supply and heating systems.
Membrane tank design
Externally, the membrane tank looks like a sealed barrel with a flange for connection to the pipeline.
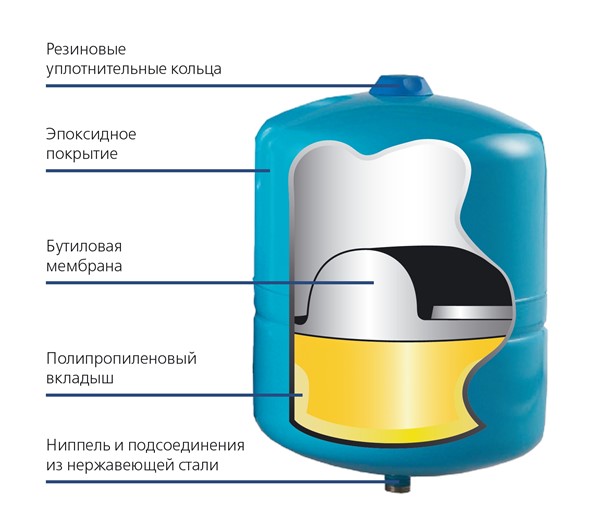
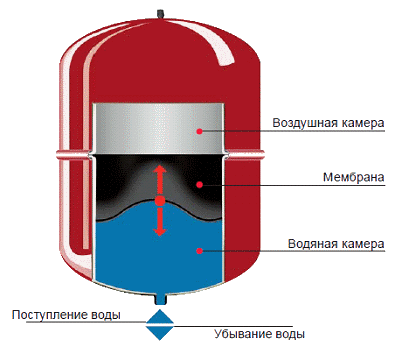
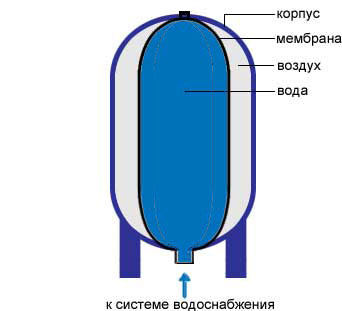
A membrane tank is a sealed vessel in which there are two compartments separated by a flexible membrane:
- the air compartment contains air under a certain constant pressure
- the water compartment is connected to the water supply or heating system; water flows into it at different pressures
The compartments are separated by an elastic membrane that can compress and stretch, thereby changing the ratio between the volumes of one and the second compartments. The air compartment has a valve with a nipple, through which you can change the air pressure, thereby regulating the operation of the membrane tank. It is the air pressure that will determine what volume of water and under what pressure can enter the water compartment.
Operating principle of a membrane expansion tank
When the water pressure in the system increases, the water compartment of the tank expands and fills with more water, and the air compartment contracts. As volume decreases, air pressure increases until the water pressure balances. When the pressure in the system drops (and becomes less than the air pressure), under the influence of air pressure the membrane contracts, the compartment with water decreases, pushing water back into the system, replenishing the pressure loss. The expansion membrane tank will “release” water into the system until the pressure of water and air balance each other.
Diaphragm expansion tank in heating systems
It is known that water increases in volume when heated (by about 4% when heated to 90 degrees), therefore closed systems For heating, it is necessary to use expansion tanks that will compensate for the expansion of water. The size of the expansion tank must correspond to the heating system: the volume of the tank must be such as to “extinguish” the expansion of all the water in the heating system. If you do not use an expansion tank, then when the water is heated, the pressure in the pipes will increase too much, which can lead to damage to the pipes and heating equipment.
Diaphragm tank as a hydraulic accumulator
In water supply systems, the expansion tank is used as a tank that allows you to heat up a certain amount of water under pressure and then use it for water supply. In this case, the pressure stored in the hydraulic accumulator is used to supply water without turning on the pump. So the hydraulic accumulator allows you to turn on the pump less often and thereby extend its service life.
Just like in a heating system, a membrane tank compensates for the expansion of water when hot water is supplied.
Using an expansion tank to protect against water hammer
When the pump supplying water is turned on abruptly, as well as when the pipeline is suddenly shut off, a pressure surge occurs that can damage both the pipeline and equipment. In this case, the expansion tank will act as a damper: under the influence of excess pressure, the membrane will stretch, the volume of the water compartment will increase, and the pressure will drop.