Diagram and features of the operation of a closed-type heating system with forced circulation, video. Do-it-yourself closed-type heating system in a private house Do-it-yourself closed-type heating systems
In the private sector within the city or outside it, there is no possibility of connecting the house to central heating, so cottage owners are engaged in installation autonomous heating. Installation of open and closed heating systems is possible
Autonomous heating is a system of interconnected elements that heat up when connected to a heat source. It can be either stove or water or electric heating– it all depends on whether the residents are there permanently or come periodically.
Properly installed water heating can be powered from any energy source - gas, solid fuel, development.
Heat supply closed type consists of pipes, boiler, circulation pump, battery and expansion tank. All elements are sealed - water does not evaporate when heated and circulated.

Differences between closed and open heating systems:
- Open autonomous system heating system involves installing an expansion tank in the highest place - in the attic under the roof; when closed, it can be placed anywhere.
- Unlike an open one, a closed heating system is sealed and isolated from air flows.
- An open heating system uses wide pipes that are installed at a certain angle for better circulation. A closed system requires smaller diameter pipes.
- For a closed heating system, it is important to install and adjust the pump correctly.
Circulation pumps ensure uniform distribution of coolant through the pipes, increase system productivity and help save fuel consumption.
Closed heating system: advantages and disadvantages
A sealed heating system with a pump operates under pressure and in complete atmospheric isolation, which leads to less oxidation of metal elements.
Pros of the system:
- The coolant is water, it does not evaporate, it is constantly in the system. If necessary, antifreeze can be used, which allows the system not to freeze, even if it is turned off for a short period.
- Using a pump to circulate the coolant allows the system to operate faster and, accordingly, heat the room faster.
- The expansion tank can be placed in close proximity to the boiler, which makes the system more compact.
- Using special taps, you can adjust the temperature in the room or disconnect a particular room from the system if it is not needed.
- When installing the system, pipes of small diameter are taken.
- The tightness of the system eliminates the appearance air jams in radiators.

Among the disadvantages is the fact that the system will not be able to function without electricity. If the power supply is turned off, the pump will stop working.
The only solution to the problem of power outages may be to install an autonomous generator, but this is an additional source of expense.
If not correct installation pipes of the system, which will cause disruption of its operation. Therefore, it is very important after installing all elements of the heating system to check it for leaks.
Closed heating system: single-pipe circuit
You can assemble a closed heating system with your own hands, having decided which scheme - one-pipe or two-pipe - will be used during installation.
Single pipe system heating is closed and is considered optimal for small cottages.
All heating devices - radiators - are connected to each other in turn. When installing the system, you need to use a powerful pump that will help the coolant quickly reach the end point of the system.

The expansion tank performs a number of important functions in the system. You can read about why it is needed and how to choose it correctly at
In this system it is not possible to install coolant return risers. During use, it is impossible to regulate the heat supply in certain rooms; if the temperature in one room decreases, the temperature throughout the house will decrease.
IN multi-storey buildings It is best to use a vertical single-pipe system, with the connection made from the highest point. It is not recommended to connect more than 10 heating devices along the riser. As a rule, the radiators on the 1st floor heat less efficiently than on the last.
What is a two-pipe closed heating system?
In a two-pipe closed-type heating system, the carrier (water, antifreeze) goes up the riser and is connected directly to a separate radiator. The heating system is characterized by high performance - water is distributed through the radiators at the same temperature, then goes down the riser back into the heating boiler.
For a private house, a two-pipe horizontal heating system is used.
With this heating scheme, you can regulate the flow and temperature on each radiator by installing a thermostat on the battery. All other batteries will not be affected by disconnecting one cell. Experts recommend installing a radiator for each to expel excess air when starting the system before the heating season.
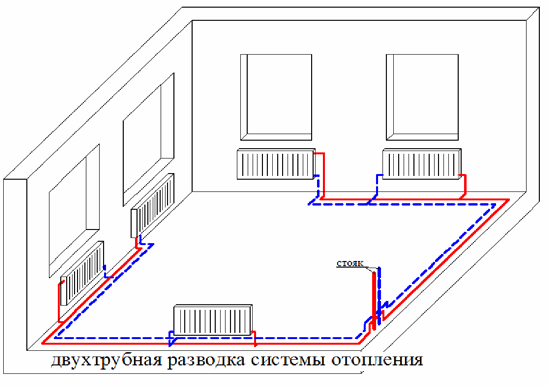
In a two-pipe closed-type heating system, there is no need to install a hydraulic pump - the coolant distributes through the pipes on its own.
When choosing between two heating schemes, you need to take into account that for all the efficiency of the two-pipe scheme, it requires 2 times more materials - pipes and fasteners.
Types of a closed heating system for a private house (video)
A closed-type heating system has many advantages, hence its popularity. With proper installation of the system elements and subsequent operation of the heating, the owner will not need to interfere with the work for a long time. It is important to periodically clean the expansion tank and air vent to avoid malfunctions.
Water heating is the most common option for heating a private home. Location of main structural elements determines the type of system and features of its operation. A competent choice of piping layout is the key to heating efficiency and occupant comfort.
Classification of water heating systems
Water heating systems are complex engineering systems with many varieties. The coolant in them is water or aqueous solutions. special purpose. Depending on the configuration of the systems, they are classified according to the following parameters:
- by the method of coolant circulation;
- by having contact with atmospheric air;
- according to the power supply diagram of the devices;
- according to the location of main pipelines.
 Heating circuit with natural circulation open type. 1 - boiler; 2 - expansion tank; 3 radiator; 4 - hot outlet of the boiler heat exchanger, goes strictly vertically to the expansion tank; 5 - main pipe filing; 6 - riser; 7 — main return pipe; 8 - ball valve; 9 - drain with ball valve for coolant discharge
Heating circuit with natural circulation open type. 1 - boiler; 2 - expansion tank; 3 radiator; 4 - hot outlet of the boiler heat exchanger, goes strictly vertically to the expansion tank; 5 - main pipe filing; 6 - riser; 7 — main return pipe; 8 - ball valve; 9 - drain with ball valve for coolant discharge
The first way to organize the movement of coolant through the system is natural circulation. This option allows you to ensure the operation of the heating without being dependent on the availability of electricity. Circulation is carried out due to gravitational forces. The liquid heated in the boiler rises due to a decrease in density, enters the radiators, gives off heat and returns to the boiler.
 Heating circuit with forced circulation closed type. 1 - boiler; 2 — air vent; 3 - pressure gauge; 4 - safety valve(numbers 2, 3, 4 make up the security group); 5 - expansion tank; 6 - radiator; 7 — coarse filter; 8 - drain; 9 - circulation pump; 10 - ball valve
Heating circuit with forced circulation closed type. 1 - boiler; 2 — air vent; 3 - pressure gauge; 4 - safety valve(numbers 2, 3, 4 make up the security group); 5 - expansion tank; 6 - radiator; 7 — coarse filter; 8 - drain; 9 - circulation pump; 10 - ball valve

The figure shows a single-pipe system with vertical distribution. Shown on different risers different types connecting devices.

The diagram below shows a typical configuration two-pipe system with vertical wiring.
 Single-pipe pressure heating system: 1 - boiler; 2 - security group; 3 — radiators; 4 - needle valve; 5 - expansion tank; 6 - drain; 7 - water supply; 8 - filter; 9 - pump; 10 - ball valves
Single-pipe pressure heating system: 1 - boiler; 2 - security group; 3 — radiators; 4 - needle valve; 5 - expansion tank; 6 - drain; 7 - water supply; 8 - filter; 9 - pump; 10 - ball valves
The simplest one-pipe system with horizontal wiring implies the sequential passage of coolant through all devices within one floor.
 Manifold circuit: 1 - boiler; 2 - expansion tank; 3 - supply manifold; 4 — heating radiators; 5 — return manifold; 6 - pump
Manifold circuit: 1 - boiler; 2 - expansion tank; 3 - supply manifold; 4 — heating radiators; 5 — return manifold; 6 - pump
A two-pipe horizontal system can have perimeter or radial (collector) wiring. In the first case, pipes are laid along the perimeter of the room, gradually powering all devices; in the second, each heating device has a separate supply line.

Pipes beam distribution laid in the floor screed along the shortest routes to each radiator. Moreover, their configuration resembles rays emanating from one source - distribution manifold. This was the reason for the appearance of the corresponding name.
Collectors in modern interiors private houses are often neatly hidden in special cabinets, which allows you to preserve the aesthetics of the room and hide the elements of setting up and regulating the system.
Radiator connection types
The connection diagram for heating devices is selected based on the selected structure of the heating system, ease of installation and maintenance, as well as interior features.
 1 - Two-pipe wiring. 2 — Single-pipe wiring
1 - Two-pipe wiring. 2 — Single-pipe wiring
The figure shows the main options for connecting radiators, typical for vertical systems.
 A - side connection; B - diagonal; B - bottom connection
A - side connection; B - diagonal; B - bottom connection
Analysis of patterns that are most often found in horizontal systems, shows that the type of connection of radiators has a significant impact on the efficiency of heat transfer. Before giving preference to a more convenient installation option, you should think carefully about whether you are ready to sacrifice some of the precious heat.
As can be seen from everything stated above, the choice of a water heating scheme for a private house is associated with the need for a thorough analysis of many options. In addition to the main varieties described, there is an even more detailed classification. Consultation qualified specialist will help you quickly navigate through all the diversity, take into account the existing nuances and achieve the best results.
An open heating system is the simplest and most energy-independent system with natural circulation. This system is based on the laws of thermodynamics. At the outlet of the boiler, increased pressure is created, then hot water passes through pipes to an area of lower pressure, losing temperature as it passes.
Next, the cooled coolant is returned back to the heating boiler, where it is heated again. Natural coolant circulation occurs. The system operates exclusively on water, since the use of antifreeze for heating leads to their rapid evaporation.
IN open system heating supply, it is necessary to have an expansion tank, since heated water expands. The expansion tank is used to receive excess water during expansion and return it to the system when cooling, as well as to remove water when its volume is excessive. The tank is not completely sealed, so water evaporates As a result, it is necessary to constantly restore its level. An open heating system does not use a pump. The system is quite simple. Consists of pipes, steel expansion tank, radiators and boiler. Diesel engines are used gas boilers and solid fuel boilers, except electric ones.
In an open heating system, water circulates slowly. Therefore, during operation, pipes must warm up gradually to avoid their damage and boiling of the coolant. This can lead to premature wear of the equipment. If in winter period heating is not used, the water from the system must be drained to avoid pipeline freezing.
In order for the coolant to circulate at the required level, it is necessary to install the heating boiler in a lower place in the system, and install it in the highest place. expansion tank, for example, in the attic. In winter, the expansion tank must be insulated. When installing piping in an open heating system, it is necessary to use minimal amount turns, shaped and connecting parts.
In a closed heating system, all elements of the system are sealed, and there is no evaporation of water. Circulation is carried out using a pump. The so-called system with forced circulation The coolant includes pipes, boiler, radiators, expansion tank, circulation pump.
 In a closed heating system, as the temperature rises, the expansion tank valve opens and takes in excess coolant. When the temperature drops coolant, the circulation pump pumps it back into the system. This heating system maintains pressure within predetermined limits. Thanks to this, it is possible coolant deaeration function.
In a closed heating system, as the temperature rises, the expansion tank valve opens and takes in excess coolant. When the temperature drops coolant, the circulation pump pumps it back into the system. This heating system maintains pressure within predetermined limits. Thanks to this, it is possible coolant deaeration function.
For stable operation of the closed heating system, an expansion tank made of high-strength metal is also used. This closed tank, consisting of two halves rolled towards each other.
Inside there is a membrane (diaphragm) made of high-strength heat-resistant rubber. There is also a small gas volume(can be nitrogen that is pumped in at the manufacturing plant, or air that accumulates in the system as needed). The membrane divides the tank into parts: one part is where excess water flows when heating the heating system, the other part contains nitrogen or air that does not come into direct contact with the water. Thus, heating fluid enters the expansion tank and penetrates the membrane. As the coolant cools, the gas behind the membrane begins to push it back into the system.
Differences between open and closed heating systems
The following are available distinctive features open and closed heating systems:
- At the location of the expansion tank. In an open heating system, the tank is located at the highest point of the system, and in a closed system, the expansion tank can be installed anywhere, even next to the boiler.
- Closed system heating is isolated from atmospheric flows, which prevents air from entering. This increases service life. By creating additional pressure in the upper nodes of the system, the possibility of formation of air jams in radiators located on top.
- An open heating system uses pipes with a large diameter, which creates inconvenience, the pipes are also installed at an angle to ensure circulation. It is not always possible to hide thick-walled pipes. To ensure everyone hydraulic rules it is necessary to take into account the slopes of flow distribution, lifting height, turns, narrowing, connection to radiators.
- A closed heating system uses smaller diameter pipes, which reduces the cost of construction.
- It is also important in a closed heating system install the pump correctly, which will avoid noise.
Advantages of an open heating system
- easy system maintenance;
- the absence of a pump ensures silent operation;
- uniform heating of the heated room;
- quick start and stop of the system;
- independence from power supply, if there is no electricity in the house, the system will be operational;
- high reliability;
- no special skills are required to install the system; first of all, the boiler is installed; the power of the boiler will depend on the heated area.
Disadvantages of an open heating system
- the possibility of reducing the service life of the system if air enters, as heat transfer decreases, resulting in corrosion, water circulation is disrupted, and air pockets form;
- air contained in an open heating system can cause cavitation, which destroys system elements located in the cavitation zone, such as fittings and pipe surfaces;
- possibility of freezing coolant in the expansion tank;
- slow heating systems after switching on;
- necessary constant level control coolant in the expansion tank to prevent evaporation;
- impossibility of using antifreeze as a coolant;
- quite bulky;
- low efficiency.
Advantages of a closed heating system
- easy installation;
- there is no need to constantly monitor the coolant level;
- opportunity antifreeze application without fear of defrosting the heating system;
- by increasing or decreasing the amount of coolant supplied to the system, you can regulate temperature in room;
- due to the absence of water evaporation, the need to replenish it from external sources is reduced;
- independent pressure regulation;
- the system is economical and technologically advanced, has a longer service life;
- possibility of connecting additional heating sources to a closed heating system.
Disadvantages of a closed heating system
- the most important drawback is the system’s dependence on the availability constant power supply;
- the pump requires electricity to operate;
- For emergency power supply it is recommended to purchase a small one generator;
- if the tightness of the joints is broken, air may enter the system;
- dimensions of expansion membrane tanks in large enclosed spaces;
- the tank is filled with liquid by 60-30%, the smallest percentage of filling occurs in large tanks; at large facilities tanks with a design volume of several thousand liters are used.
- There is a problem with the placement of such tanks; special installations are used to maintain a certain pressure.
 Everyone who is going to install a heating system chooses which system is simpler and more reliable for him.
Everyone who is going to install a heating system chooses which system is simpler and more reliable for him.
Open heating system, thanks to ease of use, high reliability, used for optimal heating small rooms. These can be small one-story country houses, as well as country houses.
A closed heating system is more modern and more complex. It is used in multi-storey buildings and cottages.
When heating private sector houses, a closed heating circuit with forced circulation is mainly implemented.
The coolant in this scheme does not evaporate due to lack of contact with environment. This makes it possible use special compounds other than water, increasing heating efficiency.
Closed heating system: what is it, how it works, pros and cons
Such circuits use expansion membrane tanks. Sealed container divided into two parts by an elastic membrane.

As the temperature increases, the valve opens and excess liquid moves into the tank.
When the temperature drops, the coolant flows back into the system, due to which the latter maintains stable pressure.
Gravity tank can be completely filled with liquid, so the pressure maintenance installation must be more compact than that of a conventional tank. It allows you to adjust the specified parameters in the circuit and automatically recharge the structure.
Closed circuit consists of the following elements:
- from sealed membrane tank;
- from batteries (radiators);
- from the heating boiler;
- from the circulation pump;
- from pipes;
- from connecting elements(valves, taps, filters).
Closed heating circuit has a number of advantages:
- possibility of using any coolant;
- durability of the structure due to complete tightness;
- absence of unnecessary noise;
- opportunity self-installation systems;
- high speed of fluid movement, ensuring maximum heat transfer;
- no need for thermal insulation for the main line;
- reducing financial costs for heating the house.
The disadvantages include dependence electrical energy and the need to purchase a membrane tank big size, the price of which is quite high. The problem of energy dependence is solved by installing uninterruptible power supplies or small generators that provide emergency power supply.
Design diagrams, use in apartment buildings
Used in private homes single-pipe or two-pipe heating circuit.
Single-pipe scheme used in rooms with a small area where heating requires no more than five radiators.

Photo 1. Diagram of a closed heating system with a single-pipe circuit. Each of the radiators is connected in series.
All batteries are connected in series in the circuit, so the last heating device will always be colder than the first. The obvious advantage of such a scheme is less pipe consumption.
If one battery fails, the others will continue to operate as normal when using bypass. Single pipe system can be horizontal or vertical. The horizontal one does not allow you to regulate the amount of coolant, so bypasses are installed when laying it. A vertical single-pipe circuit is in most cases used in high-rise buildings.
Two-pipe (double-circuit) circuit heats rooms more evenly. Liquid circulates from the heat generator to the batteries along two circuits. In this case, radiators are connected in parallel. The coolant has the same temperature in all batteries. This method is much more expensive, but it makes it possible to regulate the temperature in each room.
Calculation
In order to correctly select the circulation pump and pipe diameters, carry out hydraulic calculation of heating circuit. It allows you to identify hydraulic pressure losses in specific areas and minimize operating costs.
Attention! Circulation pump it is advisable to install in the return pipeline. In this case, the service life of the device will increase, since already cooled coolant will pass through it.
Calculations are carried out by a specialized specialist using thermal engineering calculations and after selecting batteries. As a result of the calculations, the pressure value required to circulate water through the circulation pump will be obtained. After this stage, the value is calculated to determine the volume and selection of the membrane tank.
You might also be interested in:
How to introduce coolant into the system?

When filling a closed contour there should be no air pockets left.
If the heating circuit is connected to the water supply using a tap, then in order to fill it you need periodically open the valve and release the displaced air from radiators.
This process continues until all excess air is gone and the pressure reaches the required level. calculated value.
To fill a circuit not connected to a water supply pump and container required, from which the coolant will be pumped. Before feeding it, you need to open all the taps on the radiators. The drain fitting is connected to the pipe, and the structure is filled with the help of a circulation pump.
Important! When filling heating circuit coolant it is necessary to close the taps on time to prevent leaks.
Setup and launch
After starting the coolant into the structure check all circuit connections. Before this, the air must be removed from the pump, otherwise the operation of the device may be disrupted. Next, you need to go around all the batteries and do the same procedure, slightly opening Mayevsky cranes.
The air descends until water flows from the radiators. After this, the pressure value is checked using the measuring device. If she below 1.5 atmospheres, then the liquid is added again, and the process of deaerating the equipment is resumed.

Then the system is subjected to pressure testing. The pump pumps coolant into the pipes until the pressure increases in 1.5-2 times.
The heating structure is left in this state for 15 minutes, after which the pressure is measured again. If the meter readings change, there is a leak somewhere.
Otherwise, the system returns operating pressure by draining excess coolant.
The final step is starting the heat generator, which is already prepared for use and included in the network. The equipment thermostat is set to a low temperature ( 40—50 °C), time is given to warm up the entire volume of coolant. After this, all radiators are checked. If the top parts of the batteries are colder, the air is bleed again.
After that increase the temperature of the liquid(up to 70–80 °C) and leave the heating circuit for a while. If in this mode the heating devices continue to operate normally, and the temperature of the liquid in the return pipe at 20 °C colder than the heated one, then the system functions properly and does not require additional settings.
Features of a heating circuit with a membrane expansion tank
A circulation pump in a closed circuit allows you to organize the design according to any scheme, regardless of the hydraulic resistance. Forced circulation gives possibility to use various options for organizing heating:
- sequential arrangement of radiators;
- collector circuit;
- warm floor.
Diaphragm expansion tank and circulation pump can be located together with the heat generator in the same room. This reduces the overall length of the pipelines, so when organizing the heating circuit there is no need to install pipes large diameters and pay attention to the angles of inclination.

Photo 2. Diagram of the structure of a membrane tank for a closed heating system. Arrows indicate parts of the structure.
Why does pressure drop?
The reasons for the drop in pressure may be:
- malfunctions of the heat generator (heating boiler);
- coolant leaks;
- excess air;
- aluminum radiators.
The leak may not be visually noticeable. To discover it, use special devices: thermal imagers or ultrasonic devices. You need to carefully check the sectional connections of the radiators, because their surface may be covered with corrosion. Rusty smudges indicate damage to the batteries.
To detect a leak you need to press the nipple, which is located on top of the expansion tank. If water and air are released when pressed, then we can safely conclude that there is a leak.
Closed heating with safety group
Safety unit in the heating circuit is a set of devices that prevent the occurrence of emergency situations. Any heating structure operates at certain values pressure. Depending on the heating or cooling of the coolant, this value varies. The security group monitors it and if the maximum is exceeded permissible value discharges a certain amount of liquid from the circuit.
How to organize heating of a particular building is up to the owner to decide for himself. If we are talking about a private residential building, then the most common heating option is a closed system with forced circulation. Compared to an open one, it has a number of significant advantages, and therefore is more widely used, regardless of the dimensions of the structure, its purpose, the complexity of the circuit configuration and parameters components.
What is a closed heating system with forced circulation, what are its advantages, what are the features of such a scheme - all these questions can be answered in this article.
 Open system
Open system
But before considering its specifics, you should understand the terminology. It is precisely because of ignorance of certain nuances that people who do not have professional training often get confused in definitions. The fact is that not everyone understands the fundamental difference between a closed heating system (CS) and an open heating system (OS).
Forced movement of the coolant (its circulation) can be organized in both. To avoid substitution of concepts in the future, you should immediately answer a number of questions.
What is the difference between ZS and OS? Any liquid expands when heated. Since the coolant is water (less often, antifreeze or its analogues), it is necessary to somehow compensate for the increase in pressure in the pipes, otherwise depressurization of the system cannot be avoided. To do this, an expansion tank is included in the circuit. In the OS it is open type, and the pressure is regulated by the atmosphere.
 Closed heating system
Closed heating system
IN closed scheme it is completely sealed, and its internal diaphragm (membrane) is responsible for compensating for expansion.
What is the meaning of forced circulation? The movement of liquid does not occur due to the pressure difference at the outlet and inlet of the heat generator (as they say, by gravity), but is carried out by a pump, which is one of the components of the circuit.
Comparing various systems, you can see that each has both pros and cons, although ZS has many more advantages. Her significant drawback only in one way - “binding” to the power supply/voltage. When it is turned off, the pump and boiler will stop.
On a note! When choosing this particular heating option, it is necessary to foresee in advance how to organize an alternative electricity supply. Therefore, the cost estimate should immediately include the cost of purchasing an autonomous power source.
Scheme composition
As can be seen from the figure, its main parts are:
- 1 – heat generator (boiler of any type);
- 6 – membrane tank;

- radiators and pipe system;
- 9 – water pump.

On a note! It is advisable to install the pump at the entrance to the boiler (at the end of the route). In this case, it will pump already cooled coolant, which means that the service life of the product will increase slightly.
Additional elements - valves, valves, sensors (pressure, temperature) and a number of others. The need for their installation is determined design features boiler and the specifics of the mounted circuit (its diagram).

How the system works
It is easy to understand from the picture. The direction of movement of the coolant is shown by arrows.

From the boiler outlet, water heated to the required temperature passes through a pipe system through all the batteries installed in the circuit, giving them thermal energy. Since the system is closed, the liquid returns back. This circulation is provided by the pump. The heat exchanger heats the cooled coolant, and it goes back into the circuit. This process is continuous, and all system parameters are controlled by the boiler automation. In principle, nothing complicated.
Types of closed system
Since consideration of the features of various schemes is not directly related to the topic of the article, we will note only some of their main differences.
Single-pipe

As can be seen from the figure, all radiators are connected to the circuit in series (the so-called “Leningradka”). The disadvantage is that the last battery in the chain will be much colder than the first. Therefore, such circuits are installed in relatively small buildings. An obvious plus is lower consumption of materials (primarily pipes).
Two-pipe

This scheme allows for more uniform heating of all rooms without exception. But the costs of its installation are somewhat higher. However, it is precisely this type of heating circuit design that is considered the most acceptable for a private house, especially if it has quite a lot of rooms and 2–3 floors.
There are a number of other features of closed-type systems - pipe routing (vertical, horizontal), installation membrane tank() and so on. But these are separate topics, and anyone interested in a specific option can find out for themselves on our website. Let us sum up everything that has been said.
What opportunities does ZSO provide?
Using not only water, but also low-freezing liquids as a coolant. This is important in cases where, for example, the boiler is used to heat not only a residential building, but also another (auxiliary) building located on personal plot. Or for suburban buildings, if the owners are away and the power supply line is de-energized. Using the same antifreeze as a coolant significantly reduces the risk of the system defrosting.
Connecting several additional circuits.

Long length of pipes. The main thing is to choose the right power of the boiler and pump. But the use of natural circulation systems in houses with several rooms (floors) is less effective.
In systems with forced circulation, it is possible to install pipes of a smaller cross-section than with natural ones, and their cost is lower.
High circuit heating rate. In this regard, the analogue with gravity flow is more inert.
The tightness of the membrane tank dramatically reduces the likelihood of “airing” the system.
Maximum heat transfer due to the speed of fluid movement. While it is in the pipes, it does not cool down to the same degree as in a system with an EC. As a result, less energy is spent on its secondary heating.
This is, perhaps, all you need to know in general terms about a closed-type heating system with forced circulation of coolant.
