How to calculate the diameter of a ventilation pipe. Ventilation ducts in brick walls
Comments:
- Performance standards and natural ventilation channels
- Channel parameters and ventilation calculations
- Ventilation calculation example
is a system in which there is no forced driving force: a fan or other unit, and the flow of air occurs under the influence of pressure differences. The main components of the system are vertical channels starting in the ventilated room and ending at least 1 m above the roof level. The calculation of their number, as well as the determination of their location, is carried out at the design stage of the structure.
The temperature difference at the lower and upper points of the duct causes the air (it is warmer in the house than outside) to rise upward. The main indicators that affect the traction force are: the height and cross-section of the channel. In addition to them, the efficiency of the natural ventilation system is affected by the thermal insulation of the shaft, turns, obstacles, narrowing in the passages, as well as wind, and it can either contribute to the draft or reduce it.
Such a system has a fairly simple arrangement and does not require significant costs both during installation and during operation. It does not include mechanisms with electric drives, it operates silently. But natural ventilation also has disadvantages:
- operating efficiency directly depends on atmospheric conditions, so it is not used optimally most of the year;
- performance cannot be adjusted, the only thing that needs to be adjusted is air exchange, and then only downward;
- in the cold season it causes significant heat loss;
- does not work in hot weather (there is no temperature difference) and air exchange is possible only through open vents;
- If work is ineffective, dampness and drafts may occur in the room.
Performance standards and natural ventilation channels

The optimal location for the channels is a niche in the wall of the building. When laying, remember that the best traction will be with a flat and smooth surface of the air ducts. To service the system, that is, cleaning, you need to design a built-in hatch with a door. To prevent debris and various sediments from ending up inside the mines, a deflector is installed above them.
According to building regulations the minimum performance of the system should be based on the following calculation: in those rooms where people are constantly present, the air should be completely renewed every hour. As for other premises, the following should be removed:
- from the kitchen - at least 60 m³/hour when using an electric stove and at least 90 m³/hour when using a gas stove;
- baths, toilets - at least 25 m³/hour, if the bathroom is combined, then at least 50 m³/hour.
When designing a ventilation system for cottages, the most optimal model is one that involves laying a common exhaust pipe through all rooms. But if this is not possible, then the ventilation ducts are laid from:
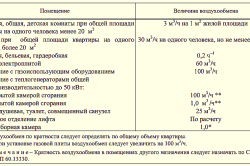
Table 1. Ventilation air exchange rate.
- bathroom;
- kitchens;
- storage room - provided that its door opens in living room. If it leads to the hall or kitchen, then only a supply duct can be installed;
- boiler room;
- from rooms that are separated from rooms with ventilation by more than two doors;
- if the house has several floors, then starting from the second, if there is entrance doors From the stairs, channels are also laid from the corridor, and if there are none, from each room.
When calculating the number of channels, it is necessary to take into account how the floor on the first floor is equipped. If it is wooden and mounted on joists, then a separate passage is provided for air ventilation in the voids under such a floor.
In addition to determining the number of air ducts, the calculation of the ventilation system includes determining the optimal cross-section of the ducts.
Return to contents
Channel parameters and ventilation calculations
When laying air ducts, both rectangular blocks and pipes can be used. In the first case, the minimum side size is 10 cm. In the second smallest area air duct cross-section is 0.016 m², which corresponds to a pipe diameter of 150 mm. A volume of air equal to 30 m³/hour can pass through a channel with such parameters, provided that the height of the pipe is more than 3 m (with a lower value natural ventilation not provided).

Table 2. Ventilation channel performance.
If it is necessary to increase the performance of the air duct, then either the cross-sectional area of the pipe expands or the length of the channel increases. The length, as a rule, is determined by local conditions - the number and height of floors, the presence of an attic. In order for the traction force in each of the air ducts to be equal, the length of the channels on the floor must be the same.
To determine what size ventilation ducts need to be laid, it is necessary to calculate the amount of air that needs to be removed. It is assumed that outside air enters the premises, then it is distributed into rooms with exhaust shafts and is exhausted through them.
The calculation is made floor by floor:
- The smallest amount of air that should come from outside is determined - Q p, m³/hour, the value is found according to the table from SP 54.13330.2011 “Residential multi-apartment buildings” (Table 1);
- According to the standards, the smallest amount of air that needs to be removed from the house is determined - Q in, m³/hour. The parameters are specified in the section “Performance standards and natural ventilation channels”;
- The obtained indicators are compared. The minimum productivity - Q р, m³/hour - is taken to be the largest of them;
- For each floor, the height of the channel is determined. This parameter is set based on the dimensions of the entire building;
- According to the table (Table 2), the number of standard channels is found, and their total performance should not be less than the minimum calculated;
- The resulting number of channels is distributed between rooms where air ducts must be present.
Maintaining the required indoor microclimate parameters is impossible without proper organization air exchange. Ventilation ducts are designed to provide the required air replacement rate in the room, so their arrangement is planned at the building design stage. The most common and reliable material used for these purposes is brick.
Ventilation ducts: the need for arrangement
Building structures are usually located in walls (inside). In this case, the brick is laid in one row if the wall thickness does not exceed 38 cm, and in 2 rows - with a wall surface 64 cm thick. One of the ventilation elements - the exhaust pipe - should be formed with walls of 2.5 bricks. It is this size that allows you to maintain a constant temperature regime inside the shaft, protect the passing air from cooling.
Multi-storey buildings are characterized by inclined rather than orthogonal ventilation systems. At the same time, the level of their outlets reaches 1 m. The maximum deviation of a vertical shaft without deteriorating ventilation performance is no more than 30 degrees.
Laying channels: technical features
Masonry ventilation ducts made of brick starts with design work. For a private house, at the initial stage of drawing up a project, one cannot deviate from the requirements set out in SNiP 2.04.05-86.
- The construction of air ducts without an approved design is prohibited.
- Smoke and ventilation outlets must not be combined.
- For wall thicknesses up to 380 mm, the masonry is single-row.
- If the thickness of the wall partition is 640 mm, the masonry is done in 2 rows.
- Before construction begins, the outline of the channel is drawn using a template, etc.
The dimensions of ventilation shafts are calculated in such a way as to ensure the required air exchange rate in the room. Power is taken as the initial data heating system heating the premises:
- Channel size (cm): 14x14 – with a power of no more than 3.5 kW;
- 14x20 (cm) – 3.5 – 5.2 kW, respectively.
The type and parameters of ventilation ducts in brickwork depend on the purpose of the building, but basically it is square section vertical shaft (140x140mm), laid out in 2 bricks in interior walls Oh. You need to focus on the following parameters of a single brick: its length is 250 mm, width 120 mm, height 65 mm.
Attention! Exhaust duct along with the removed air, it carries heat outside. A small structural detail inside it - a bend in the form of a brick staircase - will become an obstacle to the outflow of warm air masses.
In houses with stove heating Channels for air exchange are best placed parallel to the stove chimney, close to it. Air heated from exhaust gases improves draft and efficiency of their operation. If it is difficult to do this structurally, then the outlet installed in the outer wall is insulated. This ensures good traction. For a constantly operated fireplace, an independent ventilation duct must be provided in the house. Through it, smoke entering the room from fuel combustion is removed to the street.
Brick for masonry and notes on working with it
For brick walls, solid stone is usually used. It is possible to use hollow facing bricks, but with voids filled with clay or mortar.
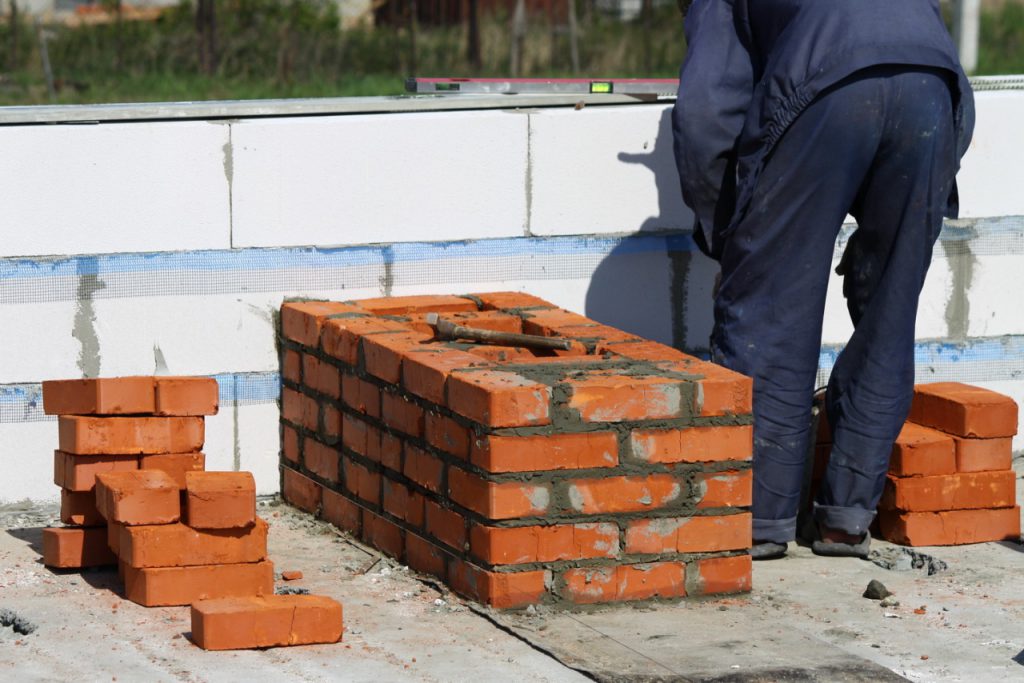

Attention! Sand-lime brick is not used to form ventilation ducts, because... sudden temperature changes provoke its destruction.
The brick is fixed in the channels with the same mortar that was used for the construction of the internal walls. In order for the batch to be of sufficient strength, the following proportions must be observed when preparing the solution:
- purified construction sand – 3 parts;
- cement M500 – 1 part.
Water is added in measured portions to the dry, pre-prepared mixture with constant stirring. The consistency of the mixture should be such that when the container is tilted at 45 degrees, it does not spill out.
Forming a ventilation duct often requires the use of bricks custom size in cases of ligation of seams, at the junction of walls, etc. For their mechanical processing, the following is used:
- chopping with a trowel or pick-hammer;
- Bulgarian;
- mechanism for cutting bricks.
In order to save money, scraps, material with broken corners, chips, etc. are processed.
Algorithm for laying a ventilation duct
- Careful study of the drawing.
- Applying markings using an inventory folding template. If it is not there, openings are made in a board with dimensions (mm): 140x2500x25, identical to those marked on the wall plan.
- The brick is laid strictly according to the level, for which buoys or a box made of boards with the dimensions of the channel are used. The straightness of surfaces and corners must be maintained.
- If the air temperature is high and the brick is dry, it is necessary to moisten it with water to improve adhesion between the material and the mortar.
- 3 or 4 rows of masonry are formed.
- Buoys are installed - bricks laid level in the cross section of the channel. They protect it from debris during work and maintain the desired shape of the hole.
- The buoy moves every 7 or 8 brickworks with a single-row or multi-row ligation system.
- If there is a possibility of fuel combustion products entering the premises, as well as nearby ventilation systems along with the supplied air, then it is better to do the masonry using the “end-to-end” method.
- Ensure that the thickness of the seams is maintained.
- Seal them all thoroughly.
How much does it cost to build a masonry

Despite the popularity of monolithic and frame house construction, masonry made from piece materials is still in demand in construction. Can do quality work experienced craftsmen, with certain skills and knowledge. If it is planned to invite specialists to perform this type of work, then an estimate must be drawn up. It is affected by:
- number of storeys of the building;
- area of premises;
- geometric complexity of channels;
- performing dressings with existing masonry;
- the need to finish sedimentary seams;
- type of material and its price, etc.
At the same time, the speed of work does not depend on such characteristics of the brick as strength grade, resistance to freezing, and color preferences. Therefore, these parameters do not affect prices.
Refined calculations take into account the real costs of working time for each type of work performed (man-hours). After timing the execution of each construction operation, its exact duration is determined. Having these data, as well as the size of the average wages For a specific region, you can calculate the hourly rate using the formula:
R – tariff (rubles);
C – salary size (average) (rubles/day);
V – duration of work per day (hour).
Example
The crew carries out the laying, working 12 hours a day. With indicator C = 900 rubles/day, the cost of work for 1 hour will be: 900/12 = 75 rubles per hour.
It is also taken into account that the tariff for laying, for example, hollow one-and-a-half bricks will be significantly lower. This is justified by the higher speed of work completion. The number of piece units per unit of masonry volume in this case will also be less. All this explains why prices for this type of service are different regions, differ at different objects.
A properly implemented ventilation system in the house will help maintain optimal microclimate parameters, promote cleanliness of the air in it, and prevent the formation of dirt in the ducts and heat loss.
Ventilation is important for any home, which will prevent mustiness, unpleasant odors and dampness from entering it. One way to get rid of this is to provide ventilation ducts in brick walls. With a hidden “hood” there will be a good microclimate in the house.
Indispensable rules of the device
 Exhaust ventilation channels are installed when laying the walls of the house, inside them. If the wall is 38 cm thick - in 1 row, if 64 cm - in 2 rows. Traditional section - 140x140 mm. The same solution is used as for masonry at home. It is allowed to use a solution of clay and sand.
Exhaust ventilation channels are installed when laying the walls of the house, inside them. If the wall is 38 cm thick - in 1 row, if 64 cm - in 2 rows. Traditional section - 140x140 mm. The same solution is used as for masonry at home. It is allowed to use a solution of clay and sand.
Before you make a ventilation duct in a brick wall, you need to have a solid ceramic brick. You will need a template that you can make yourself. This is a board (length, width, thickness - 2.5 m x 140 mm x 25 mm), in which cutouts are made corresponding to the size of the ventilation ducts and their location on the wall. We need inventory buoys - hollow boxes made of boards. Their cross section is like that of a channel, the height should be 8-10 bricks. Cleaning of the masonry will be done by mopping, checking for “cleanliness” - with a test ball on a cord with a diameter of 100 mm.
The masonry is done vertically. It must be moved away from the door opening as well as from the wall joints by no less than 380 mm. The adjacent channel and chimney are insulated with each other using heat-resistant materials and the walls of the channel are enlarged.
Practical experience
The installation of a ventilation duct is made taking into account the following important points:

And if without masonry
A homemade ventilation duct in brick walls is made using pipes. But even in this case, it is necessary that each room has its own air duct. One of the exits should be at a height of two meters above the foundation (higher is possible) inside outer wall(sucks in air from the street). The second is on the roof (removes air from the house). All channels are connected to it. The pipe should rise one meter above the roof. The inlets for the grilles are located under the ceiling, no lower than 10 cm. They are closed with dampers that regulate the air flow.
You can combine hoods from the sauna-kitchen, bathroom-toilet. All four can be combined in the attic. It is important that there are reliable seals at the joints. Information “in a bouquet” can only be done if the services are located on one side of the house. IN one-story house they can be mounted in the ceiling (they go out to the roof through the attic). Pipes in the attic should be insulated.
For natural ventilation risers, the diameter of the pipes is 125 x 150 mm, for forced ventilation - 100 x 125 mm. The choice of materials depends on what the owner likes and the price. They can be made of polymers, galvanized, asbestos cement, concrete. When installing, pipes are lowered into the space between the walls and cemented. The tightness at the point where the ventilation pipe exits onto the roof is important. To do this, use a passage element made of rubber or silicone. The air duct and the exhaust outlet are connected by a corrugated pipe.
How to make pipes yourself
You can make a ventilation duct in a brick wall yourself, even if it is thin. With a partition half a brick thick, an asbestos-cement pipe with a diameter of 120 mm (internal - 100) will “fit in”. The opening in this case should be 130 mm wide. Having lowered the pipe into it, it is strengthened with cement mortar.
In the absence of a pipe, it is made like this: two large half-waves of slate the right size fastened with wire. It is attached to a brick cabinet, which is laid out flush with the partition. But there is another way: on the sides of the partition in its upper part, lay a couple of bricks on the edge and install the structure. Under ventilation grille a hole is cut out at the bottom where it is attached. At the end - plastering. The part that ends up in the attic should be insulated with asbestos (foil will also do). On the roof it should be no closer than a meter from its highest point.
There are even thinner openings - a quarter of a brick. In this case, the cabinet will be replaced with a structure that can be made from strips flat slate(width 20 cm). They are inserted into the canal, spread out and tied with wire, and plastered.
Hood connection
In the kitchen, only the ventilation installed in the wall may be “missing”, especially if you cook often and the kitchen is small. A hood helps out by removing unpleasant air from the kitchen. It is important to connect it correctly to the ventilation duct. It is desirable that the distance to the ventilation shaft be minimal. Otherwise, the effect of the hood will be reduced. And long air ducts look ugly.
For connection, special air ducts and adapters are required. The elements are connected hermetically. For safety and efficient work a number of rules are important. When connecting an exhaust pipe, it should not block the entire ventilation duct: when it is not working, the main ventilation operates from air draft. To do this, you need to remember to place a grill over the entrance of the exhaust pipe.
To ensure that the hood does not fail, the air must not be obstructed. This is why it is important to keep the duct length shorter. And it’s better to forget about turns altogether. The smoothness of the pipe will also contribute to high-quality traction. Therefore, corrugated pipelines, which are preferred due to their flexibility, still hinder the air flow. If you can't do it, you need to smooth out the turns. Danger: if a gas heater is used in the kitchen, the hood must not be vented into its smoke duct
The most common mistakes
- The ventilation duct is not installed in the kitchen, bathroom, bathrooms, and closets without windows.
- Instead of a channel, there is a hole in the wall, closed by a grille. This does not provide traction, and therefore is not effective.
- The windows and doors are hermetically sealed and there are no ventilators. In such conditions, ventilation does not work, which will be reported unpleasant odors, condensation, mold.
- “Overkill” with ventilation. Forced ventilation, if there is a special hood, for example, a fireplace, is not allowed.
- There is no hood at all in the room with the fireplace. A properly functioning fireplace chimney is safe. But when the fireplace is lit, smoke can enter the room; it is better to have a separate ventilation duct in it.
- There is no hood in the room, which is separated from the rest by two doors. “Overcoming” them with air flow is sometimes completely impossible, as is effective ventilation.
- Uninsulated channel. If the channels are in external walls, they must be insulated, otherwise the traction force is lost.
- Gas pipes must not be installed in the wall. Do this only in fines with screens that have holes for ventilation.
- Deviation of the vertical channel may interfere with ventilation. Maximum 30°. If the job is done, there is only one way out - install an additional fan. Just not in a room where there is a fireplace!
Ventilation systems in any home perform an important function. Laying brick ventilation ducts solves one of the problems in ensuring the operation of such a system.
Ventilation ducts are designed to remove exhaust air from the room.
Depending on what the house is made of, the design of exhaust ventilation may be different. Many standard circuits and devices are offered in this direction. If the walls of the structure are brick, then laying ventilation ducts from brick suggests itself.
Device Features
Ventilation ducts are an air duct through which air moves due to the difference between external and internal pressure (natural ventilation), or the movement is set by a fan ( forced ventilation). Exhaust ventilation made up of ventilation ducts (inside the wall or attached), closed with louvered grilles, prefabricated air ducts located horizontally, and a shaft to provide exhaust. Stagnant air from the house is directed into the channel, bypassing the grille louvers, rises and accumulates in a horizontal air duct, from where it escapes out through the shaft exit. Air flow is controlled internally by a louver valve, and inside the duct and shaft by shut-off valves.
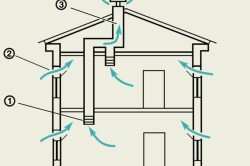
Living room ventilation diagram: 1 - exhaust grille; 2 - transom or window; 3 - ventilation duct.
In buildings with brick walls, ventilation ducts are installed inside the walls or in grooves covered with slabs. The minimum size of brick ventilation ducts should be half the length of the brick (14x14 cm). The thickness of the channel partition should not be less than half a brick. Ventilation ducts are not formed in external load-bearing brick walls. In cases where the house does not have internal brick walls, attached air ducts with a minimum size of 10x15 cm are installed. Such air ducts at normal humidity are usually made of gypsum slag and plasterboard boards, and at high humidity - from concrete panels up to 40 mm thick. Sometimes air ducts are made of asbestos cement, metal sheets or plastic.
Horizontal type air ducts located in attics or other rooms are made of gypsum slag panels up to 50 mm thick with air gap 40 mm or hollow concrete slabs up to 10 cm thick. Horizontal air ducts are installed from above ceiling covering by laying one row of slabs, then covered with a layer of cement more than 5 mm thick. The size of horizontal air ducts is at least 20x20 cm. Horizontal air ducts in rooms with high humidity (bathhouse, sauna) are made with a slope of 0.01 to the exhaust shaft.
Return to contents
Exhaust shaft system
Mine natural ventilation system installed on the roof of the house, similar to chimney stoves. They can be an individual channel or have a channel combined with a ventilation one. Shafts with their own channel are made by brickwork with insulation with fiberboard or thickened frame insulation. Shafts of the second type are made of brick filled with heat-insulating and moisture-resistant material (foam plastic, foam glass, expanded clay, etc.) or with insulation made of 40 mm thick boards covered with roofing steel over a layer of felt ( mineral wool), soaked clay mortar and plastered.
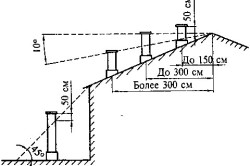
The height of the shaft above the roof must meet the following conditions:
- If it is placed near the ridge of the roof, the mouth of the shaft (hood opening) should be located above the ridge by more than 0.5 m.
- When removed from the ridge at a distance of 1.5-3 m, the mouth can be at the same level as the ridge.
- If the ridge is more than 3 m away, then the hole is located on the side of an angle of 10º to the horizon with the apex at the ridge.
- In rooms where food is prepared, the height of the shaft must be at least 1 m.
- The height of the mouth above the roof in ordinary houses taken about 1 m; and in the case of strong emissions with a pungent odor (flare emissions) - at least 2 m.
- If there is a very high risk heavy pollution air, then the shaft will have to be raised to a height of at least 3 m.
Return to contents
Requirements for ventilation ducts
One of the main requirements (according to the standard) for ventilation ducts is to provide exhaust at an external temperature of +12ºС and above, and an internal temperature of 20ºС. Such devices must be installed in rooms without windows (bathrooms, bathrooms, etc.). The cross-section of the channel must be at least 0.016 m², and the wall thickness must be at least 100 mm.

To reduce resistance to air flow, the cross-section of the channel along its length must be the same. All brickwork seams must be smoothed. The length of all brick ventilation ducts that have access to one exhaust shaft must be equal. The ventilation duct must be vertical; deviation from the vertical is allowed no more than 30º.
A decrease in temperature in the shaft or prefabricated air ducts reduces the efficiency of ventilation, which necessitates the need to apply thermal insulation to them.
Laying brick ventilation ducts has some specific recommendations. Such channels are made with a brick wall thickness of up to 38 cm in one row; with a thickness of up to 64 cm - in two rows. Dimensions should be selected according to the power of the heat source. So, with a power of up to 3.5 kW, 14x14 cm is recommended; with a power of 3.5-5 kW - 14x20 cm; with a power of more than 5 kW - 14x27 cm. Brick laying is done vertically, at a distance from the door and the joint of the walls of at least 40 cm.
If a chimney duct is laid nearby, then between the chimney and the ventilation it is necessary to place reliable thermal insulation and increase the thickness of the duct wall.
Return to contents
DIY brick laying process
Return to contents
Necessary tool
Laying brick ventilation ducts with your own hands will require the following tools:

- Master OK;
- grater;
- grater;
- putty knife;
- bit;
- hammer;
- chisel;
- mallet;
- level;
- plumb line;
- hacksaw;
- sandpaper;
- Bulgarian;
- electric drill;
- grinder.
Brick ventilation ducts are laid using a template. The template is made from plywood or chipboard and has a square or rectangular section, equal to the channel cross-section. The length of the template is equal to 8-9 brick thicknesses.
Brick laying begins from the corner of the wall. The first channel is formed after laying 1.5-2 bricks. The channel is formed using a template, which is installed strictly vertically along a plumb line. Between the channels, a distance equal to the width of the brick is established. The laying is carried out “end-to-end” with cutting of the mortar. Linking is done between the rows of bricks, i.e. vertical seams in two adjacent rows are shifted by half a brick relative to each other.

The solution used is ordinary cement-sand mixture in a ratio of 1:(3-4), thoroughly mixed in water. It is recommended to use cement grade M500. You can use the ready-made mixture for laying bricks. Before laying, the brick is moistened. The mortar is applied to the surface of the masonry and the bottom of the brick. Every 6-7 rows the template moves.
If there is a need for a drain, it is done at a distance of no more than 100 cm. The angle of inclination of the drain channel should be no more than 30º to the wall surface. The inclination of the outlet is achieved by grinding the brick at the desired angle. It is laid strictly horizontally. The cross-sections of the outlet and the main channel must match. If next to ventilation hole If the chimney will pass through, then between them it is necessary to lay a continuous masonry with a width of at least 40 cm. When forming a wall with a chimney and ventilation, you should use sand-lime brick. Seam inside ventilation device need to be carefully smoothed and rubbed.
Upon completion of the wall laying, you should check the cleanliness of the channel; to do this, a ball with a diameter of about 100 mm is lowered into it on a cord for the entire length.
