What is RAM and why is it needed? Technical characteristics of computer memory Basic characteristics of RAM.
A lot of computer users often wonder what RAM is. To help our readers understand RAM in detail, we have prepared material in which we will look in detail at where it is can be used and what are his types are now in use. We will also look at a little theory, after which you will understand what modern memory is.
A little theory
The abbreviation RAM stands for - random access memory. Essentially, it is the RAM that is primarily used in your computers. The operating principle of any type of RAM is based on storing information in special electronic cells. Each cell is 1 byte in size, meaning it can store eight bits of information. Each electronic cell has a special address. This address is needed so that you can access a specific electronic cell, read and write its contents.
Also, reading and writing to an electronic cell must be carried out at any time. In the English version, RAM is RAM. If we decipher the abbreviation RAM(Random Access Memory) - random access memory, then it becomes clear why the cell is read and written at any time.
Information is stored and rewritten in electronic cells only when your PC works, after turning it off, all information that is in RAM is erased. The totality of electronic cells in a modern RAM can reach a volume from 1 GB to 32 GB. The types of RAM currently in use are called DRAM And SRAM.
- First, DRAM is dynamic RAM, which consists of capacitors And transistors. The storage of information in DRAM is determined by the presence or absence of charge on the capacitor (1 bit of information), which is formed on the semiconductor crystal. To store information, this type of memory requires regeneration. Therefore this slow and cheap memory.
- Second, SRAM is Static RAM. The principle of cell access in SRAM is based on a static flip-flop, which includes several transistors. SRAM is an expensive memory, so it is used mainly in microcontrollers and integrated circuits, in which the memory capacity is small. This fast memory, not requiring regeneration.
Classification and types of SDRAM in modern computers
The most common type of DRAM memory is synchronous memory SDRAM. The first subtype of SDRAM is DDR SDRAM. DDR SDRAM memory modules appeared in the late 1990s. At that time, computers based on Pentium processes were popular. The image below shows a 512 MB DDR PC-3200 SODIMM stick from GOODRAM.
Console SODIMM means that the memory is intended for laptop. In 2003, DDR SDRAM was replaced by DDR2 SDRAM. This memory was used in modern computers of that time until 2010, until it was replaced by the next generation of memory. The image below shows a 2 GB DDR2 PC2-6400 stick from GOODRAM. Each generation of memory demonstrates increasingly faster data exchange speeds.
The DDR2 SDRAM format was replaced in 2007 by an even faster DDR3 SDRAM. This format remains the most popular to this day, although a new format is breathing behind it. The DDR3 SDRAM format is now used not only in modern computers, but also in smartphones, Tablet PCs And budget video cards. DDR3 SDRAM is also used in game consoles Xbox One eighth generation from Microsoft. This set-top box uses 8 gigabytes of DDR3 SDRAM format RAM. The image below shows a 4 GB DDR3 PC3-10600 memory from GOODRAM.
In the near future, the DDR3 SDRAM memory type will be replaced by a new type DDR4 SDRAM. After which DDR3 SDRAM will face the fate of previous generations. Mass release of memory DDR4 SDRAM started in the second quarter of 2014, and it is already used on motherboards with a CPU socket Socket 1151. The image below shows the format bar DDR4 PC4-17000 4 gigabytes from GOODRAM.
DDR4 SDRAM bandwidth can reach 25,600 Mb/s.
How to determine the type of RAM in a computer
You can very easily determine the type of RAM that is in a laptop or desktop computer using the utility CPU-Z. This utility is absolutely free. Download CPU-Z available from its official website www.cpuid.com. After downloading and installing, open the utility and go to the " SPD" The image below shows the utility window with the "tab" open. SPD».

In this window you can see that the computer on which the utility is open has RAM type DDR3 PC3-12800 4 gigabytes from Kingston. In the same way, you can determine the type of memory and its properties on any computer. For example, below is a window CPU-Z with RAM DDR2 PC2-5300 512 GB from Samsung.

And in this window there is a window CPU-Z with RAM DDR4 PC4-21300 4 GB from ADATA Technology.

This verification method is simply irreplaceable in a situation where you need to check for compatibility the memory you are planning to purchase for RAM expansion your PC.
Selecting RAM for a new system unit
To select RAM for a specific computer configuration, we will describe below an example that shows how easy it is to select RAM for any PC configuration. For example, we'll take this latest configuration based on an Intel processor:
- CPU- Intel Core i7-6700K;
- Motherboard- ASRock H110M-HDS on Intel H110 chipset;
- Video card- GIGABYTE GeForce GTX 980 Ti 6 GB GDDR5;
- SSD- Kingston SSDNow KC400 1000 GB;
- power unit- Chieftec A-135 APS-1000C with a power of 1000 W.
To select RAM for this configuration, you need to go to the official page of the ASRock H110M-HDS motherboard - www.asrock.com/mb/Intel/H110M-HDS.
On the page you can find the line “ Supports DDR4 2133”, which states that a RAM with a frequency of 2133 MHz is suitable for the motherboard. Now let's go to the menu item " Specifications" on this page.
In the page that opens you can find the line “ Max. capacity of system memory: 32GB", which states that our motherboard supports up to 32 gigabytes of RAM. From the data we received on the motherboard page, we can conclude that for our system, an acceptable option would be this type of RAM - two DDR4-2133 16 GB PC4-17000 memory modules.
We specifically indicated two 16 GB memory modules, and not one 32 GB, because two modules can operate in dual-channel mode.
You can install the above modules from any manufacturer, but these RAM modules are best suited. They are presented on the official page for the motherboard in the paragraph “ Memory Support List", since their compatibility has been verified by the manufacturer.
The example shows how easily you can find out information about the system unit in question. In the same way, RAM is selected for all other computer configurations. I would also like to note that using the configuration discussed above, you can run all the latest games with the highest graphics settings.
For example, on this configuration new games such as Tom Clancy's The Division, Far Cry Primal, Fallout 4 and many others, since such a system meets all the realities of the gaming market. The only limitation for this configuration is that it price. The approximate price of such a system unit without a monitor, including two memory modules, a case and the components described above, will be about 2000 dollars.
Classification and types of SDRAM in video cards
New video cards and older models use the same type of synchronous SDRAM memory. In new and outdated video card models, this type of video memory is most often used:
- GDDR2 SDRAM - bandwidth up to 9.6 GB/s;
- GDDR3 SDRAM - bandwidth up to 156.6 GB/s;
- GDDR5 SDRAM - bandwidth up to 370 GB/s.
To find out the type of your video card, the amount of RAM and memory type, you need to use a free utility GPU-Z. For example, the image below shows the program window GPU-Z, which describes the characteristics of the video card GeForce GTX 980 Ti.

GDDR5 SDRAM, which is popular today, will be replaced in the near future by GDDR5X SDRAM. This new classification of video memory promises to increase bandwidth up to 512 GB/s. The answer to the question of what manufacturers want to achieve from such a large throughput is quite simple. With the advent of formats such as 4K and 8K, as well as VR devices, the performance of current video cards is no longer sufficient.
Difference between RAM and ROM
ROM stands for read only memory. Unlike RAM, ROM is used to record information that will be stored there permanently. For example, ROM is used in the following devices:
- Cell phones;
- Smartphones;
- Microcontrollers;
- BIOS ROM;
- Various consumer electronic devices.
In all the devices described above, the code for their operation is stored in ROM. ROM is non-volatile memory, therefore, after turning off these devices, all information will be stored in it - which means this is the main difference between ROM and RAM.
Let's sum it up
In this article, we briefly learned all the details, both in theory and in practice, regarding random access memory and their classifications, and also looked at the difference between RAM and ROM.
Also, our material will be especially useful to those PC users who want to find out their type of RAM installed in the computer, or find out which RAM must be applied to different configurations.
We hope our material will be interesting for our readers and will allow them to solve many problems related to RAM.
Video on the topic
RAM, along with storage memory (hard drive), are storage devices and are necessary for storing data. What is RAM needed for? If the hard drive is used for permanent storage of files: music, movies, images, then RAM is needed for temporary storage of data that is used when the computer is running by the processor. After turning off the computer, all contents of RAM are deleted. RAM is a random access memory device, which is also the name given to this type of memory.
Types of RAM
The main characteristics that RAM should have are speed and speed of access to the data contained in it. There are two types of memory: SRAM and DRAM.
DRAM is a dynamic type of random access memory. The main advantage is availability and cost-effectiveness. Mostly installed on most personal computers and laptops.
SRAM is a static type of random access memory. Thanks to the special implementation of the module, it has increased operating speed, allowing you to operate with a large amount of data. The disadvantages include the high cost of production.
Work organization
How is work organized, and what is RAM used for? RAM is a separate module that is integrated into the motherboard by placing it in a special slot. It has a set of registers that contain data and commands addressed to the central processor. Interchange occurs through zero-level registers or through the cache.
What does RAM do? Essentially, it contains data and commands being processed at the current time, and also stores variables of the current OS session. The operating system uses memory in its work, which allows it to realize all its functionality. When the computer goes into sleep mode, it stores the current session.
RAM module size
The speed of the computer directly depends on the amount of RAM. The larger the RAM module, the faster programs function: games do not slow down, video is processed faster, and it becomes possible to use more programs simultaneously. Current sizes of RAM modules:
- 128 MB
- 256 MB
- 512 MB
At the moment in the development of computer hardware and software, the optimal installed RAM size will be from 1 to 2 gigabytes of RAM.
So we figured out why RAM is needed. All that remains is to provide a list of the most popular notations in computer jargon to keep up to date. Computer scientists also often call RAM with words such as: RAM, memory, brains.
RAM capacity
Next, let’s take a closer look at the next important characteristic of RAM – its volume. First, it should be noted that it most directly affects the number of simultaneously running programs, processes and applications and their uninterrupted operation. Today, the most popular modules are sticks with a capacity of 4 GB and 8 GB (we are talking about the DDR3 standard).
Based on what operating system is installed, as well as for what purposes the computer is used, you should choose and select the right amount of RAM. For the most part, if the computer is used to access the World Wide Web and to work with various applications, and Windows XP is installed, then 2 GB is quite enough.
For those who like to try out a recently released game and people who work with graphics, you should install at least 4 GB. And if you plan to install Windows 7, you will need even more.
The easiest way to find out how much memory your system needs is to launch the Task Manager (by pressing the keyboard combination ctrl+alt+del) and launch the most resource-consuming program or application. After this, you need to analyze the information in the “Memory Allocation” - “Peak” group.
In this way, you can determine the maximum allocated volume and find out to what volume it needs to be increased so that our highest indicator fits in RAM. This will give you maximum system performance. There will be no need to increase further.
Selecting RAM
Now let's move on to the question of choosing the RAM that is most suitable for you. From the very beginning, you should determine exactly the type of RAM that your computer's motherboard supports. There are different connectors for different types of modules, respectively. Therefore, to avoid damage to the motherboard or the modules themselves, the modules themselves have different sizes.
The optimal amounts of RAM were discussed above. When choosing RAM, you should focus on its bandwidth. For system performance, the most optimal option is when the module throughput matches the same characteristics of the processor.
That is, if the computer has a processor with a 1333 MHz bus, the bandwidth of which is 10600 MB/s, then to ensure the most favorable conditions for performance, you can install 2 sticks, the bandwidth of which is 5300 MB/s, and which in total will give us 10600 Mb/s
However, it should be remembered that for this mode of operation, the RAM modules must be identical in both volume and frequency. In addition, they must be manufactured by the same manufacturer. Here is a short list of well-proven manufacturers: Samsung, OCZ, Transcend, Kingston, Corsair, Patriot.
Finally, it is worth summarizing the main points:
- Based on the definition: random access memory or RAM is a component of a computer necessary for temporary storage of data, which in turn is necessary for the processor to operate.
- After completing any operations (closing programs, applications), all associated data is deleted from the chip. And when new tasks are launched, the data that the processor needs at a given time is loaded into it from the hard drive.
- The speed of access to data located in RAM is several hundred times higher than the speed of access to information located on the hard drive. This allows the processor to use the information it needs, gaining instant access to it.
- Today, the most common 2 types are: DDR3 (with a frequency from 800 to 2400 MHz) and DDR4 (from 2133 to 4266 MHz). The higher the frequency, the faster the system operates.
If you have difficulty choosing RAM, if you cannot determine what type of RAM your motherboard supports and what volume will best suit your needs, then you can always contact the service website. We are computer help at home in Moscow and the Moscow region. Our specialists will help with selection, replacement and installation in a computer or laptop.
The computer, quite unnoticed, but quite quickly became an integral part of our lives. Without it, it is impossible to imagine any branch of production, not a single factory or plant, not a single office. And, perhaps, no apartment can be imagined without a personal computer or laptop. But although this device has already become firmly established in our daily lives, not everyone understands its operation and design. This article will discuss one of its most important components - PC RAM.
This is not to say that every PC user should thoroughly know the theoretical fundamentals of how their computer works and be able to repair any breakdown. No, leave it to the professionals. But basic knowledge of the device is necessary - this will help to avoid many operational problems and, quite possibly, can prevent serious damage.
RAM in the structure of a personal computer
So, RAM. This is one of the most important components in a computer. It cannot be said that one part is more important and another less, but RAM (random access memory - this is how RAM is officially called) is an indispensable element in the operation of a PC. We can say that RAM is a kind of buffer zone, a connecting element between a person and a computer.
Physically, RAM is presented in the form of a removable module installed in a special connector on the motherboard, located to the right of the processor. Most motherboards have two or four of these connectors. On this module, on one or both sides, there are microcircuits, which, in fact, are memory.

When you turn on the computer, the operating system and some programs start. All the data that they need for normal functioning is placed in RAM. This is what all other programs that the user launches while working do the same. Whether it's working with text, processing photos or listening to music - all intermediate results of programs are located in RAM.
When the power is turned off, all data in RAM disappears. That is why this device is called “operational”. This is one of its two main differences from ROM - permanent memory such as a hard drive or flash drive. The second difference is the data exchange speed. For RAM it is much higher than for ROM. This, in fact, explains the purpose of RAM - to maximize the speed of the computer's response to user actions.
The hard drive can also store some operational information (the so-called paging file), which is placed there when there is not enough space in RAM. In this case, the user may experience negative phenomena - freezing and slowdown of programs or the entire system.
History, development and types of RAM
RAM has always been present in the structural diagram of computer technology. Back in the 19th century, the first samples of analytical machines were created, consisting purely of mechanical parts. Naturally, the RAM was mechanical. In the 20th century, the development of electronics was rapid. This is reflected in the evolution of RAM. At different times, electromechanical relays, cathode ray tubes and magnetic drums were used for these purposes.
With the development of semiconductor technologies, RAM based on transistors appeared and began to develop: tens, hundreds, thousands, and then millions of transistors in one microcircuit package. At first, these memory chips were simply soldered into the motherboard, which was not very convenient. With the development of computers, RAM was placed on a separate removable board.

The main modern types of RAM are SRAM and DRAM - static and dynamic random access memory. The first is based on triggers, has high speed, but low density of elements. The second is built on capacitor-transistor connections, has a high density and, as a result, low cost. But it is inferior in speed and needs to constantly recharge its capacitors. Since the cost of production is important for mass production, it is dynamic memory that has become widespread in PCs. From 1993 to this day, the most common type on the market is synchronous DRAM (SDRAM).
As for the technical design, the first were single-sided SIMM modules, which appeared in the 80s and had a capacity of 64 KB to 64 MB as they were modified. They used FPM RAM and EDO RAM memory chips. SIMMs have been replaced by double-sided DIMMs designed for SDRAM memory. They are still used in computers today.
DDR and DDR2
DDR (Double Data Rate) RAM has become the next stage in the development of SDRAM and is characterized by double the data transfer rate. The number of contacts (184 versus 168) and keys (1 versus 2) is also different. The first in the line was the PC1600 module with a DDR200 chip, an effective frequency of 200 MHz (with a memory bus clock speed of 100 MHz) and a bandwidth of 1600 MB/s. The last one was supposed to be the PC3200 (DDR400, 400 MHz, 3200 MB/s), but PC4200 (DDR533, 533 MHz) and higher modules were also produced.
In addition to the increased speed, DDR memory had the ability to operate in dual-channel mode, which theoretically should have doubled the speed (more precisely, bandwidth). To do this, it was necessary to insert into the motherboard, which also had to support this mode, two strips with absolutely identical characteristics. In practice, the speed increase is not as noticeable as it is described in theory. Subsequently, all other types of DDR memory will support dual-channel mode.

DDR SDRAM memory first appeared in 2001. Today, of course, it can still be found in old computers, but it is very rare. Already in 2003-2004, it was replaced by DDR2 SDRAM - the second generation with double the bus frequency. DDR2 memory has differences in the case (240 pins and a different key arrangement), which make it not interchangeable with DDR.
The line began with the PC2‑3200 module, running on a DDR2‑400 chip with an effective frequency of 400 MHz and a bandwidth of 3200 MB/s. The last one that worked stably was the PC2‑9600 module (DDR2‑1200, 1200 MHz, 9600 MB/s). Modules with higher characteristics were also produced, but their operation was not stable.
DDR3
The next stage of evolution was DDR3 RAM. Having appeared in 2007-2008, it did not lead to a sharp departure from DDR2, but began to systematically conquer the memory market. Today this is the most common type of RAM.
Not wanting to abandon the previous generation, manufacturers released motherboards that supported both standards. DDR2 memory is not electrically or mechanically compatible with DDR3. Although both types have 240 contacts, the key is located in different places. The main difference is that the power consumption and supply voltage (1.5 V) are even lower compared to DDR and DDR2.
In its line, DDR3 RAM starts with the PC3‑6400 (DDR3‑800) module with an effective frequency of 800 MHz and a data transfer rate of 6400 MB/s. Now such modules have become quite rare. This is due to the fact that most modern motherboards support memory frequencies of at least 1333 MHz. Top models support memory with frequencies up to 3200 MHz (PC3‑25600).
There is a small branch in the DDR3 family - low-level (low-voltage) DDR3L memory, which is characterized by a reduced supply voltage (1.35 V). It is fully compatible with DDR3.
DDR4
The most modern and fastest is DDR4 RAM. Its mass production began back in 2014, but it is still far behind DDR3 in popularity and availability. Although its stated characteristics are higher, the cost has also increased significantly. In addition, DDR4 memory is not compatible with DDR3; it is advisable to choose it only when assembling new systems, but not when upgrading old ones.

As for the characteristics, the first in the line is the PC4‑17000 module (DDR4‑2133) with an effective frequency of 2133 MHz and a bandwidth of 17000 MB/s. It is planned that the limit for DDR4 will be an effective frequency of 4266 MHz and a throughput of 34100 MB / s (PC4-34100 DDR4-4266).
Like every new type of memory, this one’s main difference from its predecessors is a reduction in power consumption and a decrease in supply voltage (to 1.2 V), and, of course, an improvement in all speed characteristics. In addition, modules now have a minimum capacity of 4 GB. The maximum volume can theoretically reach 192 GB.
Where did the RAM go?
Probably the most frequently asked question about computer memory is: “Why is RAM not used to its full extent?” Moreover, you can hear it from both beginners and experienced PC users. There may be several reasons for this, but often the answer lies in the bitness of the operating system.
As you know, the 32-bit version of the Windows operating system is capable of working with a memory amount not exceeding 4 GB. She simply won’t “see” anything beyond this. The 64-bit version has no such restrictions. Thus, when you encounter such a problem, you should first check which version of the OS is installed. This can be done by right-clicking on the “Computer” icon on the desktop (or in the “Start” menu) and selecting the “Properties” tab. The “System” section will contain all the necessary information, including the total and available amount of RAM.

Note that the 64-bit version is available for all modern Windows operating systems (XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10). Therefore, if your computer uses or plans to use more than 4 GB of RAM, you must install a 64-bit Windows operating system. In this case, all RAM will be used.
But there are other reasons for the decrease in available RAM. This may be a software limitation of the operating system edition used (several editions are available in each version). Also, some space can be reserved for the built-in video adapter, if available. Do not forget that each motherboard has its own requirements regarding the characteristics and amount of RAM. If they are not executed, the memory will not be available.
There are also hardware problems. For example, the module may not be inserted correctly or completely. It may also have damaged memory areas. Such a module cannot be repaired and requires immediate replacement. Damage can be detected using special programs.
How to check RAM
If failures and malfunctions occur that may be caused by problems with RAM (system freezes and crashes, the appearance of the so-called “blue screen of death”), it must be checked for errors. This can be done using standard operating system tools or third-party programs.
In Windows 7, RAM is checked by a program called the Windows Memory Tester. You can find it either at “Control Panel\System and Security\Administrative Tools” or by searching for the “mdsched” key in the Start menu. Of all the other utilities, the most common, accessible and reliable program for diagnosing RAM is Memtest86+.
It's important to remember a couple of points:
1. RAM is checked not from the operating system (from a bootable flash drive, disk, or after a system reboot).
2. If several memory modules are installed, it is advisable to check them one by one. This will make it easier to determine which one is faulty.
Clearing RAM
The easiest and most effective way to clear RAM is to restart the computer. But it is not suitable for all users and is not useful in all cases. An alternative would be to close unnecessary programs and thereby free up the amount of memory they have reserved. This can be done in the “Task Manager” by calling it with the key combination Ctrl+Alt+Delete.
There are also many different programs designed to optimize RAM consumption. You can note such utilities as CleanMem, SuperRam, Wise Memory Optimizer. And also CCleaner - a universal and very useful system monitoring utility that can effectively clear memory by deleting temporary files and program and system caches, and optimizing the registry.
But it is worth remembering that these methods are only a temporary solution to the problem and you should not rely on them. The main problem with a lack of RAM and, as a result, slow computer operation, is the insufficient amount of RAM for a specific computer configuration or task. You can solve this by installing an additional memory stick or buying a new one with a larger capacity.
How much RAM does a computer need?
When choosing or upgrading a computer, the following questions often arise: “How to find out the computer’s RAM?”, “How much capacity is needed?”. The answer to the first question is quite simple - you just need to use the CPU-Z utility. She will give a comprehensive answer. Volume is a little more complicated. If we are talking about upgrading, then the user has most likely already encountered a lack of memory and approximately knows how much to increase it.
When assembling a new computer, the first thing to determine is its purpose. For regular office work with documents, 1-2 GB is enough. For a mixed-use home computer, 4 GB would be acceptable. If you are building a gaming computer, you will need at least 8 GB of RAM, but it will be more comfortable with 16 GB. The same applies to serious work machines. The amount of memory required is determined by the applications with which you will work, but is usually a minimum of 8-16 GB.
How to choose RAM
Having figured out how to find out the computer’s RAM and how much capacity is needed, you can go to the store. But can we limit ourselves to this information? Definitely not. Of course, first of all you need to determine what type (for new computers it is DDR3 or DDR4) and volume needed. But there are several more factors that cannot be neglected.

First, the RAM must match the motherboard and processor not only in type, but also in the frequency they support. There is no point in buying high-speed memory if other components operate at lower frequencies. In the best case, the memory will operate at a reduced frequency, or even refuse to work at all. If the motherboard supports dual-channel mode, then it is better to buy two identical memory sticks. This will slightly improve its performance. Usually on sale you can find ready-made sets of 2 or 4 memory sticks.
Secondly, you need to pay attention to the labeling. There are special types of memory that have the ECC prefix. It means the presence of additional error control. Most motherboards do not support this type of memory. RAM for laptops differs from that used in PCs and has an SO-DIMM prefix.
Thirdly, timings are important. This is a speed characteristic meaning signal delay. Indicated by three or four digits separated by a hyphen. For example, 9-8-11-18. Naturally, the lower the number, the better, but for most users this difference will be almost imperceptible. But timings significantly affect the price.
RAM is an important and complex part of the computer, affecting the operation and performance of the entire computer system. She doesn't break down very often, but that's the catch - because they don't expect this from her. Correct diagnosis and search for errors in RAM can help avoid costly repairs and will certainly save a lot of time.
Just as two different processors differ, so can the RAM. This is also true regarding its cost. But if a higher price of a processor almost always means that it will be more productive, then the price of memory strongly depends on the frequency and timings, which, although they guarantee an increase in performance, often have little effect on the overall performance of the system. You should pay attention to them only when assembling gaming and high-performance work computers.
RAM (RAM, RAM - Random Access Memory- eng.) - relatively fast volatile computer memory with random access, in which most data exchange operations between devices are carried out. It is volatile, that is, when the power is turned off, all data on it is erased.
RAM is the repository of all streams of information that need to be processed by the processor or are waiting in RAM for their turn. All devices communicate with RAM through the system tire, and in turn exchanged with it through the cache or directly.
Random Access Memory- memory with random (direct) access.

This means that, if necessary, the memory can directly refer to one, necessary block, without affecting while the rest. Speed random access does not change from the location of the necessary information, which is a huge plus.
RAM, compares favorably from volatile memory, with virtually zero impact of the number of read-write operations on service life and durability. If all subtleties are observed during production, RAM very rarely fails. In most cases, damaged memory begins to make errors that lead to system crash or unstable operation of many computer devices.
RAM can be either a separate module that can be changed and additional ones added (for example, a computer), or a separate block of a device or chip (as in the simplest SoC).
RAM usage .
Modern operating systems actively use RAM to store and process important and frequently used data. If electronic devices did not use RAM, then all operations would be much slower and would require reading from a permanent memory source ( ROM), would require significantly more time. Yes and more or less multi-threaded processing would be practically impossible.
Use of RAM allows applications to run and launch faster. Data can be processed smoothly and wait its turn thanks to addressability(all machine words have their own addresses).
operating system Windows 7 for example, it can store frequently used files, programs and other data in memory. This allows you to start programs without having to wait for them to load from a slower disk, but to start executing immediately. Therefore, do not be alarmed if the task manager shows that your RAM loaded with more than 50% . When running an application that requires large memory resources, older data will be forced out of it in favor of more necessary ones.
Most devices use dynamic random access memory DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory ), which has a low price but is slower static SRAM (Static Ramdom Access Memory ). More expensive static memory has found its application in fast processors and controllers. Due to the fact that static memory takes up much more space on a chip than dynamic memory, during times of rapid development of computer peripherals and operating systems, manufacturers went the higher volume route rather than the higher speed route, which was more justifiable.
Since the 2000s, it has rightfully become the most popular and productive memory in personal computers. DDR SDRAM.
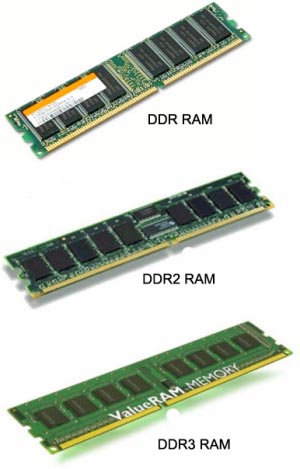
What is noteworthy is that there is no backward compatibility support for any of the versions. The reason lies in different frequencies and operating principles of memory controllers for different versions.

Therefore, it is impossible to insert, for example, memory DDR3 to memory slot DDR2, thanks to a notch elsewhere.
Subsequent versions DDR2 SDRAM And DDR3 SDRAM, received a significant jump in the growth of the effective frequency. But the real increase in speed was only when switching from DDR1 on DDR2 thanks to maintaining the delay time at an acceptable level, with a significant increase in operating frequency. DDR3 The memory cannot boast of the same, and when the frequency is doubled, the delays also almost double. There is no corresponding gain in operating speed in real conditions. But there is a significant advantage from moving to new versions that always works - this is a reduction energy consumption And heat release, which has a beneficial effect on stability and overclocking capabilities. Modern versions DDR3 rarely get hotter 50 degrees Celsius.
