Pellet business, its prospects and features
In recent years, pellets have become the main alternative to conventional fuels (coal, firewood, peat, gas, fuel oil). The only competitor to pellets today is natural gas, which is supplied through the pipeline. It surpasses pellets in terms of price and ease of use, but gas reserves are not unlimited and experts believe that at current consumption it will last no more than a century. In addition, not every house or dacha has a gas main. Therefore, the production of alternative sources of energy and heat is a promising direction that promises decent profits.
Pellet business - a way to turn waste into income
Pellets are also attractive because they are made from waste. It can be used as waste from the woodworking industry (sawdust, shavings, wood chips, substandard products) and agricultural production (sunflower husk, buckwheat, rice, straw of various crops, etc.). Pellets have a cylindrical shape and are small in size, which allows you to automate the heating process. Under this type of fuel are being developed, into which fuel pellets are automatically fed.

In Europe, pellets have long been used for heating industrial and domestic premises. In addition to the automation of the process, their popularity is due to the environmental friendliness and economic feasibility of this fuel. They are produced from waste, improving the ecological situation and converting waste into income. Particularly suitable for woodworking enterprises or large or medium-sized agricultural producers due to the lack of costs for the purchase of raw materials. In addition, during combustion, emissions into the atmosphere are ten times lower than during combustion of gas or coal, which is very important for European environmentalists. The most active use of pellets is Sweden, Austria and Denmark. They are also leaders in the production of equipment that burns pellets.
Shapes, dimensions and standards
There are no uniform standards for the production of this type of fuel. Each of the producing countries uses its own. Generally speaking, pellets can be from 5 to 10 mm in diameter and from 6 to 75 mm in length. If you are going to focus your business on imports, you need to familiarize yourself with the standards of a particular country and purchase equipment that is able to produce products of the appropriate size and characteristics.

Pellet business is promising not only for implementation in the domestic market, but also in the external one
Standardize not only the size, but also the ash content of the product. This standard also has a certain range of parameters. So, for example, in the USA, top-class pellets should have an ash content of no more than 1%, in most European countries - no more than 1.5%. The "standard" class is limited to an ash content of 3%. A higher indicator is not allowed and is not used: it is unrealistic to conclude a contract for the supply of pellets with an ash content above 3% in Europe. Unless they are used as a filler for cat litter.
Pellets differ in composition and include both pure wood and wood with bark or sunflower husks. With an increase in the content of impurities, the percentage of ash content of such fuel also increases. Therefore, the issue of the quality of purchased raw materials should be given great importance - it depends on how much the company's products will be in demand.
Production scheme
The production of pellets takes place in several stages:
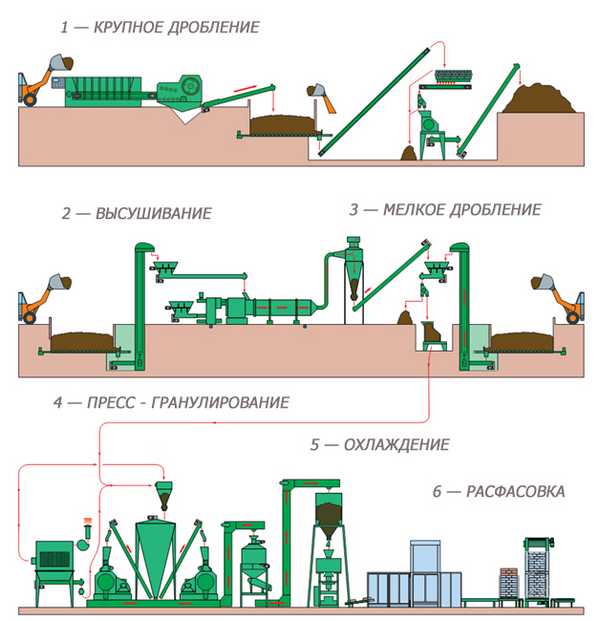
The cost of equipment for the production of pellets
The main production equipment for this type of business is granulators. These can be small plants with a capacity of 30 kg / h or a production unit that produces about 250 kg per hour. The cost of a set of equipment of average productivity is about $ 40,000, but you can purchase both more expensive and more budget installations:
- a sheporez (or a wood chipper in plain language) costs about $4,000,
- dryer of raw materials - 7000 - 20.000 dollars,
- granulator - from 1000 dollars - 10.000 dollars,
- cooler - about $ 5,000.
If we are talking about industrial lines, then the cost of a line that has a capacity of about 700 kg per hour is up to $ 130,000, and with a capacity of 2000 kg per hour - $ 200,000.
Business plan for the production of pellets
If the production of pellets will work in one shift, we take as a basis a standard working day: 8 hours, and a working month - 24 days. At the same time, production costs will amount to approximately 30% of gross profit.
The cost of raw materials is about 2 dollars per cubic meter, and 7.5 cubic meters of sawdust are needed to make a ton of pellets. So the raw materials for the production of one ton of fuel will cost $15. In the worst case, the cost of first grade pellets is $90 per m 3 , industrial pellets - $ 60 per m 3 . Gross profit is calculated as the product of the number of working days and daily revenue.

After calculations, we conclude that mini-factories will be the most profitable, while it is most profitable to use an electric drive in production. The worst option is an industrial line with a capacity of up to 1000 kg per hour, because such production will pay off in 14-15 months. However, the advantages of such production are its capital and reliability. And you can reduce the payback period if you organize work in two shifts. With such an organization of labor, it will decrease by almost half.
Demand for pellets in Russia
Pellets in Russia are still consumed in small volumes due to the presence (at the moment) of a large amount of natural gas and oil, especially since the issue of environmental friendliness of fuel in Russia is far from the most important one. The high cost of pellet boilers plays a significant role. All this causes low demand for this type of fuel in the domestic market of Russia - at best, top-grade fuel can be sold at $100/m 3 . In Western Europe, similar pellets cost up to $180. Nevertheless, it makes sense to develop a business for the production of alternative fuel in order to sell this fuel abroad. And it is definitely worth organizing it for those who have sawdust or other raw materials - waste from the main production is relatively easy to turn into income.
