How to choose and install a thermostat for a radiator
Types of thermostats
The use of thermostats in the heating system provides convenient control of the room temperature and makes it possible to economically use energy resources. Each heating system must be provided with at least shut-off valves in front of the radiators.
The ball valve is not only for economy but also for safety. If the radiator breaks down, it can be turned off without turning off the entire heating system. Designed for only two positions (on and off), a shut-off ball valve is not the best way to adjust the temperature. If you use intermediate valve positions, this will lead to a loss of tightness of the system, since solid particles contained in the coolant will destroy the closing ball. A manual cone valve, which can not be closed completely, will help to regulate the temperature in the system much better. This type of temperature control constantly requires attention, which creates certain inconveniences.
For the efficient operation of the heating system, modern thermostatic valves are used, they are often called thermostats. They allow a person to create a comfortable microclimate in the house, set the desired range of night and day air temperatures automatically. The home owner also gets the opportunity to make the cost of housing and utilities services optimal for himself.
In all cases, the temperature is controlled by changing the volume of the coolant in the radiators. By increasing the flow rate of the liquid in the radiator, we increase the temperature, while decreasing it, we lower it.
Types of thermostats by signal transmission method
All thermostats consist of two components: valve and thermocouple that controls the operation of the valve. There are three types of thermostats... They are distinguished by the method of signal transmission to the thermoelement: the signal is supplied from the coolant; comes from the air in the room; comes from the air outside the heated room.The thermostatic valve for all three types of thermostats can be the same. They differ in a control element - a thermal head.
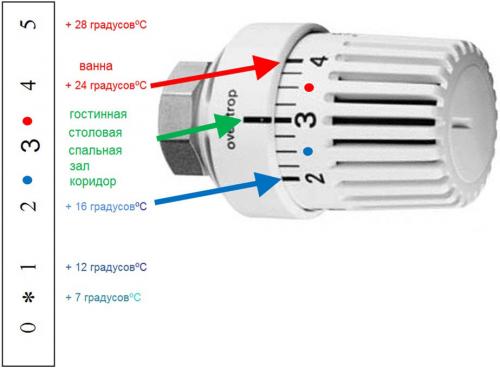
The first were created thermostats that respond to the temperature of the coolant. These are the first generation thermostats. These thermostats are manually controlled. There is a six-digit scale on the valve head of manual thermostats; by turning the crown, set the desired temperature. If "zero" is set, then the thermostat is completely closed, the coolant does not pass through it. With this position of the valve head, the radiator can be replaced without draining the coolant from the heating circuit. "Snowflake" or "Unit" indicate the minimum flow rate of the coolant through the radiator. In this case, the radiator is disconnected from heat, but is protected from defrosting. The remaining 4 digits will allow you to adjust the air temperature in the range from 14 C to 28 C.
The manual thermostat can be installed with the head vertically upward, or horizontally. If the head is installed horizontally, then over time it can be replaced with a thermal head with a bellows, which is mounted only horizontally towards the room.
Thermal head with bellows will provide automatic temperature control. Bellows is a cylinder with inner corrugated walls, filled with a special substance. When heated, this substance changes its state of aggregation or simply expands, while the bellows expands and pushes the stem that regulates the operation of the valve. The valve closes part of the pipe section, reducing the flow of coolant into the radiator. During cooling, the bellows contracts, the valve is pulled back, the pipe section opens, and the flow of coolant into the heater increases. At the moment, there are two types of bellows.: liquid and gas. Gas-filled ones react very quickly to temperature changes, liquid ones respond to temperature changes more slowly. At the same time, the liquid ones more accurately respond to changes in pressure inside the bellows and better interact with the actuator. 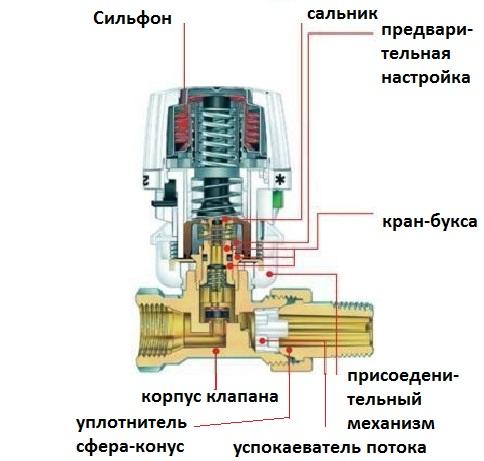
If the thermal head with a bellows is installed vertically, then it enters the zone of warm air rising from the radiator. Therefore, the closing of the coolant supply will occur earlier than in the case of the horizontal direction of the thermal head into the room.
Thus, thermostats of the second generation independently control the temperature in the room controlling the flow of the coolant. It is enough for a person to set the desired temperature regime. These thermostats consist of: a temperature sensor connected to the boiler and a thermostat connected to the coolant supply pipe.
The operation of thermal heads with bellows is affected by the obstruction of radiators with grilles or curtains. In these cases, it is better to use manual thermostats or thermal heads with remote sensors. Remote sensors measure the outdoor air temperature and send a signal to the regulator. An outdoor temperature sensor reacts to changes in the weather. If it gets colder outside, then the heating in the room is automatically increased. The third generation sensors are the most efficient, but they are quite expensive. Therefore, cheaper thermostats are in great demand. Thermoregulators of different generations are sometimes used in the same heating system.
Types of thermostats by design features
By design features, electrically controlled thermostats and direct-acting thermostats are distinguished.Electrically controlled thermostats are produced in two types: some regulate the temperature by giving a signal to the valves installed on the supply pipes in front of the radiators; others control the ignition of the boiler or pumps.
Direct-acting thermostats are installed on the coolant supply pipe in front of the radiator. The temperature is regulated by simple opening-closing of the heating agent supply.
Types of thermostats
There are only two main types of thermostats: thermostats for one- and two-pipe heating systems. The first type is designed for installation in one-pipe heating systems. Such a regulator serves to maintain the hydraulic balance in the heating system. The pressure balance is maintained due to the fact that the flow rate of the heat carrier through the consumers is maintained at a constant, pre-set level.In a two-pipe heating system, thermostats are used, designed in such a way that they can function normally even with frequent and sudden pressure drops. Such regulators have a high hydraulic resistance and a small flow area. They, in turn, are divided into two groups:
1) requiring additional adjustment of the hydraulic resistance;
2) that do not require additional adjustment of the hydraulic resistance.
When using thermostats without additional adjustment, all appliances and heating devices mounted on the same riser will have approximately the same coolant flow, although the heat losses in different rooms are different. In practice, it will look like this: if more coolant has passed through the radiator than required, then the room will be very hot and vice versa - if the coolant has not passed enough, then the room will be cold. To prevent this from happening, the thermostat must be installed for each heating device separately.
Regulators of the first group are preferable. Correct settings on the valves will ensure the optimal flow rate of the heating medium and a comfortable temperature regime in each room.
Advantages of modern thermostats
The design of modern thermostats fits well into the interior of any room. The thermostat is very convenient to use to create thermal comfort in rooms. These elements of heating systems are easy to install in both new and existing heating systems. The service life of the equipment is very long. The number of repetitive stretch-compression cycles for modern bellows is about a million times. To obtain such operating time, the equipment must work for about 100 years. During this entire time, operation without technical and preventive maintenance is possible. If the radiators are equipped with modern thermostats, then there is no need to open windows to regulate the temperature in the building. Thermostats operate in the temperature range from 5 C to 27 C. When the temperature is set at any value from this range, the accuracy of its maintenance will be about 1 C. The use of thermostats allows you to evenly distribute the coolant in the heating system. Radiators located at the periphery of the circuit effectively heat the room. Thermostats prevent excessive heating of the air in the room if the sun's rays penetrate there, the operating electrical appliances heat the air, the temperature rises due to crowds, and so on. In autonomous heating systems, the use of thermostats provides fuel savings of up to 25%. The cost of heating is reduced, the emission of harmful combustion waste is also reduced.It is important to remember that high-quality thermostats are always equipped with a quality certificate.
Features of installing thermostats for radiators
In order for the thermostats to work efficiently, correctly and for a long time, they must be installed correctly.- Mechanically operated devices must be freely accessible in order to conveniently turn the regulator.
- Do not close automatic thermostats with curtains or radiator screens, as the device will analyze the temperature behind the curtain (screen), and not the real temperature in the room.
- When installing thermostats in a finished heating system, the water must be drained from the system before installation.
- The thermostat is installed perpendicular to the radiator panel. The direction of the arrow on the regulator and the direction of flow of the heating medium in the system must match.
- During the period when the heating is turned off, the thermostats are opened completely. This helps to avoid deformation of the valve and contamination of the regulator.
Thermostat installation procedure
Before installing the thermostat for the heating radiator, it is necessary to turn off the riser supplying the coolant. Then you need to drain the water from the heating system and you can start installation work.The work is carried out in the following order:
horizontal pipes are cut off at a certain distance from the radiator; disconnect the tap from the radiator if it was installed earlier and cut off
pipeline;
disconnect the shanks with nuts from the thermostat valve and the shut-off valve,
they are twisted into the plugs of the heating battery;
the assembled piping is installed at the selected location;
connect the installed piping to the horizontal pipes of the supply line from the riser.
Installation specifics for one- and two-pipe heating systems
In a one-pipe heating system, when connecting second and third generation thermostats, it is necessary to change the connection diagram of the radiator by installing a jumper. A jumper pipe (bypass) connects the direct and return connections of the heater and ensures the circulation of the coolant when the heating battery is disconnected by the thermostat. To implement such a connection scheme, it is more convenient to dismantle the device by closing the valves at the inlet and outlet of the coolant.The regulator for heating radiators in a two-pipe system can be installed on the upper supply pipe. Its installation is easier than in the case of a one-pipe heating system.
