Heat regulation in batteries. Conventional direct-acting thermostat. How to regulate the temperature of a heating battery? Heating temperature regulators for radiators
System diagram with regulators
Each heating season brings its own surprises with difficulties in heating rooms, both for residents multi-storey buildings, and private cottages. The quality of uniform heating of all rooms of the house depends on how the temperature of the heating radiators is adjusted.
Why do you need to make adjustments?
Setting the optimal temperature of the heating radiators allows you to create the maximum indoor comfortable conditions stay. In addition, adjustment allows:
- Remove the effect of air in the batteries, allow the coolant to move freely through the pipeline of the heating system, effectively transferring its heat to the interior of the room.
- Reduce heat consumption costs by up to 25%.
- Don't hold it all the time open windows, with excessive overheating of the air in the room.
It is advisable to set up heating and adjust batteries before the start of the heating season. This is necessary so that later you do not experience discomfort in the apartment and do not adjust the heating temperature of the batteries in emergency mode. Before setting up and adjusting the radiators, initially in the summer you need to thermally insulate all windows. In addition, you need to take into account the specific location of the apartment:
- In the middle or corner of the house.
- Lower or upper floor.
After analyzing the situation, it is advisable to use energy-saving technologies to maximize heat conservation inside the apartment:
- Insulate walls, corners, floors.
- Carry out hydro and thermal insulation of the seams between the concrete joints of the panel house.
Without this work, it will be useless to regulate the temperature of the radiators, since the lion's share of the heat will heat the street.
Types of heating systems and the principle of adjusting radiators

Handle with valve
In order to correctly adjust the temperature of radiators, you need to know the general structure of the heating system and the layout of the coolant pipes.
- When individual heating, adjustment is easier when:
- The system is powered by a powerful boiler.
- Each battery is equipped with a three-way valve.
- Forced pumping of coolant has been installed.
At the stage installation work For individual heating, it is necessary to take into account the minimum number of bends in the system. This is necessary in order to reduce heat loss and not reduce the pressure of the coolant supplied to the radiators.
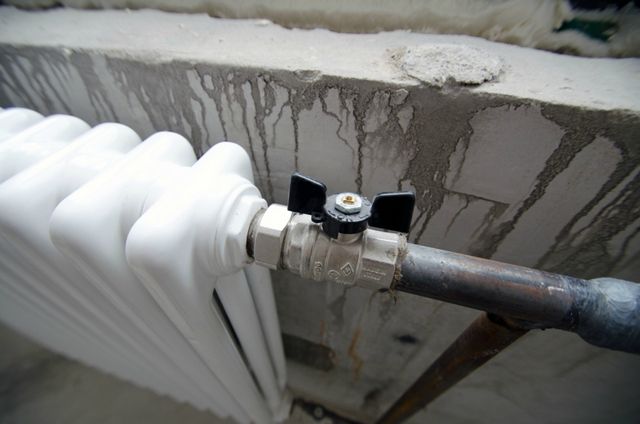
For uniform heating and rational use of heat, a valve is mounted on each battery. With it you can reduce the water supply or turn it off common system heating in an unused room.
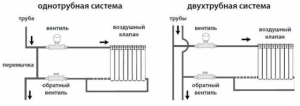
- In system central heating In multi-storey buildings equipped with a vertical supply of coolant through a pipeline from top to bottom, it is impossible to adjust the radiators. In this situation, the upper floors open the windows due to the heat, and the rooms on the lower floors are cold, since the radiators there are barely warm.
- A more advanced one-pipe network. Here, the coolant is supplied to each battery and then returned to the central riser. Therefore, there is no noticeable temperature difference in the apartments on the upper and lower floors of these buildings. In this case, the supply pipe of each radiator is equipped with a control valve.
- A two-pipe system, where two risers are mounted, ensures the supply of coolant to the heating radiator and back. To increase or decrease the coolant flow, each battery is equipped with a separate valve with a manual or automatic thermostat.
Types of control valves
Existing modern heat supply technologies make it possible to install a special tap on each radiator that controls the quality of heat. This control valve is a shut-off valve heat exchanger, which is connected via pipes to the heating radiator.
According to the principle of their operation, these cranes are:
- Ball ones, which primarily serve as 100% protection against emergency situations. These shut-off devices are a structure that can be rotated 90 degrees and can allow water to pass through or prevent the passage of coolant.
The ball valve must not be left in a half-open state, as in this case the sealing ring may be damaged and a leak may form.
- Standard, where there is no temperature scale. They are represented by traditional budget valves. They don't give absolute precision adjustments. By partially blocking the access of coolant to the radiator, they change the temperature in the apartment to an indefinite value.
- With a thermal head that allows you to adjust and control the parameters of the heating system. Such thermostats are automatic and mechanical.
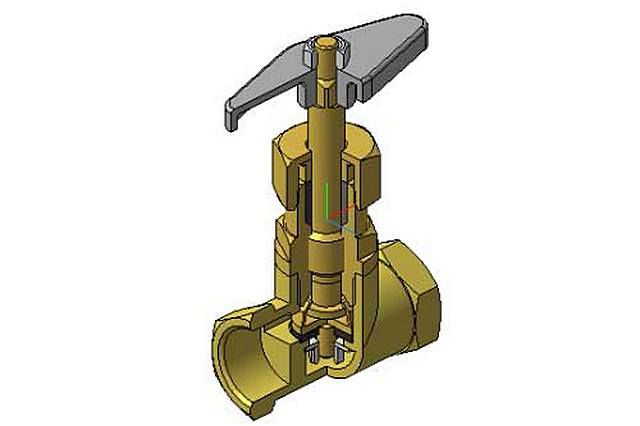
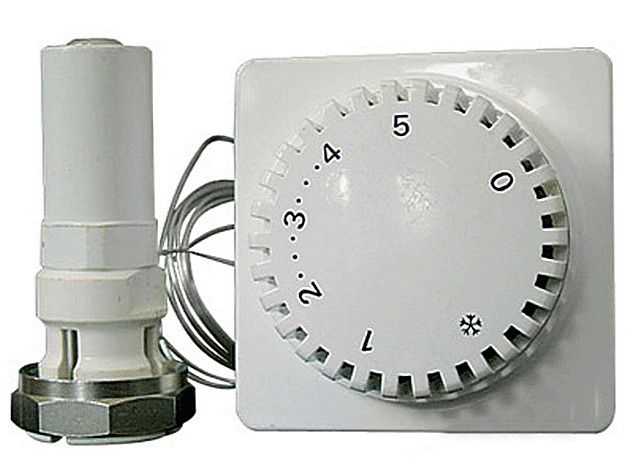
Conventional direct-acting thermostat
A direct-acting thermostat is a simple device for controlling the temperature in a heating radiator, which is installed near it. By its design, it is a sealed cylinder into which a siphon is inserted with a special liquid or gas that clearly reacts to changes in the temperature of the coolant.
As it increases, the liquid or gas expands. This leads to increased pressure on the rod in the thermostat valve. It, in turn, moving, blocks the flow of coolant. When the radiator cools, the reverse process occurs.
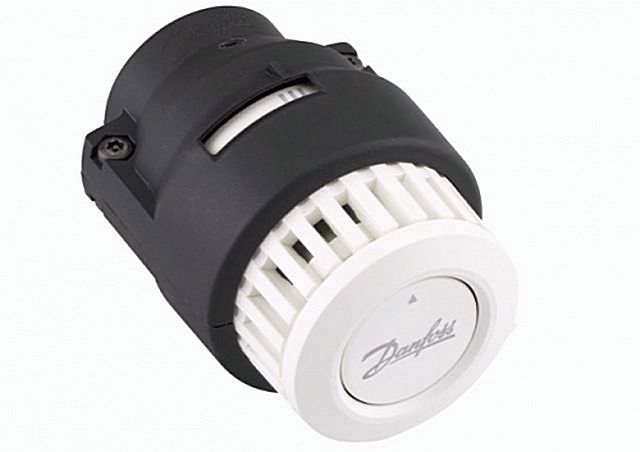
Thermostat with electronic sensor
This device is no different in operating principle from the previous version, the only difference is in the settings. If in a conventional thermostat they are performed manually, then an electronic sensor does not need this.
Here the temperature is set in advance, and the sensor monitors its maintenance within the specified limits. The electronic thermostatic sensor regulates the control parameters of the air temperature within the range from 6 to 26 degrees.
Step-by-step instructions for adjusting temperature
To ensure comfortable living conditions in the room, you need to perform some basic steps.
- Initially, it is necessary to bleed the air on each battery until water flows from the tap in a trickle.
- Then you need to adjust the pressure in the batteries.
- To do this, in the first battery from the boiler you need to open the valve by two turns, on the second - by three, and then according to the same scheme, increasing the number of turns of the valve being opened on each radiator. Thus, the coolant pressure will be evenly distributed over all radiators. This will ensure its normal passage through the pipes and better heating of the batteries.
- IN forced system heating, pumping coolant, monitoring rational heat consumption will help to implement control valves.
- In a flow-through system, the temperature is well regulated by thermostats built into each battery.
- In a two-pipe heating system, you can control not only the temperature of the coolant, but also its quantity in the batteries using both manual and automatic systems management.
Conclusion

Today to maintain comfortable temperature in an apartment, each radiator of the heating system must be equipped with an adjustment system.
Modern thermostats help not only maintain the thermal balance indoors, but also save energy costs for heating the coolant.
Ensuring stable and efficient work heat supply systems: adjustment of heating radiators
A comfortable indoor microclimate during the cold season is largely ensured by the correct choice of heating scheme for the building, correct calculation of the power of the heat source and batteries, and high-quality installation. But it must be taken into account that the ability to control and regulate the operation of both individual elements (for example, a boiler, radiators) and the system as a whole is also important.
The main parameters characterizing the level of comfort in the house are air temperature and uniform heating of each room. To determine the value and monitor these indicators, thermometers or sensors can be used. Maintaining them at an optimal level is carried out, as a rule, with the help of shut-off and control valves, incl. taps, thermal valves, regulators of various types, etc. which can be installed on boilers, heating circuit flow and return and directly on each radiator.
It should be noted that the use of such devices allows not only to ensure a favorable indoor microclimate in winter, but also to significantly save fuel consumption.
The most common and affordable option (even for owners of apartments in a multi-storey building with a centralized heating system) to maintain a comfortable temperature in the house is to regulate the radiators. It begins to be carried out at the installation stage through the use of pipes of various diameters, and adjustments and adjustments are made after the launch and during operation of the heat supply scheme using the above devices. The principle of their operation is based on changing the power of coolant flow through the radiator.
Battery Regulation Options
You can regulate the temperature of the coolant in heating devices:
- manually using ball valves, conical valves;
It must be borne in mind that ball valves have two operating positions “Open-Closed”, and attempts to install them in an intermediate mode lead to rapid wear of the device.

Figure 1 – Types of ball valves
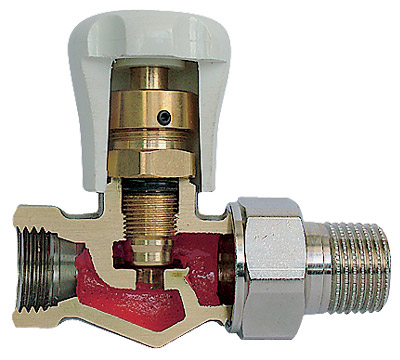
Figure 2 – Cone valve for a radiator
- using thermostats of various types: mechanical (equipped with a thermostatic head in which the sensitive element is a bellows, and control, in particular, adjustment is carried out manually); electrical (similar in principle to mechanical models, but the device changes the position of the valve automatically to ensure the specified temperature level); electronic (programmable, in which information about the controlled parameters comes from sensors, and adjustment is carried out smoothly according to a given program).
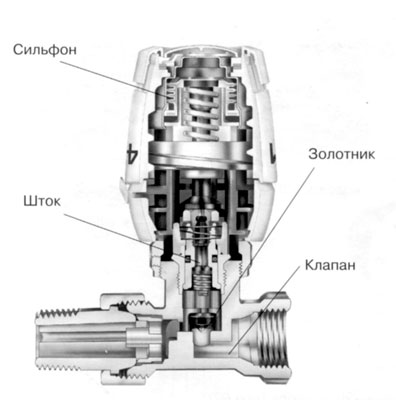
Figure 3 – Mechanical thermostat

Figure 4 – Electronic regulator for batteries
When choosing a temperature regime for a particular room, the following factors must be taken into account: the location of the room (corner, row, floor) and the frequency of its use; the number of openings through which heat leaks are possible (windows, doors); availability and quality of thermal insulation of enclosing structures and windows; outside air temperature; frequency and intensity of ventilation.
As a rule, the installation of taps and thermostats is carried out during the installation of the heating system. In this case, such devices crash into the coolant supply pipes into the batteries. The taps are usually installed vertically, and when using regulators, you must ensure that the thermal head is positioned horizontally. This is due, first of all, to the need to prevent the occurrence of stagnant zones around it, and secondly, to the ease of setting up the device.
To adjust radiators in one and two-pipe schemes, regulators should be installed on each existing heating device. But in the case when there are several sequentially in one room installed batteries, it is allowed to insert one device at the entrance to the first radiator.
In most cases, the valve of the control device is mounted directly into the hole in the plug of the heating device. Therefore, when placing the latter in a niche, behind protective screen or curtains, the use of mechanical and electrical thermostats is not advisable due to their obviously incorrect operation. In such situations, it is recommended to use electronic devices with a remote sensor that is capable of regulating the batteries, located at a distance of up to 8 m from the valve.
First of all, it must be pointed out that in autonomous systems, radiator adjustments should be carried out before the start of the heating season, but not at the height of the heating season. summer period due to difficulty or impossibility the right choice optimal temperature conditions.
In centralized schemes, during a heating shutdown, it is recommended to fully open the valve of the device, which avoids future clogging of the device or deformation of its damper.
Before adjusting the radiators, you should make sure that there is no air in the heating system. You can check this and fix the problem using Mayevsky cranes. It is also recommended to identify factors that influence the decrease in temperature in each room (for example, the presence of air conditioning, the need for frequent ventilation, etc.) and identify possible sources of additional heat radiation.
Sequence of actions when adjusting batteries
It should be noted that the adjustment of radiators in centralized heating systems comes down mainly to setting the control devices to a comfortable temperature regime. In autonomous schemes, this process is more labor-intensive, because It is not only the batteries that need to be regulated, but also the boiler. In addition, if in a closed heating circuit several heating devices are connected (one- and two-pipe systems with bottom wiring), it is necessary to achieve a balanced heating circuit.
To solve this problem, at the initial stage you should determine the coldest room in the house, because... Battery adjustment will begin with this. To do this, all taps are closed, and after the radiators have cooled, the temperature in each room is measured.
In the found room, the shut-off valve opens completely, and after reaching the required level of heating, they move to another radiator, adjusting the position of the valve, which ensures a comfortable mode. After all the batteries have been adjusted, begin setting up the boiler regulators.
There is another (simplified) option. To do this, it is necessary to determine the exact sequence of location of the radiators along the flow of the coolant. Then in the first battery the tap or thermal head is opened, for example, by one or two turns, in the next - by two or three, in the third - by three or four, etc. If the temperature in each room meets the needs, the adjustment process is considered complete. Otherwise, the procedure should be repeated, increasing or decreasing the number of turns of the tap.
See related articles:
How can you regulate the temperature of a radiator?
 In private houses and apartments, quite often a phenomenon occurs such as a difference in the level of heating of radiators connected to the heating system. Therefore, residents are forced to put up with uncomfortable living conditions, because the temperature in the bathroom can differ significantly from that in the bedroom or living room. This problem is especially typical for owners who use heating system in houses and apartments.
In private houses and apartments, quite often a phenomenon occurs such as a difference in the level of heating of radiators connected to the heating system. Therefore, residents are forced to put up with uncomfortable living conditions, because the temperature in the bathroom can differ significantly from that in the bedroom or living room. This problem is especially typical for owners who use heating system in houses and apartments.
 Helps homeowners avoid common heating system problems competent installation a device such as a radiator regulator, which is designed to control the temperature of the radiator. Modern temperature controllers for radiators are available in a wide range of models and can be used by homeowners to optimize the heating system, reduce energy costs and maintain optimal temperature conditions in every room of the house.
Helps homeowners avoid common heating system problems competent installation a device such as a radiator regulator, which is designed to control the temperature of the radiator. Modern temperature controllers for radiators are available in a wide range of models and can be used by homeowners to optimize the heating system, reduce energy costs and maintain optimal temperature conditions in every room of the house.
Main types of regulators
 To increase the efficiency of the radiator, a temperature regulator for the heating battery can be used, operating according to various principles. At the moment, there are four main groups of regulators, combining devices with a similar principle of operation.
To increase the efficiency of the radiator, a temperature regulator for the heating battery can be used, operating according to various principles. At the moment, there are four main groups of regulators, combining devices with a similar principle of operation.
Regulators with locking mechanism
 When deciding how to regulate heating radiators, homeowners quite often pay attention to shut-off valves. They are distinguished by their affordable cost, acceptable service life, provided correct operation and at the same time have an elementary design. The heating battery shut-off regulator is installed on the radiator and is used to control the amount of coolant entering the circuit.
When deciding how to regulate heating radiators, homeowners quite often pay attention to shut-off valves. They are distinguished by their affordable cost, acceptable service life, provided correct operation and at the same time have an elementary design. The heating battery shut-off regulator is installed on the radiator and is used to control the amount of coolant entering the circuit.
The simple design of the device allows you to easily control the supply of coolant from the heating system.
There are only two operating positions for shut-off valves. The first position provides for the free flow of coolant from the system, and the second position completely blocks the flow of water, as a result of which the circulation stops, the radiator cools down and ceases to participate in the process of heating the house.
 Some homeowners, using a manual heating temperature controller on a micro-district, try to leave the shut-off valve lever in an intermediate state in order to forcibly reduce the coolant circulation, but experts are against such experiments. Improper operation of the shut-off valve will quickly lead to the device failing, and the heating system itself will require complex and time-consuming repairs.
Some homeowners, using a manual heating temperature controller on a micro-district, try to leave the shut-off valve lever in an intermediate state in order to forcibly reduce the coolant circulation, but experts are against such experiments. Improper operation of the shut-off valve will quickly lead to the device failing, and the heating system itself will require complex and time-consuming repairs.
 Using shut-off valves, adjustment of heating radiators in an apartment can be carried out at a rather primitive level, since it requires continuous monitoring by the owners and involves manual control of the lever positions. Therefore, at the moment, shut-off valves are used quite rarely, and homeowners are paying attention to more advanced models of regulators.
Using shut-off valves, adjustment of heating radiators in an apartment can be carried out at a rather primitive level, since it requires continuous monitoring by the owners and involves manual control of the lever positions. Therefore, at the moment, shut-off valves are used quite rarely, and homeowners are paying attention to more advanced models of regulators.
Manual valves
 Smooth heating control in apartment building possible with the use of manual valves, the improved design of which allows for subtlety in settings. Unlike shut-off valves, which have two positions - “Open” / “Closed”, the valve has the ability to flexibly regulate the amount of coolant entering the circuit. This is accomplished by changing the internal diameter of the cross-section in the passage channel of the valve.
Smooth heating control in apartment building possible with the use of manual valves, the improved design of which allows for subtlety in settings. Unlike shut-off valves, which have two positions - “Open” / “Closed”, the valve has the ability to flexibly regulate the amount of coolant entering the circuit. This is accomplished by changing the internal diameter of the cross-section in the passage channel of the valve.
 Manual valves that control radiator heating are available in a wide range of models, varying appearance, material of manufacture and design. However, most have similar Constructive decisions. Thus, the basic valve is a valve with two pipes and a shut-off head. These components are united by a handle, on which, for the convenience of users, an engraved scale indicating changes in the diameter of the bore is engraved.
Manual valves that control radiator heating are available in a wide range of models, varying appearance, material of manufacture and design. However, most have similar Constructive decisions. Thus, the basic valve is a valve with two pipes and a shut-off head. These components are united by a handle, on which, for the convenience of users, an engraved scale indicating changes in the diameter of the bore is engraved.
 By turning the handle, the user can change the amount of coolant and the heating level specific radiator. Although the valve is more expensive than a radiator shut-off regulator, it is more profitable in the long run because it allows homeowners to save money on heating bills. The advantages of this type of device lie in its simple design and basic use, but the disadvantage lies in the need for manual adjustments and periodic monitoring of the operation of the regulator.
By turning the handle, the user can change the amount of coolant and the heating level specific radiator. Although the valve is more expensive than a radiator shut-off regulator, it is more profitable in the long run because it allows homeowners to save money on heating bills. The advantages of this type of device lie in its simple design and basic use, but the disadvantage lies in the need for manual adjustments and periodic monitoring of the operation of the regulator.
Thermostats with automatic settings
 The third group of devices includes an automatic heating control valve used in modern heating systems. This device has a number of significant advantages and greatly simplifies for users their responsibilities related to controlling the temperature in the house, because the regulator automatically sets the operating mode heating devices depending on external conditions.
The third group of devices includes an automatic heating control valve used in modern heating systems. This device has a number of significant advantages and greatly simplifies for users their responsibilities related to controlling the temperature in the house, because the regulator automatically sets the operating mode heating devices depending on external conditions.
 To adjust the heating system apartment building using an automatic device was possible, a remote temperature sensor should be integrated into the home heating system. It is he who will send signals to the regulator, which will automatically change the internal diameter of the flow area. A thermostatic expansion valve for heating operates on this principle, but more advanced models are also available for sale.
To adjust the heating system apartment building using an automatic device was possible, a remote temperature sensor should be integrated into the home heating system. It is he who will send signals to the regulator, which will automatically change the internal diameter of the flow area. A thermostatic expansion valve for heating operates on this principle, but more advanced models are also available for sale.
 Among them, electronic thermostat for a heating battery whose price is slightly higher than an analog device. It is equipped with a built-in temperature sensor, a microprocessor for setting tasks, an electromechanical relay and a control panel. The principle of operation by which the heating system is adjusted using an automatic thermostat is that, based on a signal from the control circuit, the locking head moves using a core.
Among them, electronic thermostat for a heating battery whose price is slightly higher than an analog device. It is equipped with a built-in temperature sensor, a microprocessor for setting tasks, an electromechanical relay and a control panel. The principle of operation by which the heating system is adjusted using an automatic thermostat is that, based on a signal from the control circuit, the locking head moves using a core.
 The advantages of automatic devices are that with their help you can quite accurately and conveniently adjust the operation of radiators and therefore the question of how to regulate the temperature of the heating radiator for homeowners becomes resolved.
The advantages of automatic devices are that with their help you can quite accurately and conveniently adjust the operation of radiators and therefore the question of how to regulate the temperature of the heating radiator for homeowners becomes resolved.
Radiator thermostats
 Those wishing to learn how to regulate radiators using radiator thermostats should focus on the features of these devices. If the devices discussed above worked on the principle of changing the amount of coolant supplied to the radiator, then the radiator temperature controller of the heating battery with a thermostat changes not the volume of water, but its temperature.
Those wishing to learn how to regulate radiators using radiator thermostats should focus on the features of these devices. If the devices discussed above worked on the principle of changing the amount of coolant supplied to the radiator, then the radiator temperature controller of the heating battery with a thermostat changes not the volume of water, but its temperature.
 To integrate this device into the heating system circuit, you will need certain materials and skills. In particular, homeowners will need additional pieces of pipes and connecting fittings. After the radiator thermostat is installed, you need to know how to adjust the radiators in the apartment using it.
To integrate this device into the heating system circuit, you will need certain materials and skills. In particular, homeowners will need additional pieces of pipes and connecting fittings. After the radiator thermostat is installed, you need to know how to adjust the radiators in the apartment using it.
 To do this, it is worth studying the principle of operation of the device. Its design is quite simple and is represented by a valve with three pipes and a sensitive element located inside. The internal temperature-sensitive element is connected to the locking head, and the outer body of the device is equipped with a handle for making adjustments.
To do this, it is worth studying the principle of operation of the device. Its design is quite simple and is represented by a valve with three pipes and a sensitive element located inside. The internal temperature-sensitive element is connected to the locking head, and the outer body of the device is equipped with a handle for making adjustments.
 The temperature-sensitive element, reacting to the action of water in the system, can change its volume, thereby adjusting the position of the shut-off head rod. In this case, if it is necessary to cool the water in the radiator, the return supply channel opens, and when the coolant must be heated, on the contrary, the water supply channel from the return line is closed.
The temperature-sensitive element, reacting to the action of water in the system, can change its volume, thereby adjusting the position of the shut-off head rod. In this case, if it is necessary to cool the water in the radiator, the return supply channel opens, and when the coolant must be heated, on the contrary, the water supply channel from the return line is closed.
Features of using regulators
 Some experts recommend equipping all radiators in the house with shut-off valves. This step will allow homeowners to repair the heating system with minimal effort and time; moreover, if a certain radiator leaks in the system, there will be no need to drain the coolant from the entire circuit. However, at the request of homeowners, a radiator temperature controller can be installed in certain rooms.
Some experts recommend equipping all radiators in the house with shut-off valves. This step will allow homeowners to repair the heating system with minimal effort and time; moreover, if a certain radiator leaks in the system, there will be no need to drain the coolant from the entire circuit. However, at the request of homeowners, a radiator temperature controller can be installed in certain rooms.
Most often, devices are installed in interior rooms where constant control over the temperature level is needed.
 As a rule, a thermostat on a heating battery is mounted at the inlet of the radiator in accordance with the heating circuit developed earlier, however, some homeowners install devices at the outlet, trying to reduce the influence of the outflow of cooled liquid on the operation of the regulator.
As a rule, a thermostat on a heating battery is mounted at the inlet of the radiator in accordance with the heating circuit developed earlier, however, some homeowners install devices at the outlet, trying to reduce the influence of the outflow of cooled liquid on the operation of the regulator.
 The installation process itself is quite simple and does not require any special practical skills. The work of installing regulators is not much different from the process of installing any connecting fittings used in a heating system, therefore, if you have basic equipment and basic skills in handling them, installation of regulators can be done quite quickly.
The installation process itself is quite simple and does not require any special practical skills. The work of installing regulators is not much different from the process of installing any connecting fittings used in a heating system, therefore, if you have basic equipment and basic skills in handling them, installation of regulators can be done quite quickly.
Thus, by using affordable and functional regulators in the heating system, you can achieve significant results in terms of energy savings and achieve smooth distribution of heat from heating devices in a house or apartment.
 How to effectively increase the heat transfer of a central heating battery?
How to effectively increase the heat transfer of a central heating battery?  Grille for a heating radiator: types and characteristics
Grille for a heating radiator: types and characteristics  How to properly connect heating radiators to each other?
How to properly connect heating radiators to each other?  Prices for heating batteries of popular types
Prices for heating batteries of popular types
© 2016–2017 — Leading heating portal.
All rights reserved and protected by law
Copying site materials is prohibited.
Any copyright infringement will result in legal liability. Contacts
How to regulate the temperature of a heating battery? Heating temperature regulators for radiators

These 10 little things a man always notices in a woman Do you think your man doesn’t understand anything about female psychology? This is wrong. Not a single little thing can be hidden from the gaze of a partner who loves you. And here are 10 things.

How to look younger: the best haircuts for those over 30, 40, 50, 60 Girls in their 20s don’t worry about the shape and length of their hair. It seems that youth is created for experiments with appearance and daring curls. However, already last.

Contrary to all stereotypes: a girl with a rare genetic disorder conquers the fashion world. This girl's name is Melanie Gaydos, and she burst into the fashion world quickly, shocking, inspiring and destroying stupid stereotypes.

Why do you need a tiny pocket on jeans? Everyone knows that there is a tiny pocket on jeans, but few have thought about why it might be needed. Interestingly, it was originally a place for storage.

15 Cancer Symptoms Women Most Often Ignore Many signs of cancer are similar to symptoms of other diseases or conditions, which is why they are often ignored. Pay attention to your body. If you notice.
What does your nose shape say about your personality? Many experts believe that you can tell a lot about a person's personality by looking at their nose. Therefore, when you first meet, pay attention to the stranger’s nose.
Methods for adjusting radiators of a heating system using taps, thermostats and servos
During the professional design of a heating system, three main factors must be taken into account: rated power, installation layout of devices and their adjustment. To solve the last problem, it is necessary to use special fittings, as well as devices for changing the temperature regime in a specific section of the circuit. How to properly adjust the heating system of houses and apartments: taps, radiators, radiators?
Methods for adjusting the heating system
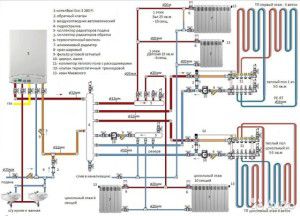
Heating system with control valves
There are several ways to change the characteristics of heat supply. Timely hydraulic adjustment of the heating system is necessary to stabilize the pressure in certain areas and the entire circuit as a whole. Temperature adjustment serves as a tool for changing the degree of air heating in a particular room. Most often, a tap is used for this to regulate the heating temperature.
All of the above characteristics largely depend on the operation of the boiler. However, to normalize the system parameters, it is necessary to install additional components. Depending on their function, they are divided into the following types:
- Temperature. They are used to partially or completely block the flow of coolant in radiators or in a separate circuit. Using taps, a thermostat or mixing units, the heating radiators in the apartment are adjusted;
- Pressure. Temperature differences between the flow and return lines can cause pressure surges. This will lead to an imbalance in the system, which will worsen its performance. To eliminate this problem, install hydraulic arrows, as they do collector wiring pipes
In practice, timely adjustment of taps on heating radiators reduces energy costs. Also, using control valves, you can change the degree of heating of the air in the room.
The actual performance of the heating system must coincide with the calculated ones. In this way, the number of adjustment elements can be reduced.
Types of regulators
![]()
Heating radiator piping
Heating adjustment in an apartment building or private cottage is carried out using special devices. They are installed in certain areas of the system and can operate in automatic or manual mode. They are installed on radiators, mixing units and manifolds.
Before choosing a specific model, you need to find out the best way changes in temperature conditions for pressure in the system. Depending on the internal device Adjustment of heating radiators in an apartment can be carried out using two methods:
- Partial blocking of the coolant volume into the battery. To do this, install taps and thermostats;
- Mixing streams of hot and cooled water to form a coolant at the desired temperature. This is done using mixing units in which two- and three-way valves are mounted.
Full adjustment of the heating system of a private home can only be carried out after a thorough study of the devices of these components.
Heating control valves

Cone valve design
The easiest way to change the operating temperature of batteries is to install shut-off valves. It is used to adjust the heating taps in an apartment or house. Depending on the design, they can perform two functions - promptly shutting off the coolant flow during repair work or adjustment hot water into the battery.
Ball valves are not designed to change the flow of coolant volume. Therefore, it is impossible to regulate the temperature of the heating battery using them. To do this, you need to use another valve model - a cone valve. In it, with the help of a rod, the bore diameter in the section of the main line is changed.
Installing a cone valve is a cheap mechanism for changing the temperature in a heating radiator. However, along with this, its operation has several disadvantages:
- Manual operating mode. When changing the degree of water heating in the pipes to reduce or increase the heat flow to the radiator, you must independently adjust the position of the rod;
- It is recommended to install a thermometer to take temperature readings in the radiator;
- Over time, the rubber gasket becomes thinner, leading to failure.
Currently, adjusting the temperature of a heating radiator using taps is not practiced. For this purpose, other mechanisms with a much larger set of functions are used.
A so-called servo drive can be mounted on an already installed cone valve. It will change the position of the rod automatically depending on the temperature in the room or heating system.
Heating thermostats

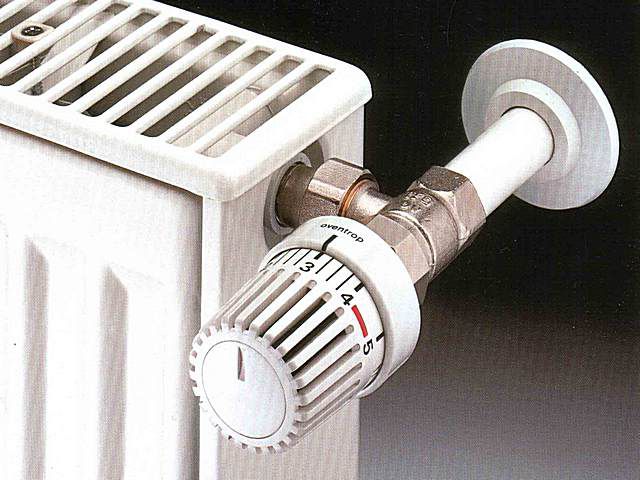
Heating radiator thermostat
It is best if the heating radiator temperature is adjusted in automatic and semi-automatic mode. This function is performed by thermostats - devices for changing the volume of water flow into the battery.
Most often, direct-acting thermostats are used for radiator piping. Structurally, they are similar to the faucets discussed above, with one exception - the position of the stem changes automatically depending on the temperature of the hot water.
This heating temperature control system consists of a mechanical part and a sensing element. The functions of the latter can be performed by paraffin or any liquid with high degree thermal expansion. As the temperature rises, the sensing block presses on the valve seat, thereby initiating the lowering of the stem. The response temperature is adjusted using a spring connected to a thermostatic element.
The advantage of such adjustment of heating radiators in an apartment is the automatic operation of the device. The user just needs to set the required radiator heating level on the thermostat. But besides this, you need to know the specifics of adjusting apartment heating radiators:
- In the vast majority of cases, thermostats do not have the function of connecting to external temperature sensors. Their operation does not depend on the degree of heating of the air in the room, which can cause some discomfort;
- After a long period of inactivity, the valve seat is fixed in the body. To eliminate it, you must manually lower and raise the rod;
- Each thermostat model is designed for a specific operating temperature.
Despite the apparent advantages of thermostats over adjusting taps on heating radiators, they cannot greatly influence the change in the degree of heating of the batteries. This function is performed by other devices.
For full operation of the radiators, in addition to the thermostat, the radiators must contain a Mayevsky valve to eliminate air jams.
Servo drives for heating control

Servo drives in heating
Another type of thermostat – a servo drive – has greater functionality. It can be mounted to adjust heating taps in an apartment with already installed fittings. In fact, the servo drive performs the functions of changing the position of the rod on the tap depending on external factors– coolant temperature or degree of air heating in the room.
Unlike a thermostat, most servo drive models have a built-in temperature sensor. But this is not a disadvantage, since for complex heating control in an apartment building, you can connect several devices to one thermometer. In this way, the flow of coolant volume will be adjusted in all radiators at once. Additionally, servo drives are used to complete the following heating components:
- In the collector group of the heated floor. They are part of a heating temperature control system in a private house, complete with a two or three-way valve;
- Connecting to a daily or weekly programmer will make it possible to automate the heating operation.
In addition, servo drives are installed in any areas of the heating system where it is necessary to automatically regulate the volume of coolant flow.
To regulate the temperature in the heating battery using servo drives, you must additionally install a temperature sensor. Therefore, most often preference is given to thermostats.
Features of installation and maintenance of regulators
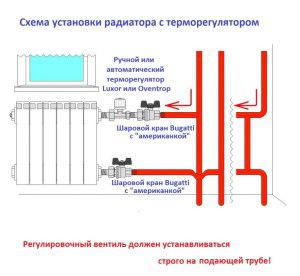
Thermostat installation diagram
After choosing the optimal model of thermostat or tap to adjust the heating temperature, you should perform them correct installation. The location of the fittings directly depends on its function and design.
Most often, the adjustment components are mounted in the trim of a specific heating radiator. They are installed on the supply pipe or on the bypass. In order to comfortably adjust the temperature of the radiators, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- The device must not be closed decorative panels or other interior items;
- The service life of thermostats largely depends on the quality of the coolant. Therefore, you should install before it strainer, which will protect the valve seat from limescale;
- When installing the heating temperature control valve, you must follow the installation diagram. On the body of the device, arrows indicate the direction of movement of the coolant;
- Many thermostats and servos are connected to the electrical network. Therefore, it is necessary to provide power supply to them.
Before installing and further adjusting heating batteries in an apartment, you must read the manufacturer's instructions. It specifies the installation conditions for the operation of a specific adjusting element.
One of the important indicators of apartment heating control valves is the maximum and minimum throughput. They must match the current system parameters.
Maintenance of regulators and valves

Pressure testing is carried out only after installing the control valves
After installation, preliminary adjustment of the taps on the heating radiators should be carried out. To do this, the operating temperature and pressure in the system must be normal. Then, by changing the degree of heating of the coolant, the operation of the control valves is checked. The system is tested in several modes. Alas, but do it self-adjustment heating in an apartment building using this scheme will not work, since consumers do not have the opportunity to change the degree of heating of the coolant.
In fact, it is possible to check the performance of a specific element only when starting up the central heating supply. Those. correct adjustment heating radiators in the apartment is carried out during the heating season.
During the startup of the heating system, the heating system of a private house must be fully adjusted. It should include the following steps:
- Checking the functionality of taps and thermostats;
- Compliance of their actual parameters with passport data;
- If, during the control adjustment of the degree of heating of the heating batteries, a faulty element is detected, it must be replaced.
In addition, you need to remember that the operation of the system is influenced by a number of external factors: the degree of thermal insulation of the house, climatic features specific region. This should also be taken into account when adjusting the temperature of the heating radiator.
Regulation of the heating battery depends on the heating system installed in the apartment. If you cannot do this yourself, it is best to invite specialists who will do everything at the highest level.
How to regulate a heating battery?
When the process is completed and the individual heating system is calculated as correctly as possible, regulators will not be needed, since the temperature in all rooms will be maintained at the same level. In high-rise buildings and large old buildings after major repairs Regulators can be useful, but their choice depends on many factors discussed below.
If you are wondering how to regulate a heating battery, you should know that this is done for the following reasons:
- saving gas when heating. To reduce your gas bill, a common house heat meter should be used. In particular, in an apartment when using an individual heating system that supports optimal temperature, regulators may not be used. The exception is old equipment. Then you will be able to save a lot;
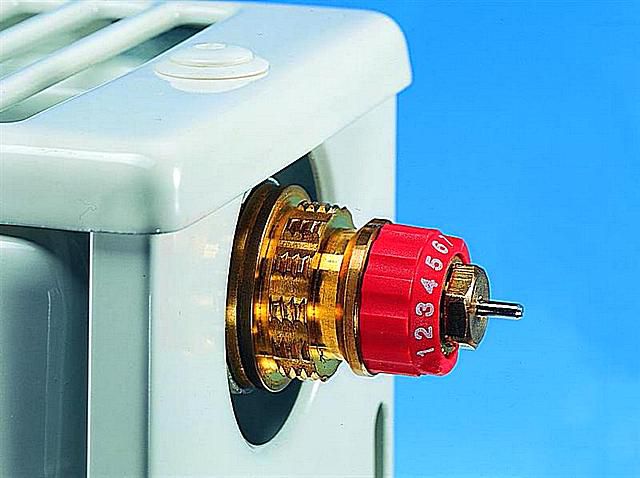
- the ability to maintain the temperature in the premises that you need. For example, in one room you want +23°C, and in another – 15.6°C. Then you need to set the values on the thermal head or close the valve, and get this warm air, as you need. It does not matter which heating system in the apartment is central or individual. Regulators are not connected with all this; they function on their own.
Perhaps you don’t know how to adjust the radiator in your apartment. Then the tips below will help you. To do this correctly, just closing/opening the control valve on the radiator is not enough. Depending on the number of radiators connected to the system, you need to open a certain number of them by a certain number of revolutions. For example, there are four batteries installed that are connected to the central heating system. To distribute the pressure over it, the first battery opens several turns, the next - three, another - four, and so on. Now you know how to adjust the radiator manually. And, as it becomes clear, this is easy to do, and your rooms in the apartment will heat up very quickly to the temperature you need.
The answer to the question of how to regulate batteries takes on a different meaning if there is an option for forced pumping of liquid. Then you have the opportunity to install three-way valves on all batteries. Then it will not be difficult to regulate the temperature in the radiators. So, in order to significantly simplify the setup, each battery should be equipped with special valves that allow you to control the flow of heat and the rational consumption of heating equipment. If the room is hot or it is closed and not in use, the valve allows you to reduce or close the flow of hot water into the battery.
How to regulate batteries using a valve
In multi-apartment buildings, valves are most often installed at the exit/input from the elevator unit of the heating system. These devices in their own housing have 2 rings made of steel, protected from corrosion. They encircle the coolant passage. Several more of these rings are located on the surface of the valve, in particular in its moving part, which is very convenient.
Next you will read how to regulate the temperature of a radiator. If the valve is located at the bottom and lowers, then it impedes the movement of liquid, and if it is moved upward, it goes beyond the circulating flow. To close it, the user must rotate the handwheel, which drives a screw-threaded rod. For hot liquids and heating systems, it is best to use a graphite valve. There is no alternative to it if the pipe diameter is over 50mm.

How to adjust a heating battery in a private house with air vents
A typical tap for a central heating system is a product by Mayevsky. This simple design, made of brass rod. When in the closed position, it closes the hole in the seat. You also need a thread to install the product in the radiator plug.
How to regulate heat in batteries using an air vent is described above. Now it’s time to learn about the features of Mayevsky’s product:
- reliability, repairs are rarely needed;
- low cross-country ability - this option is not suitable for apartment buildings where they are installed expansion tanks with top filling;
- Before adjusting the temperature in the battery, you can completely unscrew the rod, although this needs to be done quite rarely. No one has yet succeeded in putting it in place, overcoming the resistance of hot water;
- When purchasing a Mayevsky product, choose a product for a screwdriver, but not a turnkey one, which is often quite difficult to find.
An alternative to such a valve is a drilled radiator plug or an adapter into which a plug valve is screwed. In some cases, a water tap is used that is installed upside down, that is, with its nose up. The instructions telling you how to do this will help you complete this procedure correctly.

Automatic adjustment is convenient because by setting the temperature in the apartment room just once, turning the control knob to the required position, you will not need to change or twist anything later. The temperature is constantly regulated automatically. The disadvantage of this method is the high cost of the devices. And the higher their functionality, the higher the price.
If you still don’t quite understand how to adjust the temperature of the radiator in the apartment, then it’s better not to do this yourself, but to invite professionals and entrust this task to them. Call our company and order a service! You can rest assured that our employees will approach your case as carefully and responsibly as possible. In addition, you can count on free consultation, during which you will get answers to all your questions and learn how to adjust radiators. Call!
Still have questions? Call or write to us!
This is probably a familiar picture to many – it’s a frosty winter outside, and in some apartments in multi-storey buildings the windows are wide open. This only means that the owners are in this way saving themselves from the too hot, suffocating atmosphere created in the premises by heating radiators operating at full power. But there is nothing good in such an approach: drafts begin to circulate in the apartment, which can cause colds, and the waste produced by boiler rooms thermal energy thrown, literally, into the wind.
All this can be avoided if you slightly modernize your heating system - equip it with a special device that will sensitively respond to the current temperature in the rooms and make its own adjustments. This device is called a thermostat for a heating radiator. It is affordable, easy to use self-installation, easy to operate. And with all this, the thermostat creates in the room optimal microclimate for residents, also bringing the effect of serious savings on energy consumption.
The need for a device for adjusting heat transfer from heating radiators
Any heating system must be created on the basis of carefully carried out thermal calculations. In this case, a lot of different criteria are taken into account, ranging from the area, height and other features of each specific room, to the specific climatic conditions of the region of residence. Naturally, when carrying out such calculations, designers start from the most unfavorable conditions. In other words, even in the coldest ten days of the year, heating must fully cope with its tasks, that is, a certain operating reserve must be provided.
But such severe frosts, the parameters of which are included in the calculation, most often remain on the street for no longer than two to three weeks over the entire long period. winter period. It turns out that the rest of the time the calculated thermal power heating systems remains unclaimed.

In addition, it is no secret that in any region a series of severe frosts can be replaced by a fairly long thaw. It is clear that under such conditions the need for incoming thermal energy decreases sharply.
You can also remember the daily temperature fluctuations, especially in rooms facing the sunny side. And such differences on fine days can be quite impressive - during the day the rooms become untidyly hot. So we have to open the windows wide, although such a measure solves the problem only partly and can bring more harm than good.
Centralized heating systems are simply not able to respond very quickly and flexibly to such changes in air temperature. Moreover, many of the existing systems were developed to meet old construction standards, with monotonous heating radiators and the widespread installation of conventional wooden windows. Mass installation by residents of new quality windows with double-glazed windows also made its own adjustments - heat loss through them is much less, plus one of the ways has disappeared natural ventilation indoor air. When carrying out repairs, owners often discard old batteries, installing modern models with increased heat transfer. But if you do not adjust the temperature, then this is again the path to the consequences mentioned above.

It would seem that the owners of private houses with autonomous systems oh heating is much simpler, since they are able to quickly change the thermal power of the boiler itself. This is true, especially if the boiler equipment is equipped modern system weather-dependent automation. However, this does not completely solve the problem. IN different rooms At home, different thermal conditions may also be required. Plus, there are the already mentioned daily temperature fluctuations. In addition, in some premises it is often necessary to temporarily create completely individual conditions, for example, for storing certain products or materials. In temporarily uninhabited rooms, a thermal regime may be needed that would, for example, only ensure the guaranteed safety of the heating system itself. In a word, for all this it is necessary to have some means of quickly and accurately controlling the temperature directly on the heat exchange device itself - the radiator.
It was for these purposes that a thermostat for a heating radiator was developed.
Video - Thermostat for a heating radiator: installation and configuration
How does a thermostat work and what is the principle of its operation?
The principle of quantitative heat regulation
It is not for nothing that the liquid circulating through the heating circuits is called a coolant - this formulation fully describes its purpose. Taking, due to its clearly high heat capacity, a “thermal charge” from the boiler equipment, it transfers it through the heating radiators, where it releases it into the premises.
It would be natural to assume that the less coolant passes through the radiator per unit time, the less its overall heat transfer will be. It is on this principle – quantitative regulation of coolant flow – that the operation of most thermostats for heating radiators is based.
This principle is by no means new - it has always been used, including the installation of control valves in front of the entrance to the heating radiator. To this day, in houses of old construction you can find almost “antique” ones, but still functioning cast iron batteries, equipped with manual taps for adjustment and temperature.

They do this in everyday life even now - they install one or another shut-off element on the supply pipe, which regulates the intensity of the coolant passing through the radiator. By the way, many people make the mistake of installing only a ball valve. By its design, it is designed to work in only two positions - completely open or closed. An intermediate position leads to rapid wear of the spherical valve and its seat, leading to failure of the product. If the ball valve is located on the radiator (and this most often happens nowadays), then this is only for repair and maintenance work associated with completely disconnecting and even dismantling the battery. And it is not advisable to use it for adjustment.

It’s a different matter - well-known valve-type products, which are designed to regulate the flow of liquid passing through them. The forward movement of the valve plug parallel to the flow, from the position of its tight fit to the seat to its gradual raising above it, changes internal section fluid passage channel. The durability of such shut-off and control devices is much higher. Looking ahead, we can say that it is precisely this valve circuit that is, in fact, used in modern thermostats.
The manual adjustment scheme is pristine, but extremely inconvenient, since the owners have to constantly interfere with the operation of the radiator, making the necessary adjustments depending on the initial conditions - the current weather, the air temperature in the room and the coolant in the supply pipe. Of course, it would be much more convenient if the device was able to independently monitor changes and regulate the flow of coolant so that the set temperature is maintained in the room.
Such compact devices were invented and put into production in the middle of the last century by specialists from the Danish company DANFOSS. By the way, to this day it remains a leader in the field of industrial and household thermal automation, has production facilities around the world, and two factories are successfully operating in Russia.
There are practically no fundamental differences in the structure of most thermostats from various well-known manufacturers. Moreover, most of them are even adapted to uniform standards and are easily interchangeable.
Design of modern thermostats for heating radiators
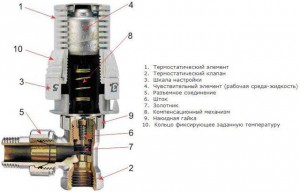
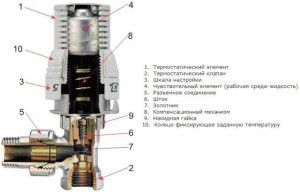
In fact, any thermostat for a radiator, which is presented in a modern assortment, can be divided into two main units. One of them is a valve that regulates the flow of coolant, and a thermal head that controls the operation of this valve.
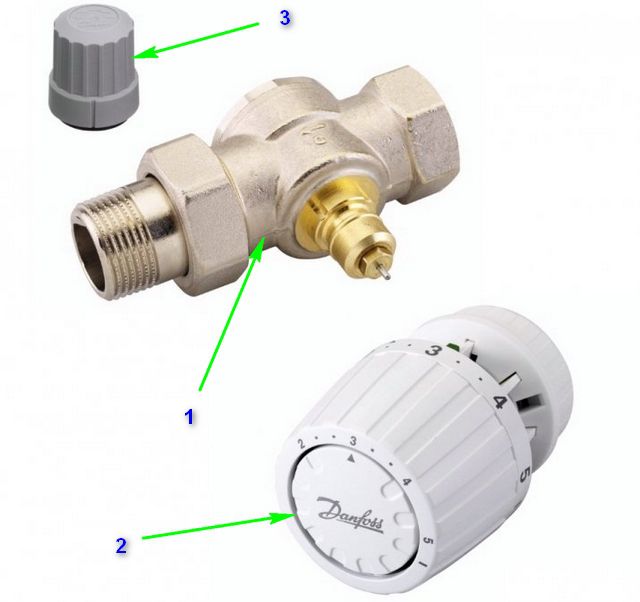

The valve itself (item 1) is a prefabricated structure made according to a design similar to a conventional valve
In the transport or non-working position, the control part of the valve with a protruding rod is closed by a protective cap (item 3). In a number of models, it can also be used to manually control the valve, acting as a flywheel, although many manufacturers do not welcome this approach. And the durability of this cap during regular use is very doubtful.
The main control element is the thermal head (pos. 3), which is installed and fixed on the valve instead of the removed cap.
The interfacing scheme of the nodes may vary, but generally manufacturers adhere to a single standard, that is, thermal heads can be replaced with others. Accordingly, in the store you can purchase either a ready-made kit or just a valve, then select the thermal head you like best and have the appropriate parameters.
Thermal valve
Let's start with the valve device. Schematic diagram shown in the figure:
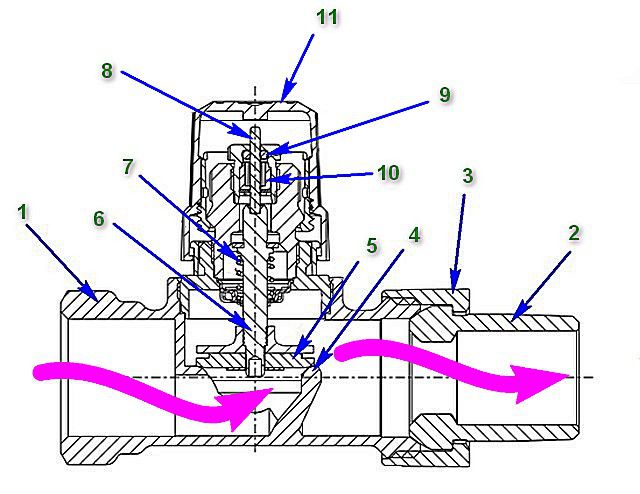
The valve body (item 1) is made of a corrosion-resistant alloy - it can be brass, bronze or stainless steel. Non-ferrous alloys are usually coated with chrome or nickel plating. You should not buy a cheap product made of silumin alloy - it will not last long.
The housing has a threaded part at the inlet (there are models equipped with a press fitting for the corresponding pipelines). At the output there is a connection with a fitting (item 2), which is usually “packed” into the heating radiator, made using an “American” union nut, making such a unit detachable. A fitting with an “American” connection must be included in the valve kit.
Wide arrows show the direction of movement of the coolant. There must be a corresponding symbol on the body itself indicating the direction of flow, and changing the correct location of the valve is unacceptable.
The valve seat (item 4) is located inside the body. The passage of liquid is closed or limited by the poppet valve itself (item 5) with a spool made of high-quality synthetic rubber.
The plate is connected to a rod (item 6), which ensures translational movement of the valve part. The body is equipped with a return spring (item 7), which always directs the valve to the open position if there is no control action on it.
Above the axis of the rod there is a pusher pin (pos. 8), which in its initial position comes out of the body. It is this pin that will take control action from any type of thermal head, transmitting it to a rod with a poppet valve that closes or regulates the flow of liquid. Of course, the seals have been thought out - ring (pos. 9) and stuffing box (pos. 10), which prevent coolant leakage along the axis of the rod. When not in use, this unit must be covered with a protective cap (pos. 11).
For those who do not understand drawings well, there is a similar valve, but in a “live section”.
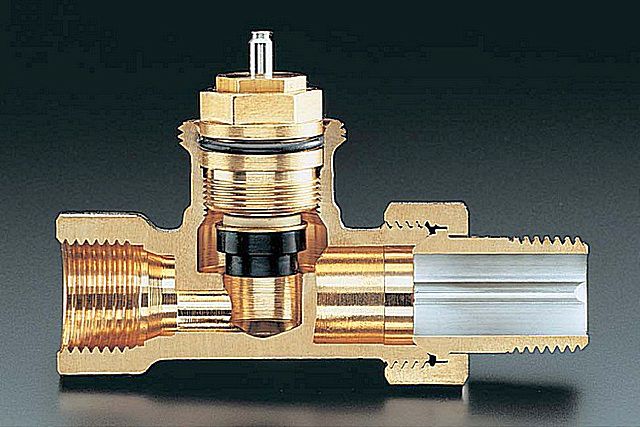
According to the principle of their design, almost all valves are the same. However, there are specific differences among them that you should definitely be aware of.
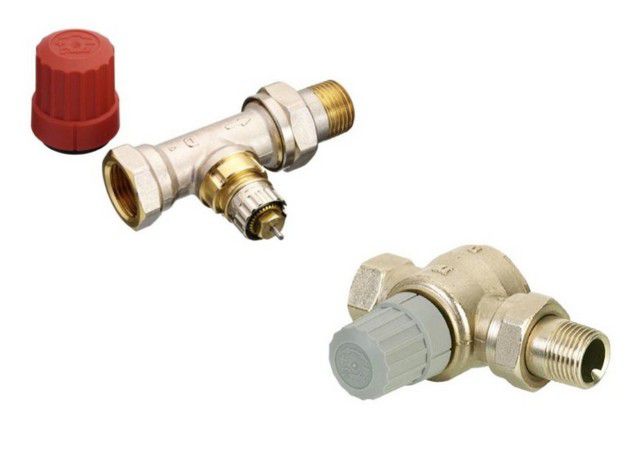
- Firstly, the valves differ in their mounting dimensions. So, for example, depending on the diameter of the connection to the heating radiator, it is fashionable to purchase thermal valves with connecting thread by ½, ¾ and 1 inch.
- Secondly, the shape of the valve body may also vary. There are straight models that provide a through flow of coolant, and angular ones that change the flow direction to perpendicular. It is clear that the choice will depend on the location and connection of the supply pipe.

The figure shows several main versions of a valve model with approximately the same design:
A- regular straight line;
b– angular vertical;
V– angular horizontal;
G– angular with placement of pipes and valve head in three perpendicular axes. Moreover, such a model can also be left-handed or right-handed.
- Thirdly, when choosing a valve, you should pay attention to what heating system it is designed to work in. There can be significant differences here.

Thus, for single-pipe systems, high levels of hydraulic resistance on the control valves are unacceptable. Therefore, valves usually have a wider cross-section and are externally somewhat larger in volume. In the accepted classification, they are usually marked with the letter index G, for example, RTR-G. In principle, they are also suitable for two-pipe autonomous systems with natural circulation coolant.
And for two-pipe systems with forced circulation, where the pressure of the passing coolant can reach considerable values, other valves are used - marked N or D (various additional combinations are possible).
This is a very important question, because when wrong choice You can end up with extremely incorrect operation of the heating system as a whole.
- Finally, fourthly, thermal valves for two-pipe systems may also have a device for pre-setting it bandwidth. So, you can set the required value in advance in the acceptable range - from 0.04 to 0.73 m³/hour for ½ inch valves, or from 0.10 to 1.04 for ¾ and 1 inch diameters.

This measure allows you to pre-set the approximate value of the required coolant flow through the radiator - the thermal head will bear a much smaller load, and it will last longer and will regulate faster and more accurately. The adjustment itself is not difficult and does not require any tools - just unlock the adjusting ring and, turning it in the desired direction, set the required value according to the existing mark. The instructions supplied with the valve provide recommendations, tables and diagrams - everything to correctly determine the required preset position. Initial values in this matter will be the thermal power of the radiator to which the thermostatic unit is connected, as well as the temperature difference in the supply and return pipes
After such a preset, when the thermal head is put on, this setting scale will become invisible and difficult to access without unauthorized intervention.
Finally, thermal valves with the letter D also provide dynamic pressure equalization. The special design of internal channels and nozzles maintains the pressure drop in such a valve at a value of only 0.1 bar. This is very convenient both for thermal calculations and for ensuring stability of the coolant flow passing through the heating radiator, regardless of the position of the valve.
Thermal heads
So, as we have seen, all thermal valves have a pusher pin protruding from the body, which transmits translational motion to the rod with the poppet valve. It remains to figure out which specific device will transmit this force, and how it all relates to maintaining the required temperature.
- The simplest solution is to install a so-called locking handle. It has exactly the same interface system with the valve body as any other thermal head. By rotating the installed handle, you can change the position of the poppet valve, that is, in principle, it makes it possible to manually adjust the temperature.

Of course, it is impossible to call such a handle a thermal head - the device will not react independently to changes in the temperature in the room. This approach is a direct analogy with a conventional plumbing valve placed on a pipe in the garden, as already mentioned above.
However, manufacturers do not position the locking handle as a regulating element of the system. Its purpose is to reliably close the valve in case of need for certain repair and maintenance work. This makes it possible to do without additional ball valve on the supply pipe - the thermal head is removed, the mentioned handle is installed, with its help the valve is tightly screwed - and the radiator can be dismantled without completely turning off the system and without draining the coolant from it. Having such a “spare part” at home is useful, but using it for effective thermoregulation does not make much sense.
- The most popular option is the use of bellows-type thermal heads, which sensitively react to changes in room temperature and create the same mechanical force on the protruding pin, through it on the rod, and then on the poppet valve itself, completely blocking or narrowing the coolant passage channel.

Since ordinary consumers most often have to deal with such thermal heads, their design will be discussed below in a little more detail.
- If the heating system of the house is fully automated, or in cases where it is necessary to place remote temperature sensors in the rooms, a servo-driven head can be used. A miniature electric motor receives a control signal from the control unit and progressively moves the valve stem up or down, ensuring the opening or closing of the channel for the movement of coolant.
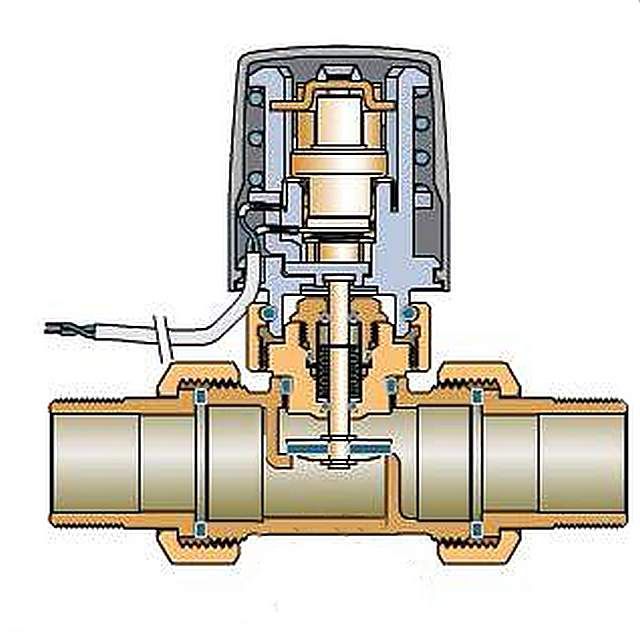
However, such complex control systems are used rarely. Usually, installing a thermal head with a bellows operating principle is quite sufficient.
How does a bellows thermal head work?
The main advantage of this type of thermal heads is that they are able to operate in a fully automatic mode, without requiring any power at all. The principle of their operation is based on one of the basic laws of thermodynamics - the expansion of substances with increasing temperature.
An example of an automatic mechanical thermal head device is shown in the illustration:
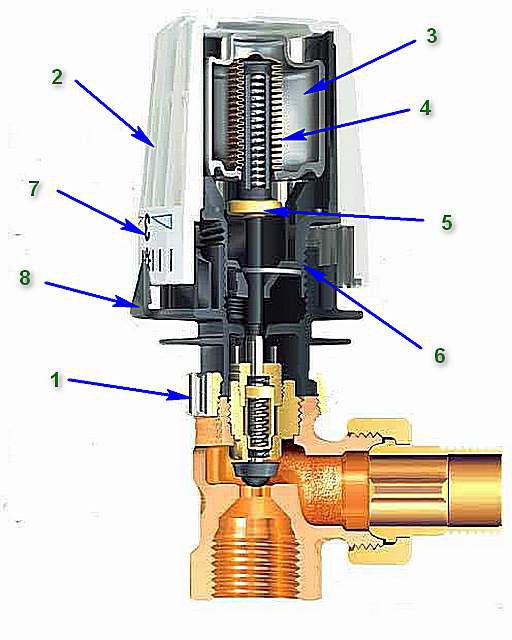
It is probably clear to everyone that in the lower part of the figure there is a section of a thermal valve, the construction of which we “already went through”. But the thermal head itself is attached to it using a union nut M30×1.5 (item 1). Some manufacturers also use other connecting units of their own design: no key is required to install the head - it is fixed in the adapter with a simple hand press. But still, the vast majority of thermal valves have a threaded part that is standardized specifically for this nut size - M30x15.
The device itself consists of two parts - a stationary one, which is attached to the thermal valve, and a movable head, rotating relative to its axis (item 2). Its body is usually made of durable plastic. The head is usually provided with holes (round or slot-shaped) to ensure contact of ambient air with the temperature-sensitive element.
This sensitive thermoelement or bellows (item 3) is, in fact, the main part of the entire device. It is a hermetically sealed cylindrical container filled with a liquid or gaseous substance (agent). The bellows body is designed in such a way that it can change in volume - most often this is achieved due to the corrugated walls of the cylinder (item 4).
The principle of operation is extremely simple. Depending on changes in temperature in the room, the liquid or gaseous agent either increases in volume or, conversely, contracts. This thermal expansion is transmitted to the bellows body, which, in turn, acts on the piston with rod (item 5). The rod is installed strictly coaxially with the pusher pin of the thermal valve, that is, it transfers to it the mechanical force to close or open the valve part. Accordingly, when the temperature rises, the channel for coolant circulation narrows, until it closes completely; when it decreases, it opens slightly, thereby adjusting the heat transfer from the heating radiator.
The movable head is connected to the fixed part threaded connection(pos. 6). Thus, by rotating the head, you can progressively change the position of the piston, rod and bellows relative to the thermal valve body. This makes it possible to pre-set the thermostat to maintain a certain temperature. To visualize the settings, there is a scale on the body of the rotating head (pos. 8), and on the stationary part there is a pointer (pos. 9). The numbers or pictograms printed on the scale allow you to set the required temperature with an accuracy of literally one degree.
There are other variations in the design of the thermal head. So, for example, if you need to take temperature readings not directly near the radiator, but to the side, then a thermal head with an external probe is used. This probe sensor is connected to the bellows of the thermal head by a thin metal capillary tube about 2 meters long.

Another option is also possible. For example, in cases where access to the radiator is difficult for one reason or another, it is necessary not only to remove the sensor, but also the adjustment mechanism. For such situations, a kit is offered that includes a head that acts only as a drive to transmit force to the valve fitting. And the control panel with an adjusting flywheel is placed on the wall in a place convenient for access and adjustments. In such devices there are two bellows - a working one, located in the control panel itself, and a drive bellows connected to it by a capillary tube, which ensures the operation of the valve device on the radiator.

There are also more complex combinations - for example, a drive head connected to a control unit, which, in turn, also has an external temperature sensor.
Video - Animated demonstration of the device and operating principle of a thermostat for a heating radiator
Electronic thermal heads
Electronic thermal heads stand somewhat apart. They are also adapted for installation on standard thermal valves, however, they differ in larger overall dimensions, since they require power to operate, and the case contains a battery compartment (usually two AA elements).

These thermostatic heads are equipped with a digital display that allows you to accurately set the temperature value. Modern models very often they provide owners with the opportunity to program operating modes. For example, you can reduce the air temperature in the room during the period when people are not in the house or apartment, so that comfortable conditions are provided only by the time they arrive home. You can lower the temperature at night - many people sleep much better in a cool atmosphere, but so that in the morning, by the time you get up, an optimal microclimate is ensured. Such settings are also carried out by day of the week, taking into account weekends or holidays. This can bring a very noticeable energy saving effect.
Many electronic thermostatic heads also have preset modes. For example, “vacation”, “economical”, “freeze protection” and others - switching to such modes is carried out by simply pressing the corresponding buttons.

Electronic thermal heads of some models can fit perfectly into the concept " smart home", unite in unified system with a common monitoring and control unit. The temperature level in the premises is controlled from one center, and control signals are transmitted via one or another wireless communication channel.
Of course, such electronic systems have a very bright future. But so far, they have not reached the peak of popularity, partly due to their considerable cost. Most consumers prefer to purchase automatic mechanical thermal heads.
How to choose a thermostat for a heating radiator?
If you decide to install thermostatic regulators on heating radiators, then when choosing optimal models certain evaluation criteria must be adhered to.
- It has already been mentioned that almost all thermal valves are adapted to most manufactured thermal heads. This makes it possible to purchase the required kit separately. If you have limited funds, it is even fashionable to split the purchase into two “steps” - first purchase and install valves, temporarily adjusting them manually, and then supplement them with thermostatic heads.
- The valves must match the type of heating system. This has already been mentioned - there are models for two-pipe systems (by the way, they are the majority in the assortment of stores), and for one-pipe. Ignoring this rule is unacceptable.
- It is necessary to evaluate in advance the locations of the intended installation of thermostats, since the shape of the valve body will depend on this - straight, angular, etc.
Important - the thermostat must be installed only on the supply pipe! In this case, the correct position of the thermal head should be horizontal. This rule was introduced so that the heated air rising from the supply pipe does not wash the temperature-sensitive element - the bellows - and does not “disorient” it, otherwise the operation of the device will become extremely incorrect.

Depending on the diameter of the supply pipe, the installation dimensions of the valve are selected.
- When choosing a control head, of course, preference should be given to models with automatic adjustment temperature. Manual valves will not provide the expected operating comfort.
- There is little point in installing devices with automatic adjustment on cast iron radiators– too high thermal inertia of such batteries interferes with the correct operation of the thermostatic unit. Here you can limit yourself to a manually controlled device.
- When choosing a location for installing the thermostat, it is necessary to take into account that the correctness of its operation can be affected by a direct hit sun rays, close proximity to other heat sources, including large household appliances, drafts, etc. If the entrance of the half-dacha pipe to the radiator is located in the listed “problem” areas, then it would be wiser to purchase a model with a remote temperature sensor. A similar approach is also practiced in places where it is impossible to install the thermal head in the correct horizontal position.
Other specific conditions for placing a radiator or heating convector can also create problems. For example, according to the interior design, the batteries are covered with decorative covers, thick curtains, or there is a very wide window sill on top of them. In such cases, it will also be more rational to use a regulator with a remote sensor, and if it is difficult to access the thermal head itself to make adjustments, use a remote control panel.

Similar measures are often resorted to when the lower principle of connecting a radiator or converter involves the proximity of the supply pipe to the floor, where the temperature readings will differ significantly from room temperature. It should be remembered that optimal height The location of the temperature sensor is 500 ÷ 800 mm from the floor level.
In principle, the speed and accuracy of the reaction in practical operation is not so noticeable, so it is quite possible to get by with a more affordable thermostat with a liquid bellows. In terms of durability, they are approximately equal.
- If there are concerns that unauthorized changes may be made to the thermostat settings, or there may be attempts to violate the integrity of the device (alas, children left unsupervised are quite capable of such “disgrace”), then you should consider purchasing a device that has special anti-vandal protection. Calling children “vandals” is, of course, an exaggeration, but still...

- The range of variable temperature settings should be assessed. Usually it lies in the range from +5 to +30 degrees, in increments of 1 degree. Often the passport indicates the value of hysteresis - the temperature difference at which the device responds. It is clear that the smaller it is, the more sensitive the device is.
Many models allow the owner-customer to narrow the range of temperature changes by installing special stoppers (usually purchased separately). These additional details limit the rotation sector of the adjusting head, that is, none of the residents will be able to, through negligence or ignorance, allow a critically high or low level room temperature.
- Such devices belong to the category of certified products. Therefore, you should only choose models from trusted manufacturers who provide their products with a factory warranty. Of course, the purchase should be made only in specialized stores, whose staff, at the client’s request, will present documents confirming the originality and certification of the proposed thermostats, and will make a note in the registration document about the date and place of sale.
Among the manufacturers of such equipment, in addition to the already mentioned Danish company Danfoss (a significant part of the products of this brand are also produced at Russian enterprises), you can completely trust the brands Oventrop (Germany), Caleffi (Italy), Royal Thermo "(Italy), "Teplokontrol" (Russia), "SALUS Controls". The choice of models is quite wide, as is the price range, so it’s quite possible to choose high-quality model from the available range. There is no point in purchasing a product from an unknown company - you can get into a lot of problems with it.
Video - Recommendations for choosing a thermostatic head
Brief overview of thermostat models for radiators
Since valves are for the most part a unified part of a thermostat, the review will mainly concern thermal heads:
| Model name | Illustration | Brief description of the model | Approximate price level |
|---|---|---|---|
| "Oventrop Vindo TH M 30x1.5" |  | Thermostatic head with liquid bellows. There is a zero position - complete closure of the valve. | 750 rub. |
| "Oventrop Uni LH M 30x1.5" |  | Thermostatic head with remote sensor, capillary tube length – 2 m. Connection to the valve – union nut M30×15. The adjustment range is from 7 to 28 degrees. There is a zero position. Possibility of user limitation of the setting range. The permissible coolant temperature is up to 120 degrees. | 1550 rub. |
| "Caleffi" |  | Model with built-in bellows temperature sensor. Connection - with a specific series of valves or using a special adapter (may be included in the kit). The adjustment range is from 7 to 28 degrees. | 1050 rub. |
| "Royal Thermo RTE 50.030" |  | The liquid filling of the bellows is toluene. Hysteresis – 0.55 degrees. The permissible coolant temperature is up to 100 degrees. Connection to the valve – union nut M30×15. Manufacturer's warranty – 5 years. | 830 rub. |
| "Caleffi 472000" |  | A set of a drive head and a control unit connected by a capillary tube 2 meters long. The temperature adjustment range is from +6 to +28 degrees. Hysteresis – 0.6 degrees. Bellows are liquid. Connection: with separate group valves - direct, with the rest - through an adapter. | 8100 rub. |
| Danfoss RTS Everis |  | Liquid bellows. Connection with Danfoss thermal valves is direct fixation, with others - through an adapter. The temperature adjustment range is from +8 to +28 degrees. Hysteresis – 0.5 degrees. Devices for limiting the range and fixing fine tuning. Protection against freezing of the system at temperatures less than +8 degrees. Ergonomic design. Warranty – 1 year | 1100 rub. |
| "Salus PH60" |  | Thermal head with electronic control. Connection to the valve – union nut M30×15. Possibility of programming - for a week, including with various operating modes. LCD screen with backlight. Indication of current and set parameters, battery charge level, device status. Four preset operating programs. The temperature adjustment range is from +5 to +40 degrees. Hysteresis – 0.5 degrees. Power supply: two AA batteries, the charge of which should be enough for a year of operation. | 3700 rub. |
Valves for thermostats are available in a wide variety of sizes, shapes and purposes for a specific system. The price of high-quality valves, for example, from the Danfoss range, depending on their installation size and type, ranges from 1200 to 2700 rubles.
Installing a thermostat on a heating radiator and setting it up
Installation of the device
Drive step by step instructions installing a thermostatic regulator on a radiator is very difficult, since there can be a great many options in this matter, depending on the type and material of the internal circuit wiring. It is better to limit yourself to a list of important recommendations and illustrations of completed strappings. Anyone who has experience in plumbing installation work will understand everything. And if you don’t have such skills, then radiators and thermostats are not the best place for training, and it’s better to practice on something simpler first.
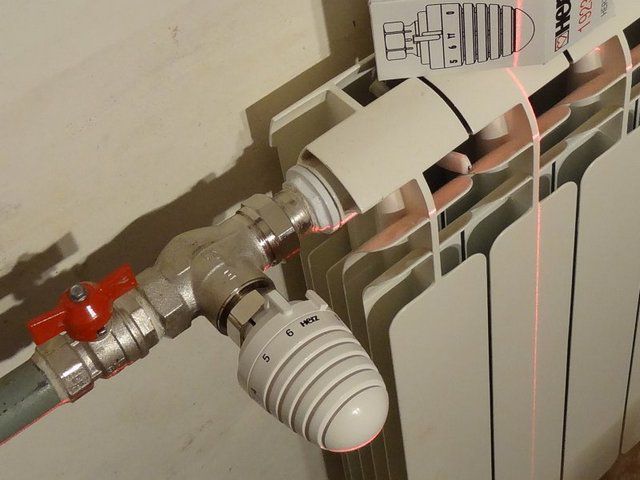


If you look at photographs of completed work, you can see such a crane in the vast majority. Just don’t mount it between the thermostat and the radiator - this would be a gross mistake.
- In the case where the thermostat is installed on a radiator connected to a single-pipe separation system, some additional rules must be observed. Firstly, the thermal valve itself must correspond to a one-pipe system - this has already been discussed. And secondly, and this is the main thing, that a bypass is installed between the supply and return pipes - a jumper pipe. The bypass diameter, according to the rules, should be one size smaller than the diameter of the liner. Any shut-off elements in the interval from the riser to the bypass are unacceptable - the same ball valve or thermostat must be located in the area between the bypass and the radiator.

What is a bypass and what role does it play?
In a properly planned heating system there are no unnecessary parts - any, even seemingly insignificant element plays one role or another. A striking example of this is, which is described in detail in a separate article on our portal.
- After the thermal valve is installed, it is necessary to fill the system with coolant and turn it on for circulation. This step will make it possible to check the tightness of the connections made - there should be no signs of leaks in the connecting nodes or from under the valve stem.
- If the valve requires presetting, now is the time to do it. The value that needs to be set on the scale is determined in accordance with the recommendations in the product’s operating instructions. The installation itself is carried out manually - the ring with the scale is removed from the stopper (pulled forward toward itself) and turned until the desired division aligns with the mark, after which it is locked again.
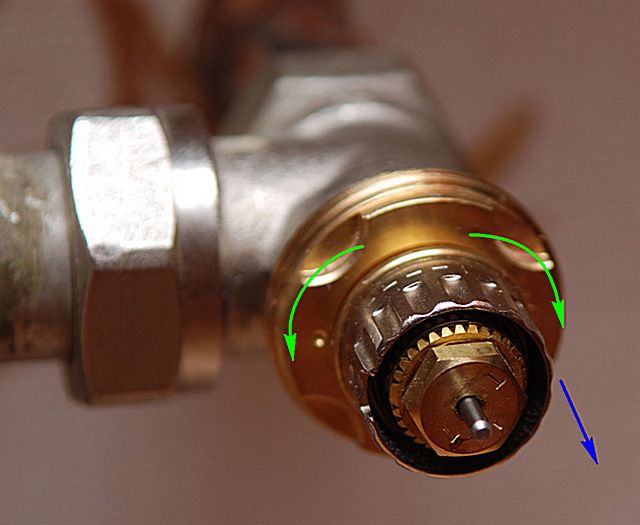

- Now you can install the thermal head. There are possible options here, which will definitely be specified in the device instructions. Some heads are fixed by simply pressing your hand until you hear a click (this is more typical for Danfoss products), others are mounted on the valve body with a union nut M30×15. Before fixing, the most convenient position of the regulator is selected - so that the visibility of the adjustment scale is ensured. After this, the nut can be tightened. They do not require much effort - often the muscle strength of the fingers is enough.
One more note. If there are two radiators installed in a room, then there is no point in installing a thermostat on each - they will only interfere with each other’s correct operation. If the radiators are of equal value, then the installation location does not matter - the device can be placed on any one, for reasons of ease of installation or use. But in the case when radiators differ in power, the thermostat is installed on the one that has greater heat transfer.
The installation and debugging of thermostats in a private residential building usually begins with the rooms on the top floor (if there is one), since warm air rises there from below. IN one-story houses or in apartments, rooms in which high dynamics of air temperature changes are observed come to the fore. This, of course, is the kitchen, where the air is very hot from the stove, rooms facing south, as well as those where traditionally there are the most people - this also changes the overall thermal background very much.
Setting up the thermostat
Thermal heads undergo appropriate calibration at the technical control stage. As a rule, the temperature values corresponding to certain divisions of the device scale are indicated in its passport. However, it should be understood correctly that calibration is carried out under certain laboratory conditions, on a thermal valve specific type, at a strictly set height of the thermal head relative to the floor level, etc. Much, by the way, in this matter depends on the type and power of the heating radiator. Therefore, under real operating conditions, deviations from the calibrated temperature indicators are quite possible.
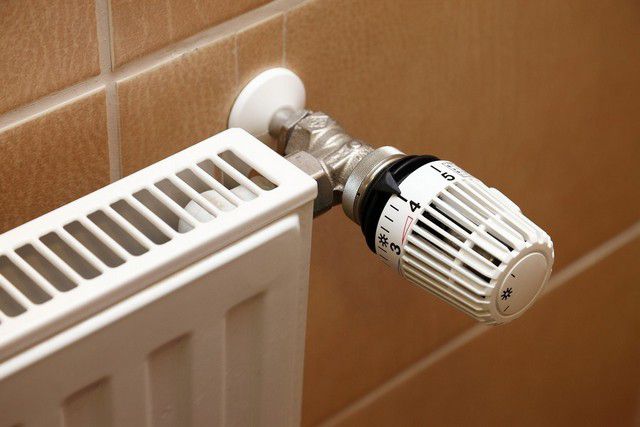

It doesn’t matter - you can fine-tune the existing heating system yourself. It is performed in several steps:
- It is advisable to place a regular thermometer in the room - this way you can rely on its readings, and not just on your own feelings. It is clear that everything in the room is brought to a “warm” position - windows and doors are closed, drafts are eliminated.
- The valve opens completely - to do this, the head is rotated counterclockwise to the extreme left position. With this position, the coolant encounters virtually no obstacles, and its maximum flow through the heating radiator ensures a rapid increase in the temperature in the room.
- When the air temperature reaches sufficiently high values, around 27÷30 degrees (it will feel hot), the head is rotated clockwise to the extreme right position. The valve is completely closed.
- Naturally, the air temperature in the room begins to gradually decrease. Here it is important to catch the moment when it reaches the most comfortable value according to personal perception (or according to thermometer readings). At this moment, you need to start very smoothly turning the head of the device counterclockwise. At some point, it will be clearly indicated both by ear and by touch that the valve has opened slightly and the coolant flow has begun through it. That's it, stop - this value, which is now on the scale, can be considered optimal and be guided by it in further operation. It probably makes sense to compare the thermometer readings and the value on the scale with the tabular data given in the product data sheet - do they differ and by how much?
During further operation of the thermostat, it will be possible to make appropriate adjustments, choosing the optimal operating mode for a specific period.
Electronic thermostatic heads are adjusted and programmed in accordance with the operating instructions supplied with them.
Conclusion and useful appendix to the article for users
What are the advantages of using thermostats on heating radiators?
To summarize, a few words about the advantages and conveniences that the installation of thermostats will bring:
- The installation itself, as we have seen, is not complicated, and can be carried out both for a heating system that is just being created, and for a heating system that has been in operation for a long time.
- The premises are maintained at an optimal temperature level that is most favorable for residents. At the same time, the microclimate is not affected by daily temperature fluctuations, sudden changes in the street, or the use of household appliances, which tend to generate a lot of heat.
- Thermostats in an autonomous system contribute to the most uniform, rational distribution of coolant throughout all rooms. This thereby levels out characteristic flaw single-pipe systems, when the temperature in the radiators drops as you move away from the boiler room.
- Thermostatic regulators are easy to operate and do not require any additional energy consumption. On the contrary, in autonomous systems of a private home they lead to significant, up to 20–25% savings in energy consumption for heating, and as a rule, they pay for themselves in just one season.
The only thing that can be blamed on the thermostat is that it can only work to lower the temperature. If the conditions are such that the heating power is clearly insufficient, then you can’t expect miracles from installing such devices; it won’t get better anyway. This means that it is necessary to carefully analyze whether the heating system is designed correctly in principle and whether its parameters correspond to real conditions. Possibly – the boiler power is insufficient, incorrectly selected and needs optimization general scheme contours. Sometimes the error lies in the incorrectly calculated parameters of heating radiators for specific rooms.
However, it also happens that the reason lies in something completely different: the owners simply need to pay close attention to the quality and effectiveness of the thermal insulation of their home.
Appendix - how to calculate the optimal radiator for a room
The calculation of the entire heating system and radiators in particular is always carried out in such a way as to ensure a normal microclimate in the most severe (but not exceeding normal) conditions. In a word, in this way, the necessary operational reserve is included in the design parameters, since at full load the entire system will operate for a rather limited time during the season.
As we have seen, the thermostat is capable of maintaining the optimal temperature, as if eliminating the imbalance between the current settings of the heating system and the actual conditions in the room. But at the same time, the radiators in the room must be able to cope with the peak, most unfavorable conditions.
The often recommended ratio is 10 square meters area requires 1 kW of thermal power - quite approximate, not taking into account a number of specific parameters characteristic of a particular room. Therefore, we recommend that readers use a more advanced calculation algorithm, which is taken as the basis for compiling the online calculator located below.
If questions arise during the calculations, the necessary comments are given below.
