How to choose heating radiators: types and characteristics
An important link in any heating system is a radiator, which is installed in each of the heated rooms. It is this device that is responsible for how comfortable living conditions will be created in your apartment or private house. How to choose the right heating battery so that it warms well, looks beautiful and does not "bite" at the price? It is not easy to answer this question right away - it is necessary to take into account many nuances. We will tell you how to avoid basic mistakes.
Radiator compatibility with heating system
The modern assortment of batteries is diverse - cast iron, aluminum, steel, copper, bimetallic devices - it is only important to understand which heating radiators will best "fit" into the specific heating system of your home. What does this mean? This means how much the technical parameters of the heater - the permissible temperature of the coolant, its pressure and composition, as well as heat transfer and inertness correspond to the indicators of your heating system.
A heating radiator not only heats the room, but also carries an aesthetic load in the interior design
When buying a radiator, its appearance, durability, and, of course, the price are also important. It should be borne in mind that there are nuances in the selection of heating batteries for open systems (apartment buildings) and closed systems (individual houses). If the indicators declared by the manufacturer do not correspond to the characteristics of your heating system, then rapid wear and even failure is possible.
Technical specifications
Paying attention primarily to the appearance and cost of the radiator, nevertheless, do not forget that the technical and operational characteristics of the device should be in the foreground.
Not every heating battery, both imported and domestic, will withstand the working conditions in existing domestic heating networks. The centralized heating system, inherited from the Soviet Union, is characterized by fluctuations in pressure and temperature, as well as poor quality of the coolant (water). The design temperature for a single-pipe open domestic system in high-rise buildings is 105 degrees Celsius, the pressure is 10 atmospheres. However, these parameters sometimes go off scale when starting the heating system after the summer period, which leads to water hammer, which some heating devices from foreign manufacturers are not designed for.
It is imperative to pay attention to the permissible temperature and pressure of the coolant in the heating system, which are indicated in the passport of the heater.
Anodized aluminum panel radiators allow operation in pressurized systems and do not require paintwork
Another fundamental parameter for a heating battery is its heat transfer. This characteristic affects the efficiency of heating the air in the room and depends on the material incorporated in the structure. It is well known that the heat transfer of steel is lower than that of aluminum, and copper is better than cast iron in this indicator. But, based on any one technical parameter, it will not be entirely correct. It is necessary to comprehensively evaluate all the pros and cons of each type of heating device in order to opt for the best option.
Types by materials
There are several types of radiators made from different materials. Let's figure out the features of each.
Cast iron
Cast iron batteries have been used in residential heating systems for more than 100 years and, until now, no type of heating devices has surpassed them in terms of corrosion resistance and durability. Possessing high heat transfer, cast-iron "accordions" are perfectly suited for operation in the vastness of the former CIS.
If there is an emergency shutdown of the heat supply, the "cast iron" will keep the accumulated heat in itself for a long time and will continue to heat the air. He is not afraid of critical pressure drops, water hammer and poor quality of the coolant. Hard alkaline water with air locks and rust particles does not have such a destructive effect on cast iron batteries as on other heating devices, and their price is much lower. All the above-mentioned advantages still encourage many of our fellow citizens to purchase these particular radiators as heating devices.
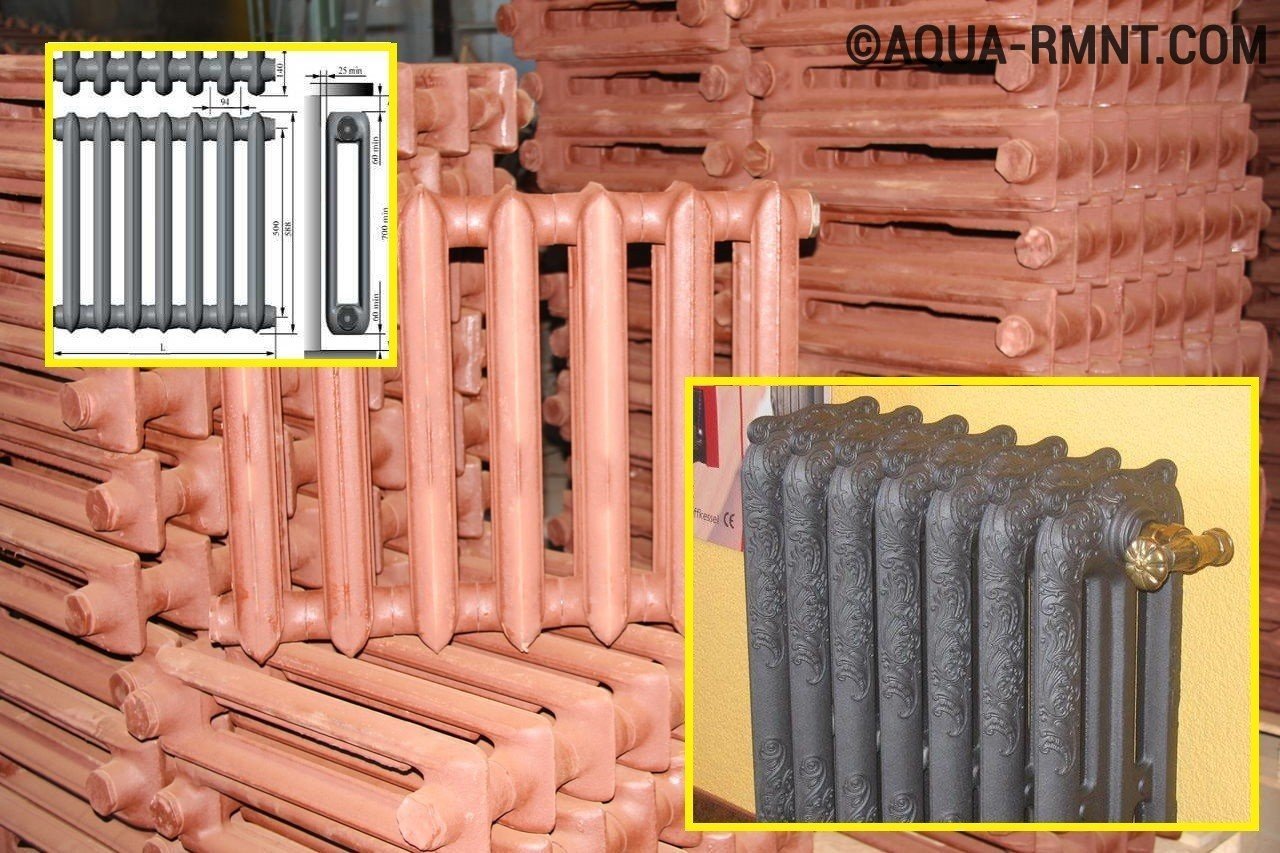
Cast iron heating radiators are not very successful in design, but they have proven themselves well in domestic operating conditions
The disadvantages include inexpressive design, bulkiness and high inertia, due to which they cannot be used in modern heating systems with thermoregulation. Although, recently, exquisite cast-iron radiators in retro style have appeared on the interior gizmos market - with monograms and patinated brass, copper and bronze colors. Such heaters will look perfect in interiors with a classic design style.

Thanks to the modern design, cast-iron radiators have a "second wind" - this is no longer the rough "accordion" that we are used to seeing
Made of aluminum
Aluminum radiators currently occupy a solid position in the heating appliance market. The sectional design, which allows you to select a heating element with the heating efficiency required for the room, raises them to the rank of universal devices for heating apartments and houses. The high heat transfer inherent in aluminum, low weight, aesthetic appearance and ease of installation are the most demanded for the arrangement of individual heating systems.
They are not inertial, which allows them to be used in conjunction with temperature regulators; also, they do not require a large amount of coolant. The disadvantages of this type of heaters are the susceptibility to corrosion at high concentrations of alkali in the water, the possibility of leakage between the sections, the tendency to gas formation inside the heating element.

Excellent heat dissipation and modern design of aluminum radiators make them one of the most popular heating devices among consumers.
Steel
When supplying heat to individual houses and offices, they are often used. These heating devices can be in the form of a tubular structure, a one-piece rectangular or type-setting panel of separate sections. This option is quite suitable for autonomous heating at home, buyers are attracted by affordable prices, neat aesthetic appearance, excellent heat transfer, corrosion resistance and low inertia.

Steel panel radiators combine radiant and convection heat dissipation
Steel radiators cannot withstand pressure increased to 25 atmospheres, so it is better not to use them in heating systems of city apartments. Also, these devices are sensitive to oxygen, which is largely present in district heating systems.

The most successful option for installation in private houses is a steel tubular radiator with good heat dissipation and a striking design.
Steel panel radiators combine two principles of heat transfer - radiation and convection. Heat transfer occurs through the walls and through the grate located at the upper end of the device. Working pressure - from 6 to 16 atmospheres, which depends on the design of the device and the thickness of the steel. The coolant temperature is permissible within 110 degrees.
Bimetallic
Structurally, it consists of a steel pipeline and aluminum fins. Such a battery scheme is optimal when choosing a heating device for operation in the centralized heating systems of our cities. The heat carrier - water, circulates through seamless pipes, welded together in such a way that does not destroy the metal structure - this prevents corrosion of the steel part. Aluminum, on the other hand, has a high thermal conductivity and perfectly transfers heat to the room, taking it from the steel core. It turns out that the bimetallic heating device has combined the best properties of steel and aluminum heating devices. From steel, he took neutrality to corrosion and the composition of the coolant, resistance to pressure drops (withstands up to 40-50 atmospheres), from aluminum - excellent heat transfer and a pleasant design.

The bimetallic radiator combines the positive qualities of a steel and aluminum radiator
Bimetallic heating devices contribute to the distribution of air masses in a turbulent manner - with vortices, which does not lead to local overheating of the air and the formation of a positive ionization field in the heater zone. It is also positive that bimetallic batteries can last about 20 years, are available on sale painted in a variety of colors and do not require regular renewal of the paintwork, such as cast iron.
The saddest thing about bimetallic batteries is their high cost, a tendency to accumulate slag deposits on the inner walls over time, and sensitivity to an increased oxygen content in the coolant. In addition, when two metals are used in the design of radiators, resistance arises at the boundary of their alloy, which reduces the efficiency of heat transfer and heat transfer in general.

The bimetallic heating radiator consists of steel pipes through which the coolant flows, and an aluminum body with high heat transfer
Copper
Copper radiators compare favorably with other options for heating devices in that they are made from a solid-drawn copper pipe without the presence of other metals. Large diameter pipe - about 28 mm, completed with copper fins, and a decorative casing made of solid wood. This option provides effective heating of the room due to the thermal conductivity of copper, which is 2 times higher than that of aluminum and 5-6 times higher than that of steel and cast iron. Possessing low inertia, the copper battery provides quick warming up of the room and allows the use of thermostats. There is little water in such a structure, which contributes to their heating literally within 3 minutes, and this is an important property for autonomous heating systems, since there is no need to heat and drive such large masses of coolant through the pipeline, as, say, in the case of cast-iron radiators.

Copper radiators have the highest heat dissipation and corrosion resistance compared to all other types of heating appliances.
Copper is characterized by ductility, corrosion resistance, high efficiency at low temperatures of the coolant and it is not subject to thinning under the influence of aggressive media, like aluminum, which makes it possible to install copper batteries in apartments of high-rise buildings. It is noteworthy that after 90 hours of operation, an oxide layer forms on the inner surface of the copper radiator, which further protects the heater from chemical and mechanical damage by water with poor composition.
Summing up the comparative characteristics of various types of heating devices, the following main points can be distinguished:
- For a centralized open heating network, present in high-rise buildings, like many years ago, a cast-iron radiator remains the best option. It is resistant to the poor quality water circulating in our pipelines and will last for many years. "Accordion" will withstand pressure drops and water shocks, while effectively heating the air in the room. The low price of this type of heating device makes it quite affordable for everyone. However, the high inertness of cast iron will not allow combining such a radiator with a thermostat.
- A good alternative to a cast iron battery in apartment buildings is a bimetallic one based on steel with aluminum or copper. Steel is tough and corrosion-resistant enough to withstand water hammer and unfavorable water chemistry in the central system, while aluminum or copper compensates for the less than outstanding heat transfer of steel. However, the high cost does not allow us to say that this will be the best option.
- For closed heating systems present in private houses, it is usually easier to choose batteries - there is no overpressure in the heating system, and the water is treated before entering the pipeline. Therefore, the best type of heating device for a home is aluminum. Its price is affordable, the design is good, and the heat dissipation is high. The low inertness of this will allow it to be used in conjunction with a thermoregulation system.
- A good alternative to aluminum batteries in conditions of autonomous heating is steel radiators. Having a lower heat transfer than aluminum, steel heating devices have many advantages - low weight, low inertia, pleasant design, and attractive price.
- Steel and aluminum batteries are produced primed along the inner plane of the heating element to prevent corrosion from an aggressive coolant environment. Scale and rust particles present in the coolant of open heating systems lead to mechanical destruction of the primer layer inside the devices, therefore manufacturers recommend using them in closed heating systems of private houses. A copper radiator can be a good option for open centralized systems, but not everyone will be pleased with its cost.
Video: how to choose heating batteries
Well, if you want to turn a heating battery into an active element of interior decoration, opt for steel tubular heating radiators with a wide range of colors and an abundance of design solutions.
