Weight of a section of bimetallic radiators. Which bimetallic heating radiators are better and stronger - technical characteristics and tips for choosing radiators
Hello Dear blog readers! At all, bimetallic radiators heating appeared a very long time ago. They became popular due to the fact that they coped well with the function of heating the room without special costs from the outside. In our article we will analyze the positive and negative aspects of these radiators. We will also pay attention to the nuances of their installation, technical characteristics and other interesting points that are definitely worth mentioning.
Summary of this article:
Positive aspects of using bimetallic radiators
- It's worth starting with design. Bimetallic radiators tend to fit perfectly into virtually any residential interior. They do not have sharp corners and take up fairly little space. If required, there is always the opportunity to hide them inside the wall.
- These radiators have an excellent service life of approximately 25 years.
- Excellent for all heating systems.
- They withstand pressure very well. Even if in the heating system it rises to 30-40 atmospheres, this will not affect their strength in any way.
- They transfer heat well into the room, which will definitely prevent you from freezing in winter.
- Thanks to a specialized thermostat, you can virtually instantly change the temperature in the room.
- If any breakdown occurs, thanks to good design repairs can be carried out directly on site without the need for dismantling or turning off the water supply.
Disadvantages of bimetallic radiators
These radiators have much fewer disadvantages:
- Due to different expansion coefficient aluminum alloy and steel, over time the radiator may creak when heated.
- If a low-quality coolant is used, the pipes may quickly become clogged.
- Price. It is significantly higher than, for example, analogues made of cast iron/steel/aluminum.

How to calculate the number of radiator sections?
You don't need to be a mathematician to make calculations. The formula is so simple that even people with a humanitarian mindset can handle it.
Before making calculations, find out the exact area of the room. The next step is to find out the production capacity of the radiator.
In order to find out the number of radiator sections (denoted by A), you need to multiply the area of the room (denoted by S) by 100 and divide by the power of the radiator (denoted by P). The diagram looks like this:
A = S×100÷P
For example, if the area of the room is 45 sq.m. and a radiator power of 200 watts we get the following:
A = 45×100÷200
A = 22.5
From this we can conclude that in order to heat a room well at 45 square meters we will need 22-23 radiator sections.
Installation (installation) of bimetallic heating radiators
The complete structure consists of pipes and, directly, the radiator itself. These two components are connected by spot welding. For these reasons, it is better to seek the help of highly qualified specialists who will do the work safely, efficiently and in the shortest possible time.
When installing bimetallic radiators, technicians advise using polypropylene pipes. This greatly simplifies the installation of the latter and minimizes the risk that the pipes may become clogged with unwanted deposits from the inside during operation.
Specifically, what you should know about installation:
- Installation occurs after preparing the workspace, marking and drilling the fasteners for the brackets.
- Install the radiator based on the distance from the floor to the bottom of the radiator. It is advisable to maintain this indicator in the region of 60-120 millimeters. This is done in order to achieve maximum heat transfer.
- Installation should be carried out strictly under the window space.

As for the technical part, you should follow these steps:
- When the markings are finished, holes are drilled for the brackets and secured with dowels and cement mortar.
- Then the radiator is equipped with a Mayevsky valve (it allows you to remove excess air from the system). It is also equipped with fittings and adapters in the place where the radiator connects to the pipes.
- The last steps are to equip the water riser with taps. Then the pipes are installed, which connects the radiator itself and the riser.
As you can see, installing a bimetallic radiator is not a complicated process if you correctly follow the step-by-step instructions.
Connection diagrams are divided into the following types:
- One-sided scheme. IN this option the pipe that supplies water to the radiator is connected to a special pipe, which is located on top of the radiator. In this case, the outlet pipe is mounted from below.
- Bottom diagram. It is used in cases where the heating system is hidden in the floor covering. In this case, the outlet and supply pipes are connected strictly from opposite sides to each other.
- The pattern is diagonal. Very well suited for multi-section radiators. The supply pipe is connected at the top of the radiator, and the outlet pipe at the bottom.
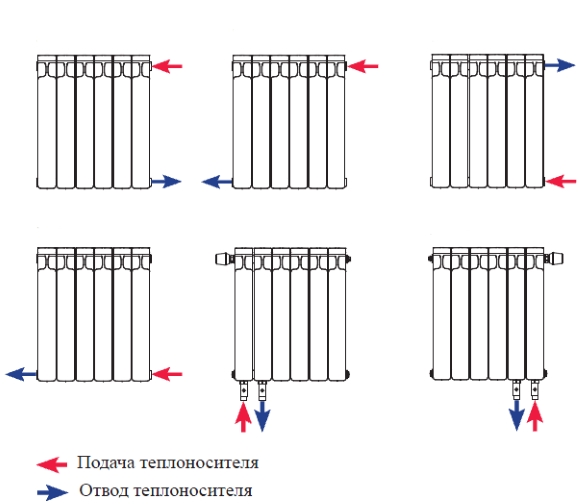
The diagrams, as you can see, sufficient quantity It is up to you to decide which scheme is more applicable to your circumstances.
Which bimetallic heating radiators are better and more durable?
In this part we will compare bimetallic radiators with semi-bimetallic ones. We will also pay attention to which of them is better - sectional or monolithic? This is a very important part, as it will allow you to approach your choice more intelligently and not spend extra money.
So which radiators are better - bimetallic or semi-bimetallic?
These two radiators differ in that in the first the core is welded and filled with aluminum, which prevents corrosion from occurring after some time. Secondly, the core contains two metals (steel and aluminum). Due to the mixture of these metals, although it is more susceptible to corrosion, it has higher heat transfer. As for the price, it is almost the same for both the first and the second.
What to choose? If service life is important to you, then the bimetallic option. If heat transfer is important, then semi-bimetallic. As you can see, everything is extremely simple.
What about the division based on sectional and monolithic characteristics?
Sectional ones differ from monolithic ones in that the former consist of so-called divided sections, while the latter are unified system without joints.

Most experts say that it is definitely worth choosing monolithic options. Monolithic ones win in terms of technical characteristics. They are as follows:
- Service life is about 50 years. For sectionals, this period is about 25 years.
- Withstand pressure up to 100 bar. In sectional ones there is only 25-35 bar (so low, as the section joints may not withstand)
The only thing in which both options are the same is the thermal power, which is equal to 100-200 watts per section.
Naturally, monolithic radiators are more expensive than sectional ones, but based on its advantages, it’s worth it.

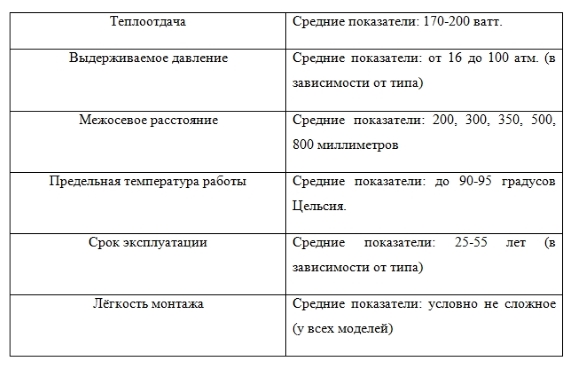
In order not to thoroughly study each manufacturer, we have compiled a table in which we present the average indicators for various signs for bimetallic radiators:
External design of bimetallic heating radiators
If you are concerned about the issue of design, then you should definitely know that each company has a unique design and is not similar to one another. On this moment There are a significant number of different companies producing bimetallic radiators. We will list the largest and most well-known to the average buyer. These are companies such as Sira (Italy), Royal (Italy), Rifar ( Russian Federation), Tenrad (Germany).



As you can see, in some ways they are all similar, but still they are distinguished by various features. Which one to choose is up to you. It all depends on your taste preferences.
What to look for when buying bimetallic radiators?
We figured out various technical characteristics, design and other tips. Now let’s specifically pay attention to what you should pay attention to when buying bimetallic radiators. This is a very important point that will allow you not to buy a low-quality product and not lose money again.
Here's a point-by-point breakdown of what you should pay attention to:
- Battery design. This is very important, since both the complexity of installation and the heat transfer from the radiator in the future depend on the design. Also the ability to add or remove sections.
- Distance between axles. The standard values are 35 and 50 centimeters. If you need more or less, then, naturally, you can find options with various non-standard values. But they are quite difficult to find.
- Exterior design radiator Bimetallic radiators are designed to be attached to straight surfaces. But if you may have any problems during installation (or you just want some non-standard solution), then modern market can offer different non-standard solutions. As a rule, almost every manufacturer will definitely have a couple of these in stock.

- Specifications. This point is clear. We talked about him above. Pay attention to specifications always worth it. After all, it is very easy to make a mistake with the choice and, for example, choose the wrong radiator size in relation to the footage of the heated room. Or make a mistake with the power and not get good heat transfer. Always remember the mathematical formula that we gave.
As practice shows, a bimetallic radiator gives off about the same amount of heat as its cast-iron counterpart. This figure fluctuates around 150-180 watts. This is written in detail in the passport of a particular model. We will again take as an example several of the most famous manufacturers that were discussed above and compile a small table with heat transfer parameters.
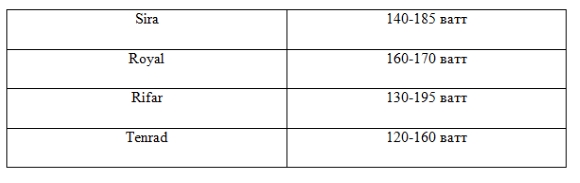
It is definitely worth saying that the higher the indicator, the better the heat transfer will be, so you should always choose models with higher indicators. Frankly speaking, the higher the indicator, the warmer the apartment will be during the heating season.
Which is better – solid or sectional bimetallic radiators?
There is no clear answer to this question. Solid bimetallic radiators consist of a “solid” core wrapped in a shell, while sectional ones, as we already know, consist of numerous sections.
You should buy sectional bimetallic radiators if the following things are important to you:
- High cooling and heating speed.
- Possibility of connecting to heating system with any types of pipes.
- Adjustment of heat transfer power by removing or adding sections.
- Light weight, which is a pleasant feature during installation.
Solid bimetallic radiators should be chosen for the following reasons:
- They can withstand pressure many times greater than sectional ones.
- Less susceptible to corrosion (which occurs during the non-heating season)
- They have greater tightness.
- It is very difficult to cause mechanical damage.
Experts advise choosing solid radiators. This is exactly the case if you are going to carry out installation at home. Sectional ones are well suited for office and other public spaces. At home, strength and service life are important. You don’t want to accidentally flood your neighbors or constantly have to repair your heating system, do you?

At the end of this voluminous article, we will summarize some results. We looked at the positive and negative aspects of bimetallic radiators. We learned how to correctly calculate the number of sections in order to achieve proper heat transfer. We paid attention to the installation and connection diagrams of the latter. Issues of design, size, nuances when choosing and others were not ignored. As you can see from all of the above, the competent choice of bimetallic radiators is another task that should be approached with the utmost rigor. After all, this is one of those things that will make your home comfortable even in the coldest months and therefore you should not neglect all the tips that we have listed. If you follow everything that has been said, it will bring joy and save your family’s budget for many decades. Stay warm!
You probably remember that with all your positive qualities These devices have a number of significant disadvantages that do not allow them to be fully used in city apartments. Now we will talk about their bimetallic analogs, which will help overcome all technical limitations when installing in multi-story buildings. residential buildings connected to public heating networks.
Construction of bimetallic radiators
A bimetallic radiator looks the same as an aluminum one. This is understandable: its outer body is made of the same metal and painted with the same paint. You can distinguish it only by its weight - this already affects internal structure a device inside which there are steel inserts that protect aluminum from direct contact with the coolant. It is thanks to them that the battery sections are not subject to the destructive effects of various impurities that are transferred along with the coolant in the utility network. In addition, steel is much more resistant to acids and alkalis, which are also rich in urban heating systems, and does not interact with copper pipes and heat exchangers.
The use of a steel core for the passage of coolant provides other useful characteristics bimetallic radiators:
- Strength. The maximum pressure that a bimetallic radiator housing can withstand is 30-40 atmospheres. Such a device is not afraid of any water hammer;
- Economical. Narrowing the coolant supply channels makes it possible to achieve optimal combination energy consumption for heating and thermal inertia of the radiator;
- Durability. The resistance of steel internal cavities to corrosion and destruction allows manufacturers to set a long service life for their products - on average up to 20 years.
If we add here the advantages inherited from aluminum models, such as high heat dissipation, elegant appearance and compact dimensions, we can definitely say that bimetallic radiators are best choice for heating a city apartment today.
Dimensions
To select a bimetallic radiator great importance have it dimensions. Typically, heating devices are installed under the window in order to create thermal curtain cold air passing through the glazing. The radiator must fit into the existing niche and provide required characteristics by heat transfer.
The heights have standard values. Devices are available with center distances of 200, 350 and 500 mm. Typically these numbers are contained in the model name.
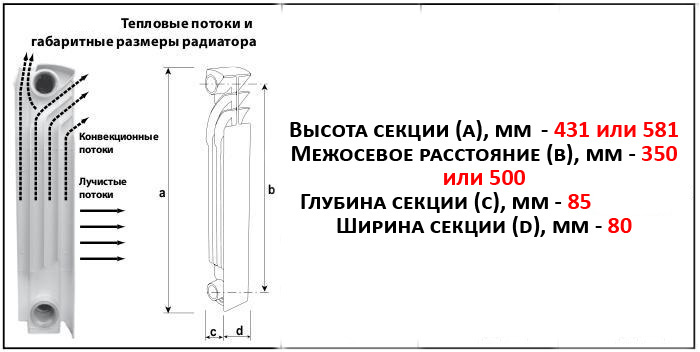
However, it should be kept in mind that center distance- is not full height housing, but only the length of the segment between the centers of the input and output manifolds. The actual height of the device can be obtained by adding 80 mm to the center distance.
So, for example, a radiator marked 350 will take approximately 430 mm, and a 500 model will take approximately 580 mm.
It must be kept in mind that technical standards provide a distance of at least 100 mm from the device body to the window sill and at least 60 mm from the body to the floor.
The width of the battery depends on the number of sections, which is determined by calculation. We'll talk about this in the next section.
Radiator calculation
Determining the number of sections for all types of radiators is carried out the same way.
Technical requirements for heating houses in middle lane In Russia, the power required to heat 1 m 2 of area is determined to be approximately 1 kW.
For each battery, the manufacturer usually indicates the power value of one section. Sometimes this parameter is called a little differently - section heat transfer. Knowing the power, the number of sections can be calculated using the formula:
where N is the required quantity, S is the area of the room, Q is the power of one section.
The standard section width of most models of bimetallic radiators is 80 mm, the heat transfer of a regular 500 mm section is about 180 W. Thus, if our room, for example, has an area of 20 m2, then to heat it we will need 12 sections, and the width of such a radiator will be about 1 m.
Design features
As we have already said, the difference between a bimetallic radiator and an aluminum one is that steel inserts are laid along its inner surface, protecting the case material from corrosion.
Steel tabs can be installed in different parts of the radiator:

Section capacity and connection dimensions
Due to the presence of steel inserts inside the bimetallic radiator, its section capacity is even less than that of an aluminum one. On the one hand, this is good, and we have already noted that the better small sizes sections are a reduction required quantity coolant and thermal inertia, and as a result - comfort in operation and energy savings. But we must not forget that too narrow channels can become clogged with debris and sludge, which are inevitably present in modern heating networks.
The width of the channel depends on the thickness of the walls of the steel insert. The thicker the walls, the better characteristics strength and durability of the radiator, but thus the channels for the coolant.
A good bimetallic radiator has wall-thick steel inserts water pipe. In this case, the section capacity depends on the center distance:
- For a battery with a distance of 200 mm - 0.1-0.16 l;
- For 350 mm batteries - 0.15-0.2 l;
- For 500 mm - 0.2-0.3 l.
As we can see, the coolant volume of such radiators is really small. For example, the popular 10-section RIFAR heater with a height of 350 mm holds only 1.6 liters. At the same time, it is capable of heating an area of up to 14 m2, and its width is 80 cm. However, it will weigh 14 kg. This just means that the radiator is bimetallic - they are usually 1.5-2 times heavier than aluminum ones.
Most bimetallic radiators are sold in one section. This is convenient because you can buy exactly as many sections as you need to provide the required power. Each section has two inlets and two outlets with an internal diameter of ¾ or 1 inch, depending on the model. For ease of assembly, two of them have a right-hand thread, and two have a left-hand thread.
It makes sense to install a bimetallic radiator only in city apartment. If you have a private house and your own heating boiler, it is better to buy an aluminum battery.
When choosing a bimetallic radiator with the desired heat dissipation, it is recommended to take into account the following characteristics:
- Operating pressure. It usually does not exceed 15 atmospheres. The radiator must withstand such a load;
- Power. It is necessary to calculate the number of sections using the above method;
- Dimensions. The width of the radiator is determined by the number of sections, and the height is determined by the center distance. For standard window sills with a height of 80 cm, the 500th model is suitable, but if it does not fit, you need to take the 350th modification;
- Thickness of steel tabs. Make sure it is not too small. An indirect indicator of the thickness of the tabs is the weight of the device;
- Price. Typically, bimetallic radiators cost at least 15-20% more than aluminum ones.
If you do everything correctly and choose a suitable radiator, there will be no shortage of heat in your home even in severe frosts.
The name “bimetallic” speaks for itself; the term means that the structure consists of two different metals. Technical characteristics of bimetallic heating radiators include various parameters: operating pressure, heat transfer, center distance, weight, overall dimensions, number of sections, Maximum temperature coolant.
In addition, to connect the radiator to existing system heating will require various adapter couplings, a head (thermostatic regulator) and other elements that are not included in the basic package.
Types of heating radiators
There are 2 basic types of design: "bimetallic" And "semi-bimetallic". In the first case, the core (i.e., the tubes with heating water inside the battery) is made of copper or steel, and the outer fins (the outer surface of individual sections of the radiator) are made of aluminum. The peculiarity of this type is that aluminum does not come into contact with water at all. Copper is practically not subject to corrosion, holds pressure well, but such products are not cheap. Structures with steel cores (that's all internal pipes) are still more suitable in price for the average family.

Different types of radiators
The difference between “semi-bimetallic” radiators is that only the vertical channels are made of steel, and in the horizontal sections the water still comes into contact with aluminum.
What do you need to know?
The main technical characteristics of bimetallic radiators are operating pressure and heat transfer. The first term means how much water pressure the structure can withstand. Pressure is marked either in atmospheres (1 atm = 10 kg/cm 2) or in megapascals (1 MPa = 10 atm). As a rule, in external heat supply networks the pressure does not exceed 14 atmospheres, and manufacturers provide a design margin in this regard.
Other important characteristic Radiators are heat output, which is measured in watts (W). It depends on two factors: design features and coolant temperature. Moreover, the last characteristic directly depends on the type of heating: when autonomous heating You can set the temperature fixedly, but with a stationary temperature everything is not so simple.
dimensions
Center distance is the size (in mm) between the lower and upper collectors (in other words, between the inlet and outlet holes in the radiator for coolant). It varies from 200 to 800 mm, and the distance from the radiator to the window and floor must be at least 150 mm.
Note!
The length of the battery directly depends on the number of sections, which, in turn, is related to heat transfer and the size of the heated room.
In principle, anyone who is familiar with the basics of heating engineering can decide on the size of the radiator himself, but it is still better to contact a specialist who will be more qualified to take into account all the factors.

Radiator section
Bimetallic and semi-bimetallic radiators
When comparing these types, a completely natural question arises: “Which bimetallic heating radiator should I choose?” In the “pure” bimetallic version, the main advantage is that the coolant does not come into direct contact with the aluminum, but flows through metal or copper tubes inside the structure.
In the semi-bimetallic version, as noted above, the steel cores are located only in the vertical channels, and the horizontal jumpers are made of aluminum (the chemical activity of which in contact with heating water is much higher than that of steel or copper).
Some technical nuances
Bimetallic radiators have a solid steel core, which affects operational reliability in positive side. In the semi-bimetallic version, in addition to the fact that aluminum is in direct contact with the coolant, there are numerous connections from dissimilar materials, which does not add any durability to it.
Another nuance is the wall thickness of the steel tubes. The thicker the wall, the lower the coolant consumption and the greater the durability. But with a thick wall, the internal diameter is smaller, which, if the water is “clean” (especially in central heating systems), can lead to clogging of the pipes.
Radiator design
Manufacturers of heating radiators
Nowadays there is a huge range of products on the market, but still a short rating of manufacturers will not be superfluous. Several companies represent Italy (RADIATORI, SIRA, ROYAL, GRANDINI, GLOBAL) and Spain (MIRADO, ESPERADO). Germany (OASIS) and Norway (LEBERG) did not stand aside either. Products from this part of the world have one thing in common - European quality.
Other regions of the world are not lagging behind Europe. These are Chinese companies (BILUX, KONNER, GORDI). CIS countries are also represented on the market: Russia (RIFAR, SANTEKHPROM BM), Ukraine (ELEGANCE), Belarus (ALTERMO).
About non-European manufacturers
The fact that a product is not made in Europe does not mean that the quality suffers. As a rule, products are manufactured using imported equipment; often the assets of manufacturing firms have a share of foreign capital; these can even be joint ventures ( joint ventures). And the price is usually lower than European goods.
A few words about Chinese products. Many people have a stereotype that the Celestial Empire can only produce one-time crafts. This is not entirely true. China is capable of producing high-tech, reliable products that are also in demand in developed countries. It’s just that Chinese goods need to be purchased in serious retail networks who do not need unnecessary complaints.

Bimetallic radiator in the room
Bimetallic heating radiatorsWhat are bimetallic batteries
When choosing a heating radiator, two criteria come to the fore: heat transfer and strength. For a long time The most popular were cast iron and aluminum batteries.
But each had significant shortcomings:
- cast iron - characterized by a low heat transfer coefficient and difficulty in installation;
- aluminum models, although they demonstrate high heat transfer, have low strength (sensitive to pressure changes and chemical composition coolant).
Bimetallic heating radiators allow you to combine the advantages of cast iron and aluminum batteries in one unit, while eliminating their disadvantages. The principle of the design of these batteries follows from the very name “bimetallic” - consisting of two metals. The upper part is made of aluminum, which provides high heat transfer, and its base is a steel pipe, which is easily mounted on supply pipes, and is not inferior to cast iron in strength properties.
Bimetallic batteries: types and their features
Bimetallic radiators come in two main types: fully bimetallic and assembled.
- In the first version of the device, only the outer casing is made of aluminum, and all internal cavities that come into contact with the coolant are made of of stainless steel.
- Bimetal-assembled batteries have only steel vertical pipes, and the collectors are made of aluminum and are integral with the body.
The first type is characterized by greater strength and lower price, and the second by a higher heat transfer coefficient.
In the production of these devices, rather complex technologies are used - injection molding and spot welding. This predetermined a rather high cost, so in terms of price they surpassed not only their cast iron counterparts, but also their aluminum counterparts.
Heating radiators bimetallic technical characteristics
Bimetallic radiators can increasingly be found in apartments, country houses And government institutions. Great popularity of the device of this type associated with its technical characteristics:
- corrosion resistance and immunity to the chemical composition of the coolant (this parameter is ensured by the presence of high-alloy stainless steel in the design);
- high heat transfer coefficient (the aluminum part of the device is responsible for this parameter);
- long period of operation (in this parameter they are comparable to cast iron batteries);
- ease of installation (relative to cast iron analogues);
- withstand coolant temperatures of up to 90 degrees and pressures of over 15 atmospheres, which allows you to quickly warm up a private home when connected to a high-temperature boiler.
When choosing devices such as bimetallic heating radiators, the technical characteristics of heat transfer prevail over the rest. However, this parameter depends not only on the thermal conductivity of the metal, but also on the temperature of the coolant. Bimetallic heating batteries may consist of different quantities sections, the number of which must be even. Prefabricated design allows you to choose required device for a room of any size, guaranteeing a normal temperature in the room.
Each radiator has quite impressive dimensions, which makes it noticeable in the room. Old cast iron radiators did not have high aesthetic properties and spoiled the interior of the room, except for some designer models with considerable cost. But this does not apply to bimetallic models. An important characteristic of these devices is their visual appeal, which allows them to fit seamlessly into any interior.
Bimetallic radiators can have different characteristics; they largely depend on the manufacturer and are indicated in the device passport. To make the right choice, you need to consider several companies that are considered leaders in Russian market- Rifar, Atm and Global.
Rifar
The model of the famous Russian company RIFAR is different good quality assembly and full bimetal, which allows it to withstand coolant temperatures of up to 135 degrees and pressures of up to 20 atm.
A special feature of this company is the production of batteries “with a radius of curvature” (curved shape).
ATM
The main advantage of Italian Atm radiators is good heat transfer, which is achieved due to the larger battery area. In addition, the manufacturer claims that they are created not using spot welding, but by injection molding, which makes them noticeably stronger than competitors.
The main advantages of ATM-Bi include the following qualities:
- in Italian stylish design;
- optimal price for maximum quality and performance;
- high-tech alloys provide strength;
- method of casting sections.
Global
Italian radiators Global also belong to fully bimetallic models and can withstand temperatures and coolant pressure similar to RIFAR. The advantage is their impeccable design and build quality.
In fact, the choice among these three models is limited only by price, since they are very similar in characteristics.
Installation Features
The lightness of bimetallic batteries and the ability to quickly connect them to a pipe were the reasons for the spread of reviews that they were very easy to install. And this is really true, especially if you compare them in this aspect with Soviet cast iron ones. However, there are some nuances in installing bimetallic radiators:
- must be installed strictly horizontally on brackets mounted into the wall;
- necessary correct installation a valve that allows you to automatically or manually (depending on the model) release the air accumulated in the radiator;
- special filters must be installed in front of the air release valve to prevent its contamination;
- the connection can occur via a lower diagonal or side pattern, so it is important to first determine the type of connection.
To connect a bimetallic radiator with your own hands, you need to carefully study the instructions that come with the kit. Each manufacturer recommends its own installation parameters, in particular, the position relative to the floor of the window and wall. Compliance with the manufacturer's rules will allow you to use the device with maximum efficiency, providing the house with heat even in the most cold winter.
In order to independently mount a bimetallic heating radiator, it is important to calculate the required power. For this purpose, professional installers use the formula: N= S*100/P, where N is the number of sections to be calculated, S is the area of the room, and P is the power of one section.
For example, for a room of 30 sq.m. you will need a radiator consisting of 16 sections, each with a power of 180 W. When calculating power, it must be taken into account that the required number of sections must be determined for each room separately. The power can be found in the passport.
To ensure uniform heating of the room, more than one battery can be used. This approach will be preferable in rooms large area(more than 25 sq. m.). And in small kitchen One is enough.
It is worth clarifying that when deriving this formula, a ceiling height of 3 meters was used, so in houses where the ceilings are much lower, it is necessary to make adjustments downwards.
For each individual room of a private house, when calculating, it is worth taking into account the number of windows and the quality of glazing. It is necessary to install a separate radiator under each window sill, so the number of sections calculated for the area of the room must be divided by the number window openings.
To make the calculation as accurate as possible, factors affecting the heat transfer of the room (coefficients K1-K4) should be taken into account. This includes:
- number of double-glazed windows (double is the norm, so the coefficient is 1; single - 1.27; triple - 0.85);
- quality of wall insulation (the coefficient is taken as when calculating with windows: quality is defined as average - it is brick or insulation, bad - there is no finishing, normal - modern insulation) and the number of external ones (one - 1.1; two - 1.2, etc.);
- minimum temperature on the street in winter period(per unit is taken - minus 15, for every +/- 5 degrees 0.1 is added or subtracted);
- the ratio of the area occupied by windows in the room to the total (the floor area is taken for calculation, the norm (1) is 30%, for every 10% 0.1 is added or subtracted).
The calculation can be carried out using the above formula, but taking into account multiplication by each of the coefficients. For example: N= S*100/P*0.85*085*1.1 (three-chamber windows, excellent insulation and one outer wall). Accurate calculation is very important as a means of saving, since excess heat goes outside.
Bottom line
At making the right choice and installation bimetallic battery the buyer receives a reliable and efficient device that will uninterruptedly heat the apartment for many years.
Many residents multi-storey buildings They look with interest at bimetallic heating radiators. Heavy cast iron batteries are becoming less popular, and aluminum products are not very suitable for apartment buildings due to pressure changes. Bimetallic batteries do not have many of the disadvantages of their competitors, while having undoubted advantages.
Positive traits
The advantages of bimetallic products include:
- Excellent aesthetic qualities - such batteries go well with any interior design without taking up too much space.
- The dimensions of the device are varied, and its body can be painted in any color (and you can apply the paint after purchasing the radiator).
- Safety - radiators do not have sharp corners or overly hot surfaces, which makes it possible to place them in children's rooms.
- The duration of operation can reach up to a quarter of a century.
- Unlike aluminum, bimetal is optimal for urban systems central heating, where the thermal fluid has a bad effect on the batteries, reducing their service life. Bimetallic surfaces are adapted for highly acidic environments and low-quality coolants due to their anti-corrosion properties.
- Bimetals are durable and highly reliable even at very high system pressures.
- High thermal energy output is one of the main advantages of bimetallic radiators.
- Due to the small cross-section of the channels in the battery, adjustment temperature regime The thermostat does this very quickly. This efficiency makes it possible to halve the volume of the working thermal fluid.
- If in any section there is a need to conduct repair work, they are easy to implement due to the well-thought-out arrangement of nipples on the radiator.
- The number of battery sections needed for heating can be easily calculated, which allows you to save both when purchasing and installing the device.
Flaws
Bimetal also has a number of disadvantages:
- Such radiators are adapted to work with low-quality coolant, but at the same time their lifespan is significantly reduced.
- The main disadvantage of bimetal is the different expansion coefficient of steel and aluminum (or rather its alloy). After a few years, squeaking and deterioration in battery strength may occur.
- If the coolant is of low quality, after some time the metal tubes will begin to clog, which will lead to a decrease in the level of thermal output.
- The high cost of bimetallic batteries is a controversial drawback, since the money spent is recouped by higher consumer qualities than those of cast iron and aluminum competitors.
Design features
The body of such heaters is ribbed and made of aluminum alloy. This alloy is characterized by excellent heat transfer. In addition, the use of aluminum seriously reduces the weight of the device.
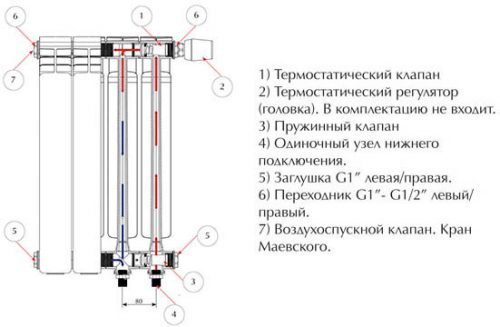
Located inside the case heating circuit made from copper or steel tubes. The core is made of very durable metal, so the battery can cope even with very high pressure: 20-40 atmospheres is a standard indicator, but in some cases resistance to hundreds of atmospheres is possible. The coolant temperature can reach 110-150 degrees. More precise information about technical parameters can be obtained from the technical data sheet of the radiator.
What to prefer: multi-section or solid battery?
Most heaters are sectional. There is always an even number of sections. Components produced at the factory are combined into a single whole. Intersectional joints are sealed with sealed gaskets on the nipples.

The one-piece design is attractive in its ability to withstand extreme pressure levels - up to hundreds of atmospheres. This strength is due to the presence of a monolithic steel core, which is stronger than a sectional one. Steel pipes have an aluminum coating. One-piece structures are not as common as sectional ones because they are more expensive.

When choosing a model, you should proceed from the needs for working pressure. If serious water hammers occur in the network, you need to opt for a monolithic device.
Selecting a radiator based on its strength and reliability
Among bimetallic models there are two types of batteries:
- entirely made of steel frame;
- radiators in which only the channels for hot coolant are reinforced with steel.
An all-steel frame is more reliable because the hot coolant in it does not come into contact with the aluminum alloy, which prevents corrosion processes. There will be no leaks in such a radiator.
Note! The cost of the battery will be higher, the greater its weight.
There are several well-known manufacturers producing batteries based on a steel frame. Here are the most famous of them:
- Global Style (Italy);
- Royal Thermo BiLiner (Italy);
- Santekhprom BM (Russia);
- Rifar (Russia).
In models with partially steel frame(semi-bimetallic radiators) higher heat transfer. And they cost about 20% less.
Among the most popular manufacturers of semi-bimetallic models are:
- Rifar (Russia);
- Sira (Italy);
- Gordi (China).
It cannot be said that there are manufacturers that are head and shoulders above others in the quality of their products, just as it would be incorrect to say that someone makes very bad radiators. The product has the necessary certificates, so with rare exceptions there is no defect at all. However, between different price categories still there are differences.
Cheaper models are characterized by:
- simpler design;
- lower metal content;
- painting is done with cheaper material.
Thus, there are differences, but they are not critical. Yes, cheap models are not so beautiful; in some places they are used less quality material, but they will perform their task - to heat the room - properly.
Below are models from the most popular manufacturers.
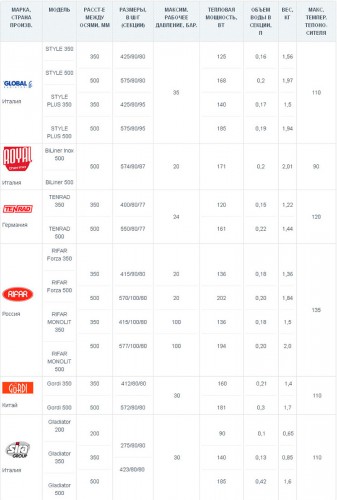
Center distance
In terms of such an indicator as the distance between the axes, radiators can vary significantly. Usually this figure is 35 or 50 centimeters, but there are models with atypical parameters. If for heating purposes batteries of minimal or maximum size, you need to take into account the following nuances:
- BiLUX, Sira and Rifar products have a minimum center distance (about 20 centimeters);
- The maximum center-to-axle distance (approximately 80 centimeters) can be offered by Sira radiators.
It is worth noting Russian company Rifar, which produces model line Monolith with solid steel cores. This manufacturer also has a FLEX line, where the buyer can receive a model with the curves that he orders.
Radiator heat output
One section of a bimetallic battery has approximately the same heat transfer as a cast iron one. In numbers - 150-190 W. More precise parameters can be found by reading the data sheet.
Calculation of the required number of sections
Power indicators can range from 160 W to 2.4 kW. The radiator is selected depending on the area of the heated room. Accordingly, the number of radiators depends on the heat needs. Here you can choose two options: either entrust the calculations to professionals, or perform them yourself.
If you decide to do the calculations yourself, minor errors are possible, but they are unlikely to be critical. The technique is not complicated. To calculate, you will need knowledge of certain standard parameters. First of all, we are talking about thermal power (W), which is necessary to warm up a square meter of a specific room where the battery will be installed. Below we will look at three situations:
- The room has a window and a wall bordering the street. Ceiling height is 2.5-2.7 meters. To heat one square meter you will need 100 W.
- The room has one window and two walls bordering the street. The ceiling height is the same as in the first example. Here you will need 120 W per square meter.
- The room has two windows and two walls bordering the street. The ceiling height is the same as in the first two cases. You will need 130 W per square meter.
- We multiply the power data by the area of the room and get the thermal power of the entire radiator. This is a general indicator of the power for heating a room. If in the building high ceilings, we use a coefficient of 1.1. This is an altitude correction.
- The characteristics of bimetallic heating radiators can be found in the data sheet. From there we take the indicator of the thermal power of a separate section. If such information is not in the data sheet, look for this parameter on the official website of the equipment manufacturer. We divide the result obtained above by the data on the thermal power of one section, and we obtain the number of required sections.
Note! If the selected model has an even number of sections, and the problem has an odd answer, it is better to round the number of sections up in order to have a power reserve. Moreover, if we are talking about sectional battery, individual stores remove or add by order of the buyer required quantity sections.
Calculation example:
We have a room with one door and a wall facing the street. Ceiling height is 3 meters. The area of the room is 20 square meters.
We calculate the total thermal power necessary to warm up a given room. For this purpose, we multiply the area (20 square meters) by the standard value (100 watts) and by the height correction factor - 1.1 (since the ceiling height in our case is higher than the standard).
100 x 20 x 1.1 = 2200 (watts).
We look at the technical data sheet of the battery and find out that each section has a thermal power of 200 W.
2200 / 200 = 11 (units).
In our case, 11 sections are needed. If the calculations do not yield a whole number, round the result up. So, calculating the required number of sections is very simple and anyone can handle it.
