How much area is heated by one section of a bimetallic radiator? How to calculate the number of sections of bimetallic heating radiators for a home
The heating equipment market today provides a wide range of different radiators, including cast iron, aluminum, bimetallic and stamped steel radiators.
Click image for a larger view
Required power of heating devices
When we are faced with the choice of which radiators to choose, then willy-nilly we have to study their features, i.e. advantages and disadvantages different designs. Usually choose from four main positions:
- Cast iron radiators, as you know, give off heat well and are used for a long time (up to 35 years, and sometimes more); do not corrode; can withstand increased pressure in the system, but are heavy and not particularly aesthetically pleasing.
- Aluminum radiators attract very high heat transfer, as well as light weight and elegant appearance, but they are expensive and not very good in terms of resistance to high pressure in the heating system.
- Bimetallic radiators, which combine in their design the advantages of both, and are made from a steel pipe for the coolant, capable of withstanding, if necessary high pressures having aluminium case, perfectly dissipates heat.
- Steel radiators, made from high-quality cold-rolled steel, due to which they have sufficiently high heat transfer and strength, consist of several flat panels for the coolant.
To optimally heat a room, you need to know the answer to the question not only about which radiators to choose, but also make the correct calculation.
We must not forget that over time, the heat-transfer properties of radiators gradually decrease. By installing more powerful radiators, we reduce the load on the heating boiler or boiler. Therefore, most often, when making a calculation bimetallic radiators, purchase radiators with the number of sections one or two more than the number of previous ones cast iron batteries, if any have been installed.

If you need to calculate bimetallic radiators for a room yourself, you must proceed from the heat-transfer properties of each section
If you need to make an approximate calculation of bimetallic radiators for a new room or house, we proceed from the heat transfer characteristics of each section. This parameter must be indicated in the technical data sheet for radiators. In usual practice, they often take the same 100 W per section and 50-100 W per 1 sq.m., so that a certain reserve is obtained, i.e. the number of sections is actually equal to the number square meters area of each room.
Which is better: a warm and large radiator or a hot but small one?
- If we install batteries not big size, then we will have to increase the heat transfer by increasing the temperature of the coolant. This option is called high-temperature heating.
- You can install large radiators taking into account a certain heat transfer. Means more low temperature on their surface. This option called called low temperature heating. Obviously, it attracts with greater security, and you can save money.
If we choose high-temperature heating, the radiators in the house will be so hot that it will be almost impossible to touch them. This option is bad in that it is dangerous due to overheating of the water, but it is also not economical - there is no reserve for regulation. In addition, when high temperatures The surrounding dust deposited on the batteries may begin to decompose, which does not at all contribute to the improvement of the surrounding air.
This means that we conclude that the high-temperature type of heating is not very suitable for residential premises.
Radiator selection and calculation

In practice, as a rule, they take 100 watts per section, and 50-100 watts per 1 sq. meter, so that the calculation of bimetallic heating batteries is calculated with some margin
So, we chose the low-temperature option for heating the house as the more optimal one. In this case, our radiators heat up and release heat into the space, but they are warm, not super hot. And here you need to calculate the correct area of the radiators to make it both safe and comfortable.
In order to roughly calculate the number of radiators we need to heat a specific area of the room, be it a living room, a kitchen or a bedroom, as well as the entire house as a whole, we must first determine the volume of a particular room. To do this, the length of the room is multiplied by its width and height.
The required amount of thermal energy for optimal heating of a room depends on its type. If you take a standard room in panel house, then per 1 cu. m is required according to the average standard of 0.041 kW.
The heating level depends on the efficiency of insulation of a particular room. That is, it depends on what the house is made of, what the thermal insulation is, whether it has plastic windows and insulated doors. Depending on this, the level of thermal energy per 1 cubic meter. m can be reduced to 0.034 kW. If we are talking about new houses built according to modern technologies thermal insulation and taking into account the latest building codes, it is possible to reduce the required thermal power per 1 cubic meter almost doubled - up to 0.02 kW.
After performing preliminary calculations of heating radiators, select the brand and type of batteries. Each radiator has its own characteristics. And one of the most important is the nominal heat flow. This unit is designated by the symbols Q nom., [kW]. Usually this characteristic indicated in the catalog for a separate radiator section (sometimes for several).
If this information is not available in catalogs, check with sellers. Only after understanding the parameters of your room and choosing the type of radiator that suits you, begin to calculate the number of sections needed for your home.
Calculation of the number of sections

Accurate calculation of bimetallic radiators is considered quite difficult. Known formulas for calculations must contain many variables. It is mandatory to take into account the height of the ceiling and the thermal insulation qualities of plastic or wooden windows. It’s no secret that up to 70% of heat can escape through windows alone!
The number of sections is indicated by the symbol S (pieces). This is exactly the parameter we need. It is determined by the formula:
S = (V Q pom) / Q nom [pieces],
where V – denotes the volume of a given room;
Q pom – the amount of thermal energy, depending on the specific parameters of the room;
Q nom – nominal heat flow of the battery.
Round the result you received to whole numbers (upwards). So, if the result is S = 9.3, round it to exactly 10.0.
It now remains to resolve the issue of the number of radiators in the room. Do you need a device with one 10-cell battery, or would it be better to install two 5-cell batteries?
It depends on the area of the room. The room is more than 25 sq. It is optimal to use several radiators. The fact is that this is more favorable for air circulation. In addition, the heating of the room will be more uniform.
If you have chosen a stamped steel radiator, then you need to take into account its dimensions and, of course, the nominal heat flow (the numbers must be indicated in the catalog).
It should be understood that the method we have given for calculating radiators is quite simplified. It uses average numbers and coefficients. Such calculations are used in standard situations, when radiators are installed in a typical apartment or individual house with central heating, where a number of conditions are met. These include ceiling height (no more than 3 m); and the temperature (coolant) in the system should not be more than 70 degrees. WITH.
Possible errors and nuances
If the ceiling height is higher than 3 m, the thermal power should be increased in proportion to the increase in this parameter. If the ceilings of the room, on the contrary, are smaller, the amount of required thermal power will decrease.
If the house has plastic windows with fairly low heat loss, the thermal power can be reduced in the range of 10-20%.
If the coolant temperature is far from 70 degrees. C, the output power changes by 15-18% for every 10 degrees decrease/increase in temperature.
So, if the temperature of the liquid in the batteries (coolant) is about 50 degrees. C, the power must be increased by 1.5 times.
If there are two windows in the room, it would be better to install a couple of sections - one under each window - as for the total thermal power, it should be 1.7 times higher than the nominal one.
What to pay attention to
If you need a more accurate calculation, it makes sense to turn to specialized literature for information, where heating radiators are discussed in more detail and in depth. For more accurate calculations, you will need to take into account such quantities as indoor and outdoor temperatures; composition and temperature of the coolant; probable heat loss; thermal conductivity different materials and many other parameters.
If your time is valuable to you, the best way out will give you a calculation of heating radiators qualified specialists in thermal engineering. Then they will not only accurately calculate the number of required radiator sections for your room or home, but will also install the most suitable radiator for your living space.


Warmth in the room, especially in winter time necessary. And this problem is solved, including by bimetallic heating radiators.
Today the market is saturated heating equipment, and radiators act as leaders on it. Among the huge number of cast iron, steel and aluminum batteries, bimetallic radiators have found their niche and rightfully occupy it.
This is completely justified. They have a large margin of safety and provide full heating. Their operating pressure reaches 30 atmospheres, and this is not the limit. In addition, they have an attractive appearance.
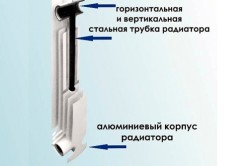
They combine the main advantages aluminum radiators and strength characteristics of steel.
A bimetallic radiator is heating device, having a body made of aluminum and steel pipe with coolant moving through it.
How to do the calculations correctly?
There are ways to determine how many sections there should be on a bimetal heating radiator in order for there to be enough heat.
In one of them, the number of radiators is calculated based on the area of the room.
The area (S) is multiplied by the heating power of 1 m² of room (P room) and divided by the power of 1 radiator section (P nom.). The result obtained, rounded to a whole number, is the desired figure.
Each manufacturer uses its own heat transfer indicators. In our case, the value of P pom. will correspond to 50-100 W. The figure is taken from practice, averaged.
This method allows you to make calculations in standard rooms with one window, door, external wall and a ceiling with a maximum height of 3 m.
If the room is corner or end, coefficients with dimensions of 1.1-1.3 are applied.
Another method uses volumetric indicators.
- The volume of the room is calculated (height, width and length are multiplied).
- The brand and type of bimetallic heating radiator is determined.
- The formula calculates the required number
N = V x Q room / Q nom.,
where N is the number of sections in pieces,
Q nom. — heat flow of 1 radiator section, nominal,
Q room — thermal energy required to heat 1m³
standard room,
V is the volume of the heated room.
Q room - the indicator has different sizes and depends on the type of room. In practice, for convenience, they operate with values from 39 to 41 W.
Q nom. — information is contained in the technical data sheet of the product, and only the power of 1 section is indicated.
The resulting result is rounded up to the nearest whole number.
This calculation is simplified. It uses averages. It is applicable to standard rooms with central heating and compliance with certain conditions, such as a coolant temperature not exceeding 70 ° C, a ceiling height of up to 3 m.
What do you need to know when making calculations?
- The power range of standard bimetallic sections is about 120-220 W.
- It is necessary to take into account accidents, for which heat reserves should be increased by 25%. The methods do not matter: either due to the number of sections, or due to their power.
- To regulate the temperature in the rooms, bimetallic radiators should be installed special means(additional taps).
- For a room area of 25 m² or more, it is advisable to install several radiators with fewer sections instead of 1 long heating radiator.
This will improve air circulation, ensure a more uniform flow of heat into the room, and reduce the likelihood of leaks.
- High-quality insulation will make the calculation more accurate.
- An increase or decrease in ceiling height leads to a change in the required amount of thermal energy in appropriate proportions.
- Plastic windows reduce thermal output by up to 20%.
- Fluctuations in coolant temperature from the base 70°C change the output power in the ratio of 18% to 10°C.
- If there are several windows, it is advisable to place each section of the heating radiator under the window. The total thermal energy of bimetallic radiators should be 1.5 times greater than the nominal one.
To accurately calculate the number of sections of a bimetallic heating radiator, a huge number of variables are required. Here are the height of the ceilings, the presence of windows, the type of double-glazed windows, the temperature inside and outside the room, the coolant, the number of external walls, their thermal insulation properties, thermal conductivity of materials and much more.
It's difficult, but possible. You only need special literature or the services of a professional.
It's time to change the batteries.
Comfort during the cold season depends on calculations of the number of nodes.
How to make all the calculations and measurements correctly?
Everything is quite simple if you follow the instructions below.
Before purchasing heating batteries, we will consider ways to calculate the number of their elements.
The first method is based on the area of the room. Construction standards (SNiP) state that for normal heating 1 sq. m. requires 100 W. thermal power. By measuring the length and width of the room, and multiplying these two values, we get the area of the room (S).
To calculate the total power (Q), substitute into the formula, Q=S*100 W., our meaning. The passport for heating radiators indicates the heat transfer of one element (q1). Thanks to this information, we will know the required number. To do this, divide Q by q1.

The second method is more accurate. It should also be used with a ceiling height of 3 meters or more. Its difference lies in measuring the volume of the room. The area of the room is already known, let's measure the height of the ceiling, then multiply these values. We substitute the resulting volume value (V) into the formula Q=V*41 W.
According to building codes, 1 cubic meter. m. should be heated by 41 W. thermal power. Now let's find the ratio of Q to q1, obtaining the total number of radiator nodes.
Let's sum up the interim results data that will be needed for all types of calculations.
- Wall length;
- Wall width;
- Ceiling height;
- Power standards, heating a unit of area or volume of a room. They are given above;
- Minimum heat dissipation radiator element. It must be indicated in the passport;
- Wall thickness;
- Number of window openings.
A quick way to calculate the number of sections
 If we are talking about replacement cast iron radiators bimetallic, you can do without scrupulous calculations. Taking into account several factors:
If we are talking about replacement cast iron radiators bimetallic, you can do without scrupulous calculations. Taking into account several factors:
- The bimetallic section gives a ten percent increase in thermal power compared to cast iron.
- Battery efficiency decreases over time. This is due to deposits that coat the walls inside the radiator.
- It's better to be warmer.
Amount of elements bimetallic battery, should be the same as its predecessor. However, this number increases by 1 - 2 pieces. This is done to combat future decreases in the heater's efficiency.
For a standard room
We already know this method of calculation. It is described at the beginning of the article. Let's look at it in detail by turning to specific example. Let's calculate the number of sections for a room of 40 square meters. m.
According to the rules of 1st quarter. m requires 100 W. Let's assume that the power of one section is 200 W. Using the formula from the first section, we will find the required thermal power of the room. Let's multiply 40 square meters. m. at 100 W, we get 4 kW.
To determine the number of sections, divide this number by 200 W. It turns out that a room of a given area will require 20 sections. The main thing to remember is that the formula is relevant for apartments where the ceiling height is less than 2.7 m.
For non-standard
Non-standard rooms include corner, end rooms, with several window openings. Dwellings with a ceiling height of more than 2.7 meters also fall under this category.
For the former, the calculation is carried out according to the standard formula, but the final result is multiplied by a special coefficient, 1 - 1.3. Using the data obtained above: 20 sections, assume that the room is corner and has 2 windows.
The final result is obtained by multiplying 20 by 1.2. This room requires 24 sections.
If we take the same room, but with a ceiling height of 3 meters, the results will change again. Let's start by calculating the volume, multiply 40 square meters. m. by 3 meters. Remembering that per 1 cu. m requires 41 W., let's calculate the total thermal power. The resulting 120 cc. m multiplied by 41 W.
We get the number of radiators by dividing 4920 by 200 W. But the room is corner with two windows, therefore, 25 needs to be multiplied by 1.2. The final total is 30 sections.
Accurate calculations with many parameters
 It is difficult to make such calculations. The above formulas are valid for a normal room in central Russia. Geographical position houses and a number of other factors will introduce additional correction factors.
It is difficult to make such calculations. The above formulas are valid for a normal room in central Russia. Geographical position houses and a number of other factors will introduce additional correction factors.
- The final formula for corner room , must have an additional multiplier of 1.3.
- If the house is not located in middle lane countries, the additional coefficient is described building codes this territory.
- It is necessary to consider the installation location of the bimetallic radiator And decorative elements. For example, a niche under a window will take 7%, and a screen up to 25% of the thermal power of the battery.
- What will the room be used for?
- Wall material and thickness.
- How much do frames cost? and glass.
- Door and window openings introduce additional problems. Let's look at them in more detail.

Walls with windows, street and with doorways, change the standard formula. It is necessary to multiply the resulting number of sections by the heat transfer coefficient of the room, but it must first be calculated.
This indicator will be the sum of the heat transfer of the window, doorway and wall. All this information can be obtained by contacting SNiP, according to your type of premises.
Electrical oil radiators, operating principle and how to choose
Useful tips for properly arranging your heating system
Bimetallic radiators come from the factory connected in 10 sections. After calculations, we got 10, but we decided to add 2 more in reserve. So, it's better not to do it. Factory assembly is much more reliable and comes with a warranty of 5 to 20 years.
Assembly of 12 sections will be carried out by the store, and the warranty will be less than a year. If the radiator leaks shortly after the end of this period, repairs will have to be carried out on your own. The result is unnecessary problems.
Let's talk about the effective power of the radiator. Characteristics bimetallic section specified in the product passport, assume that the temperature difference of the system is 60 degrees.
This pressure is guaranteed if the temperature of the coolant in the battery is 90 degrees, which does not always correspond to reality. This must be taken into account when calculating the room radiator system.
Below are Some tips for installing the battery:
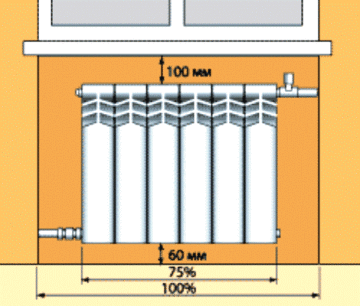
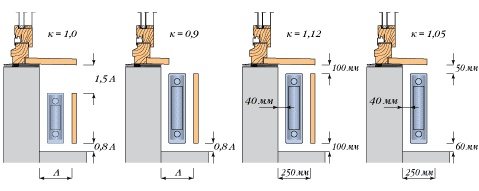
- Distance from the window sill to the top edge of the battery, should be at least 5 cm. Air masses will be able to circulate normally and transfer heat to the entire room.
- The radiator must be separated from the wall by a length of 2 to 5 cm. If reflective thermal insulation will be attached behind the battery, then you need to purchase extended brackets that provide the specified gap.
- The bottom edge of the battery is allowed a distance from the floor equal to 10 cm. Failure to follow the recommendation will worsen heat transfer.
- A radiator mounted against a wall, and not in a niche under a window, must have a gap with it, at least 20 cm. This will prevent dust from accumulating behind it and help heat the room.
It is very important to make such calculations correctly. This determines how efficient and economical the resulting heating system will be.
