How many radiator sections are needed per room? Calculation of the thermal power of heating radiators.
We build or reconstruct a private house, got involved in a major renovation of the apartment. We will equip the office, warm garage, heated premises for other purposes. We thought through the heating system, selected the main equipment: the boiler and its piping, the boiler, underfloor heating systems. Or, if this is an apartment, you decided to replace the existing heating device with a more aesthetic and efficient one, maybe add a few additional sections old battery. We will assume that we have already made a choice of the type of heating devices: stacked sectional cast iron, aluminum batteries, bimetallic devices or ready-made panels steel radiators. Let's not forget that the batteries must withstand the coolant pressure in the system, which multi-storey building an order of magnitude higher than in a cottage. To achieve thermal comfort, it is important for us to correctly calculate heating radiators.
Principles of calculation
To ensure the required temperature in the room, the calculation of the power of heating radiators and the entire system must take into account heat loss from each room and the climatic conditions of the region. When preparing a project, heating engineers determine the thermal balance of the external walls, roof, basement of the building, window and door designs. The air exchange in the ventilation system, the height of the premises, the movement of air flows and many other factors are also taken into account. The fundamental document prescribing the principles of designing a heating system is SNiP 2.04.05-91. Designers also use a number of regulations ( total number up to two dozen) regulating heating devices for buildings and premises for various purposes.
Accurately calculating sections of heating radiators according to all the rules is quite complicated, and doing it yourself without having special knowledge, not easy. During the construction of a serious country house it makes sense to turn to specialists and order a complete heating project: included in it rational decisions, thermal comfort and optimal fuel consumption will justify the costs. If this is not possible, you can make an approximate calculation of the heating batteries yourself.
What is the thermal power of heating radiators
Thermal power, heat output or heat flow of a heating device indicates the amount of thermal energy (in kilowatts or watts) that a radiator or one modular element (section) is capable of transmitting to the room per unit of time (hour). Less common is the designation in calories/hour. One watt equals 0.86 calories. The amount of heat transfer depends not only on the design of the radiator, its size, and the material from which it is made. Equally important are the parameters of the coolant: its temperature and the speed at which the liquid flows through the batteries. For most heating devices Thermal power is indicated at standard coolant temperatures of 60/80 °C. Accordingly, when the operating services, from the generosity of the budget, turn up the heat and put boiling water into the system (rarely, but it happens), the heat transfer will increase. If lukewarm water flows at a low speed (this happens much more often) it will drop. Significantly affects the amount of heat flow and the method of connecting the device.
Please note that not all connection diagrams provide complete heat transfer from the heating device. The most common is the standard side (1); for other cases (3, 4) a reduction factor is introduced in the calculation.
Heat transfer of one section in a traditional cast iron radiator Soviet model - 160 W. To determine the total battery power, multiply this figure by the number of sections.
Aluminum radiators are also sectional. The heat flow depends on the model, but with a standard center height of 500 mm it averages 200 W for one section. That is, such aluminum sections it will require approximately 20% less than cast iron.

Design aluminum radiator. In the standard version, value A is 500 mm. You should pay attention to the distances from the outer edges of the device to the floor and window sill. If they are less than specified, the heat transfer will decrease slightly
Panel steel radiators are non-separable and have a fixed heat transfer rate. As an example: depending on the design, a panel of standard height and length of 800 mm can produce a heat flux of 700 to 1500 W.
Simplified calculation
IN central regions Russia for heating a living room with one outer wall in standard panel house you will need approximately 100 W of thermal energy per square meter of area. This is a very approximate figure. If the apartment is located on the first or last floor, it is worth adding approximately 20%. For corner room increase the figure by one and a half times. Let's not forget that there is a dependence on the connection diagram; if necessary, we will take into account the correction factor. This is a battery of ten cast iron sections. Naturally, for Yakutia and Krasnodar the value of heat transfer per unit area will be significantly different. Thus, for the Moscow region, a room with an area of 16 m2 in a standard “socket” will require 1600 W.
Modern house with walls made of “warm” cellular blocks, and even with a “thermal fur coat”, energy-efficient glazing will have much lower heat loss and the required radiator power should also be lower. Some sellers heating equipment facilitate potential buyers choice by posting a calculator on your website to calculate the number of sections of heating radiators. With the help of such an online service, it is possible to make a more or less accurate calculation of the heating radiator per room.
Radiator layout plan, one of many pages of the “correct” heating system design. For each room indicated calculated value heat loss (numbers in a rectangle). When building expensive apartments, save on design work not worth it
Do you need power reserve?
Preferably. You won’t always get the coolant at the required temperature from the ZPS, so it’s worth increasing the battery power by 20-25%. It is advisable to install a heat regulator at the entrance: a thermostat or a regular one ball valve.
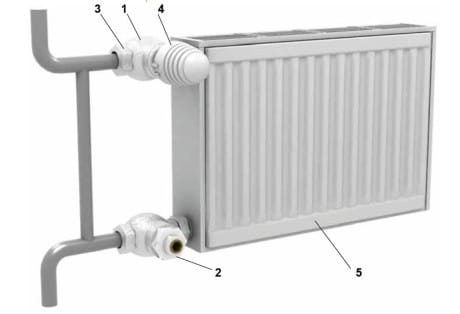
“Correct” installation of the radiator (5). Thermostatic valve(4) will ensure constant maintenance set temperature in the room, connecting parts (1-3) will help you quickly remove and reinstall the battery. A bypass (a jumper between the inlet and outlet pipes) will allow the coolant to circulate through the riser even when the device is removed, so as not to infringe on the interests of neighbors in the house
Low temperature heating systems and radiator calculations
Modern low-temperature heating systems prevail in Europe, and in Russia they are increasingly used. They are built on the basis of energy-efficient condensing heating boilers and heat pumps. To get the maximum economic effect, for radiator heating, as for heated floors, use a coolant with a low temperature - 40-55 °C. The heat transfer of radiators is reduced by approximately 1.8 times. Accordingly, they must have greater power and dimensions. Despite the increased cost of the system, this approach is justified: a rationally designed, correctly installed and properly configured low-temperature system allows you to achieve significant gas savings. A heat pumps do not require fuel at all. To calculate such systems, everything famous manufacturers indicate the heat transfer of devices for various parameters coolant. Calculating the number of heating radiators should also take into account the influence of underfloor heating.

Efficiency ratio of traditional and modern condensing gas boilers. To achieve the specified savings, a low-temperature coolant must also circulate in the radiators. Accordingly, the heat transfer of devices should be taken based on indicators of 40-55°C
In conclusion, we will say that the heating device should not be covered with anything: thick curtains, a solid decorative screen, furniture pushed closely together will significantly reduce its efficiency. If a fashionable table top-window sill completely covers the radiator from above, warm air passes the surface window glass, and it can be excessively cold and “cry”. In this case, ventilation grilles should be placed in the window sill.
When replacing batteries or switching to individual heating In an apartment, the question arises of how to calculate the number of heating radiators and the number of instrument sections. If the battery power is insufficient, the apartment will be cool during the cold season. An excessive number of sections not only leads to unnecessary overpayments - with a heating system with a single-pipe distribution, residents of the lower floors will be left without heat. You can calculate the optimal power and number of radiators based on the area or volume of the room, taking into account the features of the room and the specifics of different ones.
The most common and simple method is the method of calculating the power of devices required for heating based on the area of the heated room. According to the average norm, for heating 1 sq. meter of area requires 100 W of thermal power. As an example, consider a room with an area of 15 square meters. meters. According to this method, heating it will require 1500 W of thermal energy.
When using this technique, you need to consider several important points:
- the norm is 100 W per 1 sq. meter of area belongs to the middle climatic zone, in the southern regions for heating 1 sq. meter of room requires less power - from 60 to 90 W;
- for areas with harsh climates and very cold winter for heating 1 sq. meter requires from 150 to 200 W;
- the method is suitable for rooms with standard ceiling heights not exceeding 3 meters;
- the method does not take into account heat loss, which will depend on the location of the apartment, the number of windows, the quality of insulation, and the material of the walls.

Calculation method for room volume
The calculation method taking into account the volume of the ceiling will be more accurate: it takes into account the height of the ceilings in the apartment and the material from which the external walls are made. The sequence of calculations will be as follows:
- The volume of the room is determined by multiplying it by the height of the ceiling. For a room of 15 square meters. m. and a ceiling height of 2.7 m it will be equal to 40.5 cubic meters.
- Depending on the material of the walls, heating one cubic meter of air requires different quantities energy. According to SNiP standards for an apartment in brick house this figure is 34 W, for panel house– 41 W. This means that the resulting volume must be multiplied by 34 or 41 W. Then for a brick building, heating a room of 15 square meters will require 1377 W (40.5 * 34), for a panel building - 1660.5 W (40.5 * 41).

Adjusting results
Any of the selected methods will only show an approximate result if all factors affecting the reduction or increase in heat loss are not taken into account. For an accurate calculation, you need to multiply the obtained radiator power value by the coefficients given below, from which you need to select the appropriate ones.

Window
Depending on the size of the windows and the quality of insulation, a room can lose 15–35% of heat through them. This means that for calculations we will use two coefficients associated with windows.
Ratio of window area to floor area in the room:
- 10% – coefficient 0.8;
- 20% – 0,9;
- 30% – 1,0;
- 40% – 1,1;
- 50% – 1,2.
Glazing type:
- for a window with a three-chamber double-glazed unit or two-chamber with argon - 0.85;
- for a window with regular double-glazed window – 1,0;
- for frames with conventional double glazing – 1.27.

Walls and ceiling
Heat losses depend on the number of external walls, the quality of thermal insulation and the type of room located above the apartment. To take these factors into account, 3 more coefficients will be used.
Number of external walls:
- no external walls, no heat loss - coefficient 1.0;
- one outer wall – 1,1;
- two – 1.2;
- three – 1.3.
Thermal insulation coefficient:
- normal thermal insulation (wall 2 bricks thick or a layer of insulation) – 1.0;
- high degree of thermal insulation – 0.8;
- low – 1.27.
Accounting for the type of room above:
- heated apartment – 0.8;
- heated attic – 0.9;
- cold attic – 1.0.

Ceiling height
If you used the method of calculating by area for a room with non-standard height walls, then to clarify the result you will have to take it into account. The coefficient can be found out as follows: divide the existing ceiling height by standard height, which is equal to 2.7 meters. Thus we get the following numbers:
- 2.5 meters – coefficient 0.9;
- 3.0 meters – 1.1;
- 3.5 meters – 1.3;
- 4.0 meters – 1.5;
- 4.5 meters – 1.7.

Climatic conditions
The last coefficient takes into account the outside air temperature in winter time. We will start from the average temperature in the coldest week of the year.
- -10 °C – 0.7;
- -15 °C – 0.9;
- -20 °C – 1.1;
- -25 °C – 1.3;
- -35 °C – 1.5.

Calculation of the number of radiator sections
Once we know the power required to heat the room, we can calculate the heating radiators.
In order to calculate the number of radiator sections, you need to divide the calculated total power by the power of one section of the device. To carry out calculations, you can use average statistical indicators for different types radiators with a standard axial distance of 50 cm:
- for cast iron batteries, the approximate power of one section is 160 W;
- for – 180 W;
- for aluminum – 200 W.
Help: the axial distance of the radiator is the height between the centers of the holes through which coolant is supplied and discharged.
For example, let’s determine the required number of sections bimetallic radiator for a room of 15 square meters. m. Let's assume that you calculated the power in the simplest way based on the area of the room. We divide the 1500 W of power required to heat it by 180 W. We round the resulting number 8.3 - the required number of sections of the bimetallic radiator is 8.
Important! If you decide to choose batteries custom size, find out the power of one section from the device passport.

Dependence on the temperature regime of the heating system
The power of radiators is indicated for a system with a high temperature thermal regime. If your home's heating system operates in medium-temperature or low-temperature thermal mode, to select batteries with the right amount sections will have to make additional calculations.
First, let's determine the thermal pressure of the system, which is the difference between the average temperature of the air and the batteries. The temperature of heating devices is taken as the arithmetic average of the coolant supply and outlet temperatures.
- High temperature mode: 90/70/20 (supply temperature - 90 °C, return -70 °C, average room temperature is taken to be 20 °C). We calculate the thermal pressure as follows: (90 + 70) / 2 – 20 = 60 °C;
- Medium temperature: 75/65/20, thermal pressure – 50 °C.
- Low temperature: 55/45/20, thermal pressure – 30 °C.
Formulas allow you to obtain results of varying degrees of accuracy, since they take into account different quantity parameters.
Average standard power values of radiator sections made of different materials:
- Steel – 110-150 W
- Cast iron - 160 W;
- Bimetallic – 180 W;
- Aluminum - 200 W.
The number of devices themselves usually corresponds to the number of windows in the room; it is possible to install additional radiators on blank, cold walls.
Calculation by room area
All calculations required power heating devices are based on building codes adopted to date:
To heat a living space with an area of 10 square meters, with a ceiling height of up to 3 meters, a thermal power of 1 kW is required.
For example, the area of a room is 25 meters, multiply 25 by 100 (W). This turns out to be 2500 W, or 2.5 kW.
The steel radiator has low power
We divide the resulting value by the power of one section of the selected radiator model, let’s say it is 150 W.
Thus, 2500 / 150, it turns out 16.7. The result is rounded up, so 17. This means that to heat such a room you will need 17 radiator sections.
Rounding can be done downwards if we are talking about rooms with small heat losses or additional heat sources, for example a kitchen.
This is a very rough and rounded calculation, since it does not take into account any additional parameters:
- Thickness and material of the building walls;
- Type of insulation and thickness of its layer;
- Number of external walls in the room;
- Number of windows in the room;
- Availability and type of double-glazed windows;
- Climatic zone, temperature range.
Taking into account additional parameters
- 20% should be added to the result if the room has a balcony or bay window;
- If the room has two full window openings or two external walls (corner location), then 30% should be added to this resulting value.
- If you plan to install decorative screens for radiators or fences, add another 10-15%.
- Installed high-quality double-glazed windows will subtract 10-15% from the total.
- A decrease in coolant temperature by 10 degrees (norm +70) will require an increase in the number of sections or radiator power by 18%.
- Features of the heating system - if the coolant is supplied through the lower hole and exits through the top, then the radiator does not provide about 7-10% of the power.
- In order to make some reserve power in case of atypical cold weather, etc. It is customary to add 15% to the final result.
Climatic region coefficients
- For middle zone In Russia the coefficient is not used (it is taken as 1).
- For the northern and eastern regions, a coefficient of 1.6 is used.
- Southern regions 0.7-0.9, depending on minimum and average annual temperatures.
Thus, to correct for climate zone, you need to multiply the resulting thermal power result by the required coefficient.
It turns out: Room area (length * width) / 10 (kW) * climate coefficient
Number of radiators
The number of radiators for the room is determined based on the resulting number of sections.

Radiators are usually installed near cold air sources
It is intended to be installed under each window opening; if there are long, cold external walls, then they may also require installation of a radiator.
For example, if the result is: 16 sections are required, then if there are 2 identical windows in the room, it is possible to install two radiators of 8 sections each. If the lengths of the windows are different, the proportions of the sizes change accordingly.
Advice: in practice, it is recommended to install radiators more than 10 sections in length, since the efficiency of the outer sections will be reduced.
Calculation by room volume
Calculating the required power of heating devices based on the volume of the room gives more accurate results, since the height of the room’s ceilings is also taken into account.
This calculation method is used for premises with high ceilings, non-standard configurations and open living spaces, such as halls with second light.
The general principle of calculations is similar to the previous one.
According to the requirements of SNIP For normal heating 1 cubic meter of living space requires 41 W of thermal power of the device.
Thus, the volume of the room is calculated (length * width * height), the result is multiplied by 41. All values are taken in meters, the result in W. To convert to kW, divide by 1000.
Example: 5 m (length) * 4.5 m (width) * 2.75 m (ceiling height), the resulting volume of the room is 61.9 cubic meters. The resulting volume is multiplied by the norm: 61.9 * 41 = 2538 W or 2.5 kW.
The number of sections is calculated, as above, by dividing by the power of one radiator section indicated in the model data sheet by the manufacturer. Those. if the power of one section is 170 W, then 2538 / 170 turns out to be 14.9, after rounding, 15 sections.
Amendments

Cast iron batteries - a classic with a new twist
If the calculation is made for apartments in a modern multi-storey building With high-quality insulation And installed double glazed windows, then the power norm per 1 cubic meter is 34 W.
In the radiator passport, the manufacturer may indicate the maximum and minimum value thermal power per section, the difference is related to the temperature of the coolant circulating in the heating system. To make correct calculations, either the average or the minimum value is taken.
Calculation for a private house
To calculate the required power of heating devices and the number of radiators in a private house or in non-standard housing (loft, attic floors etc.) an even more precise calculation principle is applied.
In this case, additional coefficients are included in the formula.
Consideration of related technical factors and individual parameters, characteristic of a particular room, allows you to obtain the optimal value of the required thermal power in a particular case.
IN general view The calculation formula is:
KT = 100W/sq.m. * P * K1 * K2 * K3 * K4 * K5 * K6 * K7
- KT – amount of heat (calculated value);
- P – room area in square meters;
- K1 – coefficient of the type of glazing of window openings
- Standard double glass – 1.27
- Double glazing – 1.0
- Triple glazing – 0.85
- K2 - wall thermal insulation level coefficient
- Low thermal insulation - 1.27
- Average thermal insulation (increased thickness or layer of insulation) - 1.0;
- High degree of thermal insulation of walls ( double layer insulation) - 0.85.
- K3 - coefficient reflecting the ratio of the areas of windows and floors in the room:
- 50% - 1,2;
- 40% - 1,1;
- 30% - 1,0;
- 20% - 0,9;
- 10% - 0,8.
- K4 is a coefficient that takes into account the usual air temperature in the coldest week of the year:
- -35 degrees - 1.5;
- -25 degrees - 1.3;
- -20 degrees - 1.1; d
- -15 degrees - 0.9;
- -10 degrees - 0.7.
- K5 - coefficient taking into account the number of external walls in the room
- one wall - 1.1;
- two walls - 1.2;
- three walls - 1.3;
- four walls - 1.4.
- K6 - correction for high location of the room
- For a cold attic - 1.0;
- For a heated attic - 0.9;
- Heated living space top floors - 0,8
- K7 - coefficient to take into account the height of the ceilings in the room:
- Ceilings 2.5 m - 1.0;
- Ceilings 3.0 m - 1.05;
- Ceilings 3.5 m - 1.1;
- Ceilings 4.0 m - 1.15;
- Ceilings 4.5 m - 1.2.
Calculation required quantity thermal power produced using this formula allows you to determine the exact amount of heat needed to heat a specific room. When dividing the resulting value by the power of one radiator section, the required number of sections is obtained.
Video clip about the features of calculating the power of heating radiators, expert answers:
Tables for calculations:

Table: comparison of the required number of sections for one room area when installing aluminum and bimetallic radiators
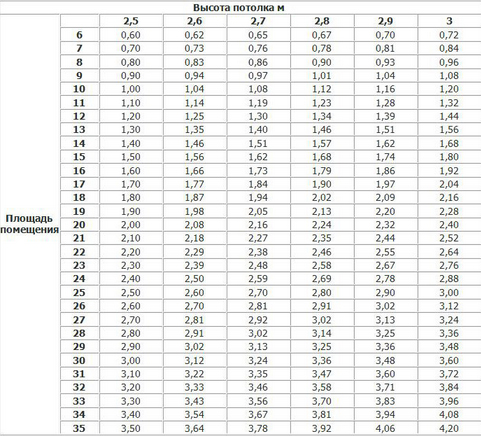
Table: estimated room volume
To provide residential or production premises comfort mode, it is necessary to equip the heating system. An important factor Its efficiency and economy is the competent calculation of heating radiators. It involves calculating the total power (heat output) of the device transmitting thermal energy from the heated liquid into the room. After choosing the design type of the battery, it is mathematically found how many sections are needed to assemble it. If the calculation procedure is carried out correctly, even in severe frost, a private house or apartment will warm up well, and when it warms up, it is easy to adjust the heating by changing the coolant supply and its temperature.
The main initial data for calculations are the dimensions of the room and the passport characteristics of the battery or a separate section. For premises corresponding standard projects, the radiator is selected according to its area. In case of too high or low ceilings, volume is taken as a basis. To make the results more accurate, they use a rather labor-intensive technique that takes into account the degree of thermal insulation of the home, the number external walls, windows and doors, average coefficient winter temperatures. Below is a detailed description of several options for selecting heating radiators.
Approximate and refined area calculations
Using a simplified method, with an acceptable error, they calculate for rooms whose walls are below 2.5 m. Measure the length and width, multiply them and get the area in m2. The method is based on the fact that in low buildings each section provides heating 1.8 square meter(in this case, its power must be at least 60 W). Let the room have an area of 18 m2. To find out how many sections the radiator should consist of, perform a division operation: 18: 1.8 = 10 sections.

Building codes and regulations (SNiP) state: in the middle climate zone, high-quality heating of a living space with ceilings 270 cm high is possible with a minimum specific thermal power R per. = 100 W/m2, excluding the material from which the battery is made. In this case, the number of sections is calculated using formula 1:
- N = S x 100/ P;
- where S – area, m2;
- P – section power, W/m2.
Table 1 allows you to adjust the calculation of radiator sections. It shows specific power indicators and correction factors taking into account additional factors, increasing heat loss.
Table 1.
The power of the element (P) depends on the material from which the heating radiators are made. Its value is found among the technical data specific model, and indicative indicators are given in Table 2.
A steel plate radiator does not consist of individual elements; its thermal power depends on the length of the device and the insertion method. This data is also found in the passport. For example, Korad 22 (500x700 mm) with side connection has a P equal to 936 W. The same model with bottom connection P = 842 W.
Example 1. It is required to find the number of sections of an aluminum radiator (the distance between the axes is 350 mm). Room area - 25 m2, ceiling height - 2.5 m. The room is corner (2 external walls), windows face south and east.
The initial data and tabular coefficients are entered into formula 1:
- N = 25 x 130/145 = 22.4.
Rounding the result upward, we get 23 sections.
Example 2. The initial data is the same. A steel Korado 22 (300x1000 mm) with a side connection, P = 1248 W, will be installed.
The number of batteries is calculated as follows:
- N = 24 x 130 x 1.1/1248 = 2.75 (rounded to the nearest three).

If an apartment or private house has high ceilings (more than 2.7 m), it is not enough to know the square footage to determine the number of heating devices. It is more correct to make a calculation based on the required specific power per cubic meter. For buildings from concrete panels this norm reaches 41 W/m3; for thermally insulated rooms with Euro-windows it is reduced to 34 W/m3.
Example 3. Task: find out how many heating sections ( cast iron batteries) is needed to heat a room occupying 22 square meters. m, with a ceiling height of 2.9 m. The apartment is located in a panel house.
The calculation of heating radiators begins with determining the cubic capacity of the room: V = 22 x 2.9 = 63.8 m3. The total power is calculated as follows: P rev = 63.8 x 41 = 2616 W. The number of sections is found by dividing the result by the nameplate value of the power of an individual battery element: N = 2616/160 = 16.35. Rounding up results in 17 sections.

Improved calculation method
None of the above methods gives an accurate result. Heating of the room may be insufficient if a private house or apartment is located in the northern region. And, conversely, the selected radiator may be too powerful if the private house is decorated with modern heat-insulating materials. To make a more precise calculation of the number of heating radiator sections, you will need the following data:
- wall height;
- room area;
- quadrature of window openings;
- quality of thermal insulation of surfaces;
- actual temperature indicators for the region in winter.
Total thermal power, which the battery must transmit, is calculated as the product of the average power indicator (Rud = 100 W/m2) and area (S) by correction factors (formula 2):
- R ob = 100 * S * K ost * K walls * K ok * K t * K ns * K sweat * K high.
Amendments are selected according to Table 2 and substituted into the formula. The number of sections is calculated according to the standard method.
Table 2.
| Designation | Influencing factors and coefficient value | |||||||||||||||||||
| K ost | Glazing option | |||||||||||||||||||
| ordinary | PVC windows with double glazing | PVC windows with triple glazing | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1,27 | 1,0 | 0,85 | ||||||||||||||||||
| To the walls | Wall insulation | |||||||||||||||||||
| absent | insulation in one layer or masonry in two bricks | in several layers | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1,27 | 1,0 | 0,85 | ||||||||||||||||||
| K ok | What percentage of the floor area is made up of window openings? | |||||||||||||||||||
| 50 | 40 | 30 | 20 | 10 | ||||||||||||||||
| 1,2 | 1,1 | 1,0 | 0,9 | 1,8 | ||||||||||||||||
| K t | Average outdoor temperature during the coldest winter week °C | |||||||||||||||||||
| -35 | -25 | -20 | -15 | -10 | ||||||||||||||||
| 1,5 | 1,3 | 1,1 | 0,9 | 0,7 | ||||||||||||||||
| K ns | Number of external walls | |||||||||||||||||||
| one | two | three | four | |||||||||||||||||
| 1,1 | 1,2 | 1,3 | 1,4 | |||||||||||||||||
| K sweat | What's above the ceiling | |||||||||||||||||||
| Attic without insulation | Attic heated with a hood | Heated attic | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1,0 | 0,9 | 0,8 | ||||||||||||||||||
| To the highest | Ceiling level above floor, cm | |||||||||||||||||||
| 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | ||||||||||||||||
| 1,0 | 1,05 | 1,1 | 1,15 | 1,2 | ||||||||||||||||
If the heating system is designed independently, an online calculator will help speed up the selection of radiators. This service program makes it possible to do without many adjustments: they are chosen by the system itself. The basic data includes the characteristics of the room, climatic features, Battery Type. Initial information is entered manually or parameters are selected from drop-down lists.
It is very important to buy modern, high-quality and efficient batteries. But it is much more important to correctly calculate the number of radiator sections so that during the cold season it properly warms the room and does not have to think about installing additional portable heating devices that will increase the cost of heating.
SNiP and basic regulations
Today we can call great amount SNiPs, which describe the rules for the design and operation of heating systems in various rooms. But the most understandable and simple is the document “Heating, ventilation and air conditioning” numbered 2.04.05.
It describes in detail the following sections:
- General provisions regarding the design of heating systems
- Rules for the design of building heating systems
- Features of the heating system
Heating radiators must also be installed in accordance with SNiP number 3.05.01. He prescribes following rules installation, without which the calculations made for the number of sections will be ineffective:
- The maximum width of the radiator should not exceed 70% of the same characteristic of the window opening under which it is installed
- The radiator must be mounted in the center of the window opening (a minor error is allowed - no more than 2 cm)
- Recommended space between radiators and wall is 2-5 cm
- The height above the floor should not be more than 12 cm
- The distance to the window sill from the top point of the battery is at least 5 cm
- In other cases, to improve heat transfer, the surface of the walls is covered with reflective material
It is necessary to follow such rules so that air masses can circulate freely and replace each other.
Read also various types heating radiators
Calculation by volume
To accurately calculate the number of sections heating radiator necessary for effective and comfortable heating living space, its volume should be taken into account. The principle is very simple:
- Determining the heat requirement
- Find out the number of sections capable of giving it away
SNiP prescribes taking into account the heat requirement for any room - 41 W per 1 cubic meter. However, this indicator is very relative. If the walls and floor are poorly insulated, it is recommended to increase this value to 47-50 W, because some of the heat will be lost. In situations where a high-quality heat insulator has already been laid on the surfaces, mounted quality windows PVC and drafts are eliminated - this figure can be taken equal to 30-34 W.
If there are heating systems in the room, the heat demand must be increased to 20%. Part of the thermal heated air masses will not be passed through the screen, circulating inside and quickly cooling.
Formulas for calculating the number of sections by room volume, with an example
Having decided on the need for one cube, you can begin calculations (example using specific numbers):
- In the first step, we calculate the volume of the room using a simple formula: [height length Width] (3x4x5=60 cubic meters)
- Next stage– determination of the heat requirement for the specific room under consideration using the formula: [volume]*[requirement per cubic meter] (60x41=2460 W)
- You can determine the desired number of ribs using the formula: (2460/170=14.5)
- It is recommended to round up - we get 15 sections
Many manufacturers do not take into account that the coolant circulating through the pipes is far from maximum temperature. Consequently, the power of the ribs will be lower than the specified limit value (this is what is written in the passport). If there is no minimum power indicator, then the available one is underestimated by 15-25% to simplify calculations.
Calculation by area
The previous calculation method is an excellent solution for rooms with a height of more than 2.7 m. In rooms with more low ceilings(up to 2.6 m) you can use another method, taking the area as a basis.
In this case, calculating total thermal energy, demand per sq. m is taken equal to 100 W. There is no need to make any adjustments to it for now.
Formulas for calculating the number of sections by room area, with an example
- At the first stage, it is determined total area premises: [length Width] (5x4=20 sq.m.)
- The next step is to determine the heat required to heat the entire room: [area]* [requirement per sq. m.] (100x20=2000 W)
- In the passport attached to the heating radiator, you need to find out the power of one section - average modern models 170 W
- To determine the required number of sections, use the formula: [total heat demand]/[power of one section] (2000/170=11.7)
- We introduce correction factors ( discussed below)
- It is recommended to round up - we get 12 sections
The methods discussed above for calculating the number of radiator sections are perfect for rooms whose height reaches 3 meters. If this figure is greater, it is necessary to increase the thermal power in direct proportion to the increase in height.
If the whole house is equipped with modern plastic windows, in which the heat loss coefficient is as low as possible, it becomes possible to save money and reduce the result by up to 20%.
It is believed that the standard temperature of the coolant circulating through heating system– 70 degrees. If it is below this value, it is necessary to increase the result by 15% for every 10 degrees. If it is higher, on the contrary, reduce it.
Premises with an area of more than 25 square meters. m. heating with one radiator, even consisting of two dozen sections, will be extremely problematic. To solve this problem, it is necessary to divide the calculated number of sections into two equal parts and install two batteries. In this case, the heat will spread throughout the room more evenly.
If there are two window openings in the room, heating radiators should be placed under each of them. They must be 1.7 times more powerful than the rated power determined in the calculations.
Having purchased stamped radiators where sections cannot be divided, it is necessary to take into account the total power of the product. If it is not enough, you should consider buying a second battery of the same type or one with a slightly lower heat capacity.
Correction factors
Many factors can influence the final result. Let's consider in what situations it is necessary to make correction factors:
- Windows with regular glazing – magnifying factor 1.27
- Insufficient thermal insulation walls – magnifying factor 1.27
- More than two window openings per room – magnifying factor 1.75
- Collectors with bottom wiring– magnifying factor 1.2
- Reserve in case of unforeseen situations – increasing factor 1.2
- Application of improved thermal insulation materials– reduction factor 0.85
- Installation of high-quality thermal insulating double-glazed windows – reduction factor 0.85
The number of amendments made to the calculation can be huge and depends on each specific situation. However, it should be remembered that it is much easier to reduce the heat output of a heating radiator than to increase it. Therefore, all roundings are made upward.
Let's sum it up
If it is necessary to produce the maximum exact calculation the number of radiator sections in a complex room - do not be afraid to turn to specialists. The most precise methods, which are described in specialized literature, take into account not only the volume or area of the room, but also the temperature outside and inside, thermal conductivity various materials, from which the frame of the house is built, and many other factors.
Of course, you can not be afraid and add several edges to the result. But an excessive increase in all indicators can lead to unjustified expenses, which are not immediately, sometimes and not always, able to be recouped.
