We understand how to regulate the temperature of the battery heating. Regulation in underfloor heating systems
In this article I want to tell how and on the basis of what the coolant temperature is regulated. I do not think that this article will be useful or interesting for the employees of the power system, since they will not learn anything new from it. But ordinary citizens, I hope it will be useful.
4.11.1. The mode of operation of the heat and power plant of the power plant and the district boiler house (pressure in the supply and return pipelines and temperature in the supply pipelines) must be organized in accordance with the task of the heat network manager.
The temperature of the network water in the supply pipes in accordance with the approved for the heating system temperature chart must be set to the average outdoor temperature over a period of time between 12 and 24 hours, determined by the heat network controller, depending on the length of the networks, climatic conditions and other factors.
Temperature schedule is developed for each city, depending on local conditions. It clearly defines what should be the temperature of the network water in the heating network at a specific outdoor temperature. For example, at -35 ° the coolant temperature should be 130/70. The first digit determines the temperature in the supply pipe, the second - in the opposite. The heat network controller for all heat sources (CHP, boiler houses) sets this temperature.
The rules allow deviations from the specified parameters:
4.11.1. Deviations from the specified mode for the head valves of the power plant (boiler room) should be no more than:
- on the temperature of water entering the heating network, ± 3%;
- pressure in supply pipelines ± 5%;
- pressure in return pipelines ± 0.2 kgf / cm2 (± 20 kPa).
4.12.36. For water heating systems, the basis of the mode of heat supply should be a schedule of central quality regulation. Qualitative-quantitative and quantitative schedules for regulating heat supply are allowed with the necessary level of equipment for heat sources, heating networks and heat-consumption systems by means of automatic control, and the development of appropriate hydraulic modes.
So, dear citizens, do not try to somehow affect the heating network, if you feel very hot in spring. They will not do anything for you, since they have neither the right nor the opportunity. Complain to the administration, then, perhaps, they will order to stop the heating season earlier. But remember that in spring the temperature outside is variable and if it is warm today and you have turned off the heating, then it can become very cold tomorrow and turn off the equipment much faster than turning it on.
Now let's talk about how it is cold in an apartment in the winter, especially when it is thoroughly frosty. If the apartment is cold, then who is usually to blame? That's right - heat networks! That is what most citizens think. In part, they are right, but not everything is so simple.
Let's start with the fact that in extreme cold gas supplying organizations can enter gas supply restrictions. Because of this, the boiler has to maintain the temperature of the coolant "how much will happen." As a rule, degrees are 10 lower than those laid down in the temperature graph. Power plants are simpler - they are switching to burning fuel oil, and boiler rooms, which often stand almost in the middle of residential areas, are allowed to burn fuel oil only in emergency cases (for example, a complete cessation of gas supply) so that people do not freeze at all. Due to gas supply restrictions turn off the hot waterin order to reduce the costs of the coolant and thereby maintain the temperature in the heating systems at the right level. So do not be surprised if something happens.
Also, the reason that it is cold in apartments in winter is the high degree of deterioration of the heating networks themselves, and in particular thermal insulation of pipelines. As a result, in houses that are quite far from the heat source, the heat carrier “reaches” already cooled down.
Well, the last reason I’ll talk about is the poor insulation of the apartments and houses themselves. The gap in the windows, doors, lack of insulation of the house itself - all this leads to the fact that the heat goes into the environment and we are cold. This cause can be eliminated by you. Install new windows, make the apartment heat insulation, change the radiators to new ones, because over time, the cast iron batteries become clogged and the heat transfer is significantly reduced. By the way, if paint the battery blackthen it will warm better. This is not a joke, experiments confirm this fact.
Well, it seems, and everything that I wanted to tell in this article. I also want to make a reservation that I wrote the article, based largely on personal experience. In different regions of our country, the situation may be different and radically different from what I have written here. But in general, I think the situation is similar. At least in large cities.
Today, when the cost of everything, including utilities, is constantly increasing, and the economic situation is not stable, the installation of sensors for heating is a profitable option that allows significant savings on a communal. In addition, it is a natural desire for every person to ensure effective heating of their home, and regulation of the temperature of the heat transfer medium in the heating system allows it to be done at minimal cost.
Ways to improve the work of the heating system
Improving the overall operation of the system by installing a water temperature controller in the heating system is convenient and very beneficial. It makes it possible to significantly save money, and make housing not only warm, but also financially profitable.
Many are interested in how to make the heating system more balanced, so that it gives the amount of heat required at the moment. To accomplish this goal, you can use several ways that have passed the test of time:
- The first way is to install automatic temperature controllers in the heating systems on each individual battery in the room.
- The second is to regulate the degree of coolant before serving in each particular room of the house or the building as a whole, depending on their role. This is done using a special automatic device, whose operation depends on what the readings of the sensors are, which are installed inside buildings or outside of them, depending on the purpose.
- The third way is to use the flow of coolant from special boilers that generate energy.
What can and should be saved

The temperature sensor for heating is quite a profitable option for use in a private house. Why? The reasons are more than enough:
- You can choose the preferred mode system for each individual room at home. For example, it is very important that the nursery or bedroom be warm, because these rooms are constantly used, while the various outbuildings are not so important, and it is absolutely unprofitable to spend extra heat on them. Hydraulic balancing of heating allows you to set the minimum amount of heat for rooms that you rarely use, and vice versa - to increase it for frequently used rooms. There is a clear heat savings, for the month resulting in a rather impressive amount that you can spend on yourself.
- The heating temperature regulator brings additional benefits due to the fact that it monitors the overall comfort in the room. For example, the room is located on the sunny side of the house, and is quite well warmed by the sun. In this case, it will not allow excessive overheating of the air, and will make the heat consumption less. Sensors that are used in the usual centralized automation, almost never have such functions.

- The temperature sensor for heating differs from other devices by another pleasant feature - it monitors the level of heat right where the batteries are installed, and does not display its average value in any particular room. This allows you to configure the most comfortable mode for you in any single room that will meet all your requirements and preferences.
The use of valves

Some users instead of regulators of water temperature put on their batteries one of the types of valves, namely - ordinary taps. Undoubtedly, this method is very cheap, but in this case you will not get a number of significant advantages. Let's look at them in more detail:
- If you make adjustment using conventional cranes, you can not achieve compliance with a particular mode. And the use for this purpose of modern devices for adjusting the heating system allows you to do this without much difficulty, and efficiently and very accurately.
- Another important advantage is that when you adjust the temperature of the batteries with taps, you spend a lot of extra time you could spend on something else. The work of the regulators is fully automatic, and by setting them up once, you can forget about their existence for a long time.
- The operation of the crane is possible only in two modes - “closed” and “open”. And the use of such a principle can lead to the disruption of steady-state flows or to air risers, which is generally very bad. So if the question of how to adjust the heating batteries in a private house arises, this small but very useful device is simply an ideal option, since it does not completely block the flow, but simply reduces it.
When installing heating in two- and more-floor houses, the number of valves should be at least 2 times larger. The more it will be, the easier it is to continue to care for the boiler.
How the regulator works
The temperature sensor on the heating battery is a locking type valve, which is installed at the entrance to the heating devices.
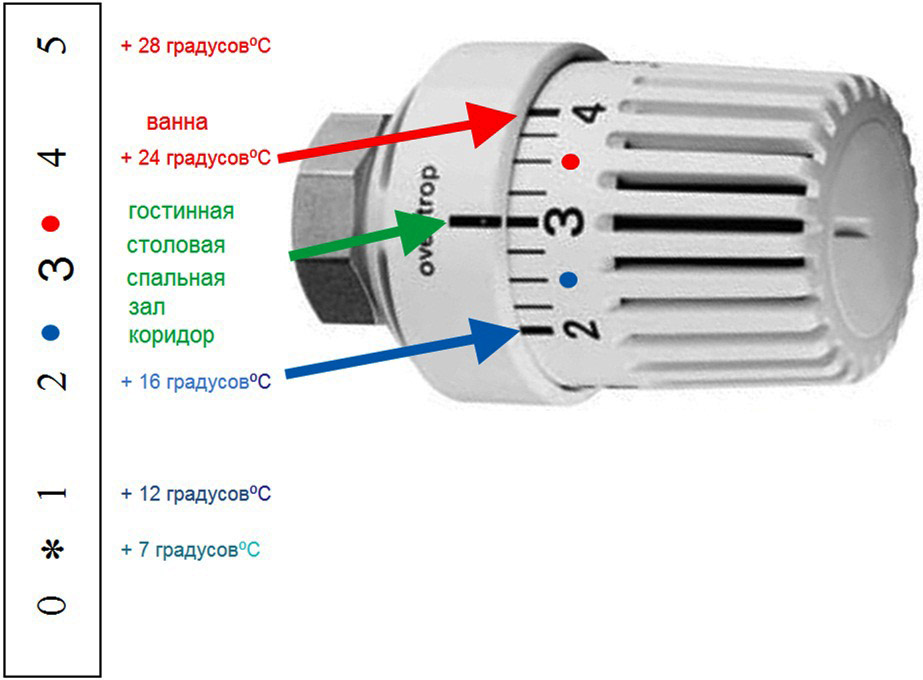
The extension of the rod to the required length for regulation is due to the pressure created by the bellows with the substance, which begins to expand strongly from hot water. To return the rod back, the installed spring is used, and in order to regulate the opening, a special mechanism is used to compensate for the opening, with a scale attached to it.
How is the heating system regulated:
- From exposure to high temperature, the substance in the bellows begins to heat up. The rod becomes longer, begins to press on the rod, and the fluid supply decreases to the desired value.
- The drum allows you to choose the initial degree, which will be lengthened bellows. Accordingly, the required temperature mode is set in this way, after reaching which the regulator blocks the water supply.
Proper installation of the regulator
You do not need to have specific knowledge to install hydraulic controllers. Just keep in mind a few nuances:
- Embed the device is necessary not at the exit, namely at the feed.
- Pick up a device having a diameter as close as possible to the diameter of the pipes for the supply.
- To properly adjust the temperature setting, install the device so that it does not fall into direct sunlight.
- When installing the regulator, pay special attention to the head with the bellows in a horizontal position. Otherwise, stagnation zones may appear. For its blowing do not use air from pipes - only air directly from the heated room.
- If the room has a certain number of radiators installed in series, there is no need to install it on every single device. Enough regulation of the flow of coolant at the entrance to the first radiator. If each battery has its own riser, you will have to install a regulator on each radiator.
As you can see, you can reduce costs if you consider such details as regulators for the heating system.
VIDEO: Automatic temperature control in the house
Adjusting the heating temperature in your own homes allows you to achieve a more comfortable stay in the premises during the heating season.
How was it done before? No adjustment of the temperature of heating systems and speech was not. There were stoves, countermarks and they melted to the conditional state of "heat". And as a result, often on the first day after the fire in the house was too hot, the second time, and on the third day I had to drown again.
With the advent of water heating systems, the situation has improved slightly, and thanks to water heating, ways to adjust the temperature of heating systems have been developed.
Exact regulation of the temperature of heating systems solves two especially important tasks:
- -Most comfortable stay in the house where you use exactly the temperature that you set;
- - Economy of energy carriers and your money due to exact adjustment.
2 ways to adjust heating systems
In fact, there are two methods of temperature adjustment.
- Quantitative . This is a method of changing the speed of movement of heated water with the help of special valves or a circulation pump. In fact, we limit the flow of coolant into the system through heating equipment.
The simplest example of implementing this method is to change the speed of the pump. The colder, the stronger the pump works and the faster the coolant moves through the heating system.
- Qualitative . This method involves adjusting the temperature of the entire system on the heating device (on the boiler, etc.)
Ways to adjust heating radiators
The easiest way to adjust the temperature of radiator heating systems is to install directly on the radiator.
The principle of operation of the thermal head is as follows: The head is filled with liquid. The volume of liquid depends on the temperature of the coolant. When heated, the volume of liquid increases and the thermal head valve closes. When cooled, the reverse occurs.
![]()
This method of adjustment is quite simple and reliable. The disadvantages include manual adjustment of the thermal head on each radiator.
A more advanced method is to install instead of a thermal head, then install the thermostat in the room and connect all the nodes into a single system.

It sounds difficult at first sight. But in fact, everything is quite simply implemented. On the servo throw two cables. One for food, the other for connecting a thermostat. On the thermostat set the desired temperature and the servo automatically adjusts it.
Ways to adjust the temperature of warm floors
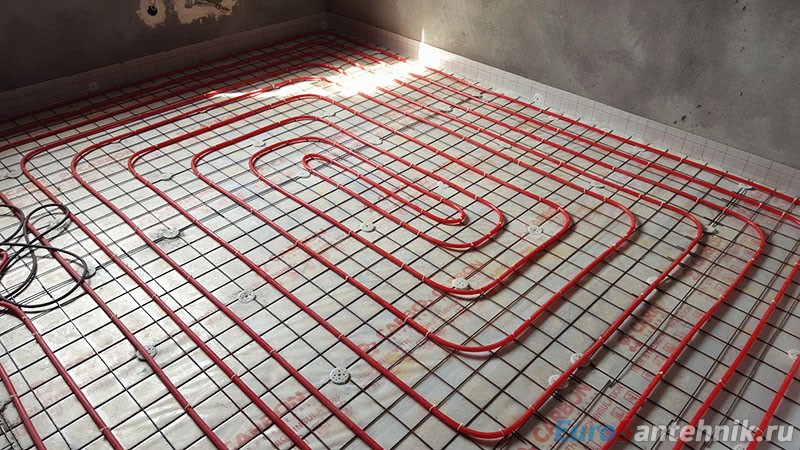

Adjusting the temperature of the floor heating is not dedicated to one article on our website. If in brief, then there are the following options:
- Adjusting the temperature of the floor heating in conjunction with the overhead temperature sensor on the collector and the circulation pump. The sensor senses the temperature at the collector (initially overestimated) and, as soon as it receives the necessary temperature, turns off the power at the pump.
- Installation of the pump for supply in pairs with. Thanks to the three-way valve, the floor is mixed up to the required temperature.
- Installation of underfloor heating using a mixing module. The mixing module has everything you need to adjust the temperature of the floor heating system.
- Similar radiator. Installation on the collector of servos in conjunction with thermostats.
Read more in the article.
The floor heating, which was once considered luxury, has become in European countries practically one of the standard options for individual housing. It is comfortable, hygienic, durable and requires minimal maintenance. In addition, the work of heating in the low-temperature region can reduce energy costs. However, the above-mentioned advantages of the “warm floor” are not always confirmed by the owners of the housing equipped with them. The reasons for this are often incorrect calculation and hydraulic adjustment of the system.
To maintain a given temperature in the room, the heating system must continuously supply heat in an amount that compensates for its loss through the walls, floor, ceiling, windows and doors. The amount of heat loss depends on the outdoor temperature. In accordance with its value, the automation of modern heating systems regulates the flow of heat into the room. The temperature of the coolant for all areas of the house is the same.
In addition to the heat of the heating system, heat from solar radiation (especially through large windows on the south side), decorative stoves and fireplaces, stoves and lighting devices, televisions, computers, and people themselves enters the house.
The intensity, duration and frequency of the supply of such heat are variable. The heat supply through the glazing of the southern walls in February can be up to 70% of the total heat load. The fireplace is able to fully cover the thermal need of the room. Other third-party heat sources usually account for less than 25% of the load.
Despite the presence of room thermostats, the rapid response of underfloor heating to the supply of outside heat is impossible due to the inertia of this system. When laying heating pipes in a seamless concrete screed, the response time of a “warm floor” to a change in the amount of incoming heat is about two hours.
Thus, the room thermostat that quickly responded to the intake of outside heat switches off the floor heating, which continues to give off heat for about two more hours. With the termination of the supply of outside heat and the opening of the thermostatic valve, full heating of the floor is achieved only after the same time.
Although it is reasonable to regulate the room temperature from the point of view of energy saving, it does not work when the temperature changes rapidly. Only the self-regulation effect is effective.
Self-regulation effect
Self-regulation is a complex dynamic process. However, in practice, the heat supply by floor heating is regulated in a natural way without the intervention of mechanical devices due to the following two regularities: 1) heat always spreads from a more heated zone to a cooler one; 2) the amount of heat flow is determined by the temperature difference.
Below are four simple examples illustrating the effect of self-regulation. The air temperature outside the room, inside it, the floor temperature and the amount of hot water entering the heating system are assumed to be unchanged. Only the air temperature in the room changes due to the influx of extraneous heat and cold air through the leakiness of the room.
In fig. 1 shows an example of the average operating state during the heating period. Receipts of outside heat is not. At an average outdoor temperature, a floor with a temperature of 24 ° C gives off all the heat to the room air, in which the temperature is maintained at 20 ° C. At 0% of third-party heat gains, the heat dissipation of the floor is 100%.
Example 2. The boundary conditions are the same, but due to the influx of external heat, the temperature in the room has increased to 22 ° С (Fig. 2). As a result, the heat emission of the floor decreased by half, since the difference in temperature between the floor and the air decreased to 2 ° C. In this case, the "warm floor" covers only 50% of the heat load, the remaining 50% of the heat comes from third-party sources.
Example 3. Due to the large heat input from outside, the room temperature increased to 24 ° С, equaling the floor temperature (Fig. 3). As a result, the heat output of underfloor heating dropped to zero. That is, the entire heat load is covered in this case with heat from third-party sources.
Example 4. Windows were opened for ventilation in the room, and the temperature of the room air was briefly reduced to 16 ° C (Fig. 4). The temperature difference between the floor and the air reached 8 ° С, which resulted in an increase in the floor heat transfer up to 200%.
The document requires the organization to regulate the temperature of the coolant supplied to the building depending on the outdoor temperature (EnEV § 12/1). This ensures that the amount of heat that can be used in the near future is delivered to the distribution network.
In addition, the amount of heat supplied to the premises should be regulated depending on the temperature of their internal air (EnEV § 12/2), which makes it possible to adjust the heating operation taking into account the external heat input — from solar radiation, household appliances, etc.
In fig. 5 shows a schematic diagram of the floor heating of a building, including the following elements of regulation with regard to the requirements listed above: AT - outdoor temperature sensor; MV– three-way valve of the building; RF - air temperature sensor in the room; RV - room control valve.
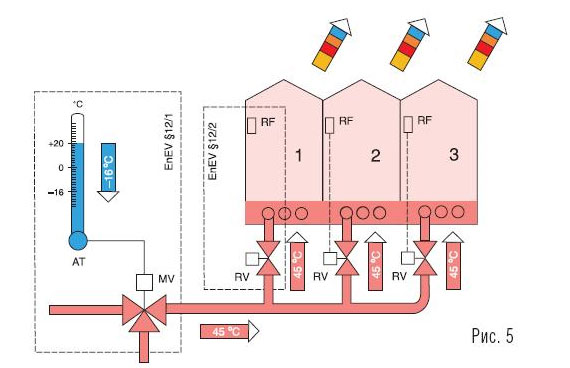 With a correctly calculated and hydraulically adjusted heating installation, it would be sufficient only for weather-dependent regulation with a change in the temperature of the coolant supplied to the building, provided that there is no external heat input. However, the effect of self-regulation is an indispensable component of real processes.
With a correctly calculated and hydraulically adjusted heating installation, it would be sufficient only for weather-dependent regulation with a change in the temperature of the coolant supplied to the building, provided that there is no external heat input. However, the effect of self-regulation is an indispensable component of real processes.
Regulation of temperature in rooms by changing the amount of coolant supplied saves energy. However, if the flow control is carried out in the "on / off" mode, underfloor heating may not ensure the maintenance of a comfortable temperature.
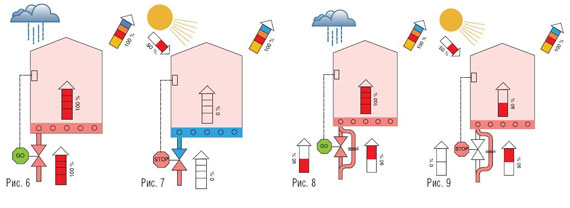
Let there be no external heat supply: heat is supplied to the room only from the floor, and it enters the environment through the enclosing structures (Fig. 6). If the room begins to be heated by the sun, the inlet valve closes (Fig. 7), and after about two hours the floor and the room are cooled.
In the case of short-term intensive intakes of third-party heat, the control system does not cope with the work, as a result of which there are fluctuations in the temperature of the room and the floor.
This disadvantage can be eliminated by increasing the heat transfer of the floor by laying a heating pipe with a smaller pitch (artificial overheating of the room increases the frequency of the thermostatic valve).
However, the best result is provided by the installation of a control valve, which does not completely shut off the flow of the coolant, but reduces it in terms of compensation for the maximum possible supply of third-party heat. This allows you to reduce fluctuations in floor temperature and air in the room. Favorable effect and the use of floor temperature sensors.
In fig. 8, 9 the principle of operation of the underfloor heating control system with a bypass connected in parallel with the thermostatic valve is shown. The bypass is adjusted to skip such a quantity of coolant so that the heat loss of the room is fully compensated for in total with the heat coming from a third-party source. (In the example shown, this is 50% of the flow.) Compact modules with a thermostatic valve and adjustable bypass are offered by Oventrop.
How UPONOR is looking at the task of automatic control (one of the largest manufacturers, who by the way agree with this point of view):
Automatic control
Automatic control system warm
the floor must support admission
heat with the same intensity with which
the room loses it under the influence
dynamically changing conditions, supporting
thereby stable and comfortable
indoor temperature.
The results of tests in real conditions
show that with proper operation
control systems and due to the high
degree of autonomy of management,
underfloor heating system is capable
compensate for all the heat loss of the room.
For optimum performance
a combination is recommended
centralized regulation and
regulation in separate rooms.
Centralized control system
controls temperature
the coolant supplied in accordance with
weather conditions outside.
Regulatory system in individual
indoors controls the flow of coolant
in each circuit depending on the readings
temperature sensors (thermostats),
located in the appropriate rooms
and user-defined parameters.
This allows you to control heat dissipation.
floors in each room individually,
what the comforr most accurately provides
and energy savings.
Temperature in separate rooms
Local (individual) regulation
used when controlled
heat supplied to the heated room.
The main idea of individual control
is a local increase
comfort in a certain room
and in saving energy by setting
estimated indoor temperature
directly by any person.
Room temperature control
necessary to create the best
comfortable climate inside the building. AT
depending on external factors (orientation
buildings, wind, etc.) or internal factors
(lighting, open flame sources,
residence time, etc.)
There are different heat requirements.
mode inside the building.
Underfloor heating systems can
satisfy all these requirements. In each
the room can be exact
temperature adjustment by
temperature sensors (thermostats).
However, with an open layout, various
"Rooms" can be considered as one
space (zone control). In this case
Uponor recommends using
only one room thermostat for
regulation in all open space,
at the same time the thermostat is installed in
"Room" with the greatest need
in heating. This is usually a room with
the largest number of exterior walls or windows.
Zone control
Zone regulation is applied in
when heat is controlled,
served in any zone consisting
usually from several rooms (rooms).
Zone control is used to control
certain group of rooms or
rooms with open plan.
Centralized control
Centralized regulation applies
in cases where the heat supplied to the whole
building or in a collector controlled by the system
centralized remote control
management or from the thermal point (ITP).
Principles of coolant temperature control
...
internal heat carrier
at constant flow
Some climate specialists in
premises believe that the adjustment is
internal temperature is the best
a way to maintain a comfortable temperature.
The rationale for this is the fact that
most buildings have very high
thermal inertia. This means that when
rapid change in outdoor temperature
changing the internal temperature can
delay for several days. In other words,
internal temperature control
in harmony with the thermal inertia of buildings.
The use of this regulatory technology
minimizes temperature fluctuations in
premises.
Temperature control
heat carrier on outside temperature
at constant flow
In contrast to the above
Some experts believe that the best
way to maintain a comfortable
temperature is regulation on the outside
temperature The reason for this is
in that it becomes possible to work
with a predetermined temperature schedule
the coolant as a function
outside temperature. Here is the main
the advantage is that when raising
outside temperature control system
Immediately lowers the flow temperature
thereby reducing unwanted losses
heat On the other hand, lowering the outer
temperature always creates a sharp jump up
internal room temperature.
Feed temperature compensated
according to outdoor temperature.
The regulation system setting works by
programmed heating schedule
for this building. Regulating device
is a 3-way valve centralized
control systems.
System diagram with regulators
Each heating season presents its surprises with the difficulties of heating the rooms, both for residents of high-rise buildings and private cottages. The quality of uniform heating of all rooms in a house depends on how it is adjusted.
What is the need to make adjustment
Setting the optimal temperature of the radiators allows you to create the most comfortable conditions of stay indoors. In addition, the adjustment allows:
- Remove the effect of airing in the batteries, enable the coolant to move freely through the heating system pipeline, effectively giving up its heat to the interior space of the room.
- Reduce heat consumption costs to 25%.
- Do not keep the windows open at all times if the air in the room is excessively overheated.
Adjusting the heating and adjusting the battery, it is desirable to engage before the start of the heating season. This is necessary in order not to experience discomfort in the apartment and not to set the heating temperature of the batteries in an emergency mode. Before adjusting and adjusting radiators, it is necessary in the summer to make all windows insulated. In addition, you need to take into account the particular location of the apartment:
- In the middle or in the corner of the house.
- Lower or upper floor.
After analyzing the situation, it is desirable to use energy-saving technologies to maximize the heat inside the apartment:
- To warm the walls, corners, floors.
- Carry out the hydro and thermal insulation of the joints between the concrete joints of the panel house.
Without these works, it will be useless to regulate the temperature of radiators, since the lion's share of heat will warm the street.
Types of heating systems and the principle of radiator adjustment

Handle with valve
In order to properly adjust the temperature of the radiators, you need to know the general arrangement of the heating system and the heat carrier wiring.
- In the case of individual heating, the adjustment is easier when:
- The system is powered by a powerful boiler.
- Each battery is equipped with a three-way valve.
- Mounted forced pumping of the coolant.
At the stage of installation work of individual heating, it is necessary to take into account the minimum number of bends in the system. This is necessary in order to reduce heat loss and not reduce the pressure of the coolant supplied to the radiators.
For uniform heating and efficient use of heat, a valve is mounted on each battery. With it you can reduce the water supply or turn it off from the general heating system in an unused room.
- In the central heating system of multi-storey buildings equipped with coolant supply through the pipeline from top to bottom vertically, it is impossible to adjust the radiators. In this situation, the upper floors open windows because of the heat, and it is cold in the rooms of the lower floors, as the batteries there are barely warm.
- More perfect one-pipe network. Here the coolant is supplied to each battery and then returned to the central riser. Therefore, there is no noticeable temperature difference in the apartments of the upper and lower floors of these houses. In this case, the feed pipe of each radiator is equipped with a control valve.
- The two-pipe system, where two risers are mounted, provides the flow of coolant to the radiator and back. To increase or decrease the coolant flow, each battery is equipped with a separate valve with a manual or automatic thermostat.
Types of adjustment valves
Types of cranes
Existing modern heating technologies allow installing a special faucet on each radiator that controls the quality of heat. This adjustment valve is a heat exchanger of valves, which is connected via pipes to the radiator.
According to the principle of their work, these cranes are:
- Ball, which are primarily 100% protection from emergency situations. These shut-off devices are a structure that can be rotated 90 degrees, and can pass water or interfere with the passage of coolant.
The ball valve must not be left half open, as in this case the sealing ring may be damaged and leakage may occur.
- Standard where there is no temperature scale. They are represented by traditional budget valves. They do not give absolute accuracy of adjustment. Partially blocking the access of the coolant to the radiator, they change the temperature in the apartment to an indefinite value.
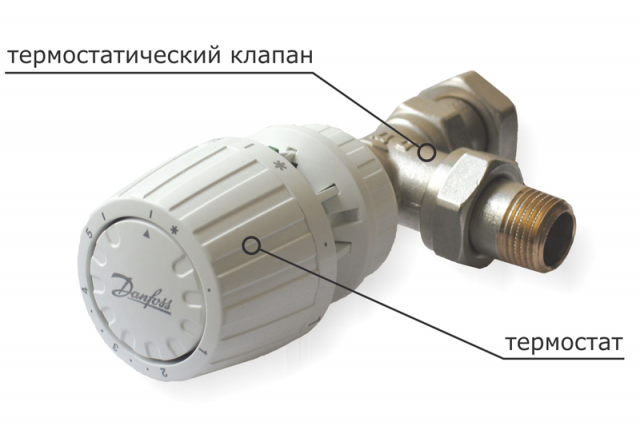
- With a thermal head that allows you to adjust and control the parameters of the heating system. Such thermostats are automatic and mechanical.
Normal direct thermostat
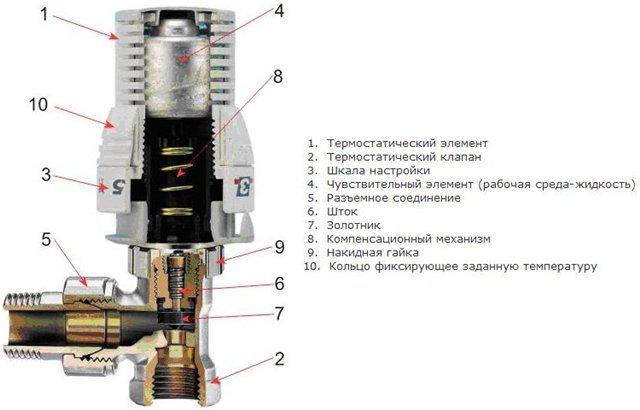
Principle of the device
Direct-acting thermostat is a simple device for controlling the temperature in a heating radiator, which is installed next to it. According to its design, it is a hermetic cylinder into which a siphon with a special liquid or gas is inserted that clearly reacts to changes in the temperature of the coolant.
When it rises, the liquid or gas expands. This leads to an increase in pressure on the stem in the thermostat valve. He, in turn, moving, blocks the flow of coolant. When cooling the radiator, the reverse occurs.
Thermostat with electronic sensor
This device does not differ in principle from the previous version, the only difference is in the settings. If they are performed manually in a conventional thermostat, the electronic sensor does not need it.
Here the temperature is set in advance, and the sensor monitors its maintenance within the specified limits. The control parameters of air temperature electronic thermostatic sensor adjusts from 6 to 26 degrees.
Step by step temperature adjustment instructions
To ensure comfortable conditions in the room you need to perform some basic actions.
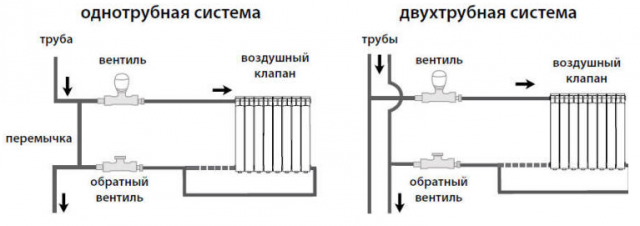
Wiring diagrams
- Initially, on each battery, it is necessary to bleed air before water flows from the tap in a trickle.
- Then you need to adjust the pressure in the batteries.
- To do this, in the first battery from the boiler you need to open the valve two turns, the second - three, and then follow the same scheme, increasing the number of turns of the open valve on each radiator. Thus, the pressure of the coolant is evenly distributed over all radiators. This will provide him with a normal passage through the pipes and the best heating of the batteries.
- In a forced heating system, the pumping of the coolant and the control of rational heat consumption will help to make control valves.
- In a flow system, the temperature, temperature controllers built into each battery, is well controlled.
- In a two-pipe heating system, it is possible to control not only the temperature of the heating medium, but also its quantity in batteries using both manual and automatic control systems.
Conclusion

Installation completed
Today, to maintain a comfortable temperature in the apartment, each radiator of the heating system must be equipped with an adjustment system.
Modern thermostats help not only maintain the heat balance indoors, but also save energy for heating the coolant.
