Bloating in a child of 5 years. Treatment and causes of flatulence in children
N. Sturov, RUDN
The anatomical and physiological features of the children's body predispose to the occurrence of functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT); they are most frequent in children of the 1st year due to the complex process of adaptation to extrauterine life. Functional disorders include conditions caused by imperfections of the motor (physiological gastroesophageal reflux, impaired peristalsis of the stomach and antropilaric body, dyskinesia of the small and large intestine) and secretory (variability of the amount and activity of digestive enzymes - lipases, pepsin, disaccharidases) of the gastrointestinal tract, which leads to the appearance of symptoms of regurgitation, intestinal colic, flatulence, etc. More frequently affected are weakened children: with chronic eating disorders, premature, with rickets, anomalies of the constitution. Predisposing factors consider the nature of food that does not correspond to the child’s age, a quick transition to artificial feeding, a sharp predominance of fat, protein or carbohydrates in food, too frequent feeding, overfeeding.
Flatulence (bloating as a result of the accumulation of gases in the intestinal lumen and the difficulty of their discharge) is one of the manifestations of the so-called lower dyspepsia. Increased flatulence is accompanied by a feeling of fullness, rumbling in the stomach, colic, followed by discharge of gases (flatulency).
About 70% of the gas contained in the baby’s gastrointestinal tract is air, swallowed by crying, crying, feeding. A significant proportion of gases are formed in the lumen of the intestine itself with the participation of microflora, which begins to colonize the gastrointestinal tract. Some of the gases diffuse from the blood plasma into the lumen of the intestine due to the difference in partial pressure, mainly nitrogen (due to the greatest gradient of partial pressure between the lumen of the intestine and blood).
Depending on the cause of flatulence with functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract can be divided into alimentary, digestive, dysbiotic, dynamic, psychogenic, although usually there are mixed forms.
Alimentary meteorism occurs due to the use of products, the process of digestion of which is accompanied by an increased release of gases in the intestine (oligo- and polysaccharides). The individual characteristics of the organism also have a certain value: the composition of the microflora, the absorptive capacity of the child’s intestines, the rate of gastric emptying. A great contribution to the development of alimentary meteorism in childhood is made by aerophagy due to the reasons indicated above.
Digestive meteorism is a consequence of a violation of the processes of digestion in a child: the imperfection of the work of digestive enzymes in parallel with other functional disorders leads to the accumulation of a large number of underdeveloped products that are exposed to microflora with the formation of gases.
In preterm infants with a body weight deficit, intestinal lactase levels are often lowered, which is transient in nature; it is associated with the morphofunctional immaturity of the intestines and is triggered by the transition to mixed or artificial feeding. Excessive carbohydrates become a substrate for microflora and provoke the development of flatulence. The diagnosis of "lactase deficiency" in this case is based on the increase in carbohydrate feces to the level of\u003e 0.25%. This condition is considered the reason for the correction of the child's nutrition and a significant restriction of the diet of a nursing mother, which is not always true. It should be remembered that practically healthy children are often found in pediatric practice, in which in the first months of life the carbohydrate content of feces is significantly higher than the specified level, but, as a rule, it normalizes itself by the 6th-8th month of life.
Dysbiotic meteorism develops due to excessive activity of microflora in the intestines of a child, since at an early age the mechanisms for suppressing the excessive growth of bacteria do not work effectively enough. Microorganisms process food components already in the upper small intestine with the release of gaseous substances. At the same time, rotting and fermentation are significantly activated in the lower parts of the digestive system, which release an increased amount of gases and create quite favorable conditions for increased reproduction of microflora, since many substances formed during the fermentation process affect the nerve plexuses of the intestine and inhibit peristalsis (constipation), contributing to the development dynamic flatulence.
Dynamic meteorism is also observed when a violation of the gastrointestinal tract motor function is initially present. Due to reduced motility, the gases cease to flow away and accumulate with the underdeveloped food components; the latter begin to be metabolized by microflora with the release of gaseous compounds. The meteorism that occurs in some anomalous variants of the structure and position of the large intestine with its lengthening or pathological mobility can also be attributed to the dynamic.
Among the causes of flatulence are various nervous disorders and excessive emotional anxiety of the child. Over-stimulation of the nervous system easily leads to hypertonicity and spasm of the smooth muscles of the intestine, which slows down peristalsis and causes the development of pain of varying severity up to colic.
Intestinal colic is a particular manifestation of abdominal pain syndrome that serves as a sign of many diseases of the digestive system. In infants, the equivalent of pain is anxiety, cry, and rejection of the mother’s chest. Sometimes pain can manifest itself as a feeling of rapid satiety and overflow of the stomach. Another component of pain in intestinal colic is due to increased gas formation and stretching of the intestinal wall. Gas filling the intestines against the background of feeding or in the process of digestion is accompanied by a spasm of intestinal areas and pain syndrome.
Another important reason for a child to develop flatulence and colic is defects in the mother’s diet. breastfeeding: the use of spicy, spicy foods, whole cow milk and products that cause increased gas formation. In general, the causes of flatulence and intestinal colic are similar.
When diagnosing flatulence and colic, it is important not to miss any pathological condition that can objectively manifest, like children's intestinal colic, crying, anxiety, abdominal distension, impaired stool, etc. . With colic, the child’s general condition does not deteriorate, there is no lag in body mass and psychomotor development; complete blood count, urine, scatological research - without significant pathological changes.
The treatment of meteorism and colic associated with it is based on several principles. The main one is to eliminate as far as possible the causes of increased gas formation; for this, it is necessary to choose the right diet, restore the intestinal biocenosis, eliminate existing diseases of the upper digestive tract, etc. Another principle is the actual removal of accumulated gases from the intestinal lumen. For this purpose, use several groups of drugs.
Drugs that enhance the motility, promote the rapid removal of gases from the intestine. These include, in particular, include prokinetics, dill, cumin preparations. Plantex is widely used as a phytopreparation that stimulates digestion and reduces gas formation. The fruits of fennel and essential oil of fennel, included in its composition, increase the secretion of gastric juice and increase motility of the intestine. The active ingredients prevent the accumulation of gases and contribute to their discharge, and also have an antispasmodic effect. In addition, Plantex has antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, vasodilator, analgesic, choleretic and enveloping effect, contributes to an increase in appetite. Plantex is indicated for flatulence, spastic pains in the intestines with minor digestive disorders, as well as when switching from breastfeeding to other types of food. Plantex is recommended for use in children from 2 weeks of age.
It is possible to use adsorbents that absorb excess amounts of gases and with them are removed from the body. The most famous drugs of this group are activated carbon, as well as preparations based on dioctahedral smectite. When using adsorbents, microorganisms, minerals and vitamins can be removed from the intestinal lumen together with gases, the lack of which later must be compensated.
The action of defoamers is based on the release of gases from mucous bubbles, which reduces the total volume of gas and facilitates its discharge. Simethicone, a mixture of dimethylsiloxane polymer with silica, is widely distributed among defoamers.
It should be remembered about the physical methods of correcting flatulence and intestinal colic. Traditionally, it is customary to hold the child upright or lying on the stomach, preferably with legs bent at the knee joints, on a warm heating pad or diaper; useful massage of the abdomen. It is possible to facilitate the passage of gases and feces with the help of the vapor tube or enema, it is possible to introduce suppositories with glycerin. Some researchers propose to prescribe drug therapy using prokinetics and antispasmodics only in the absence of a positive effect from physical methods (staged therapy).
The question of the expediency of including enzymes and biologics in the complex correction of the state of children with intestinal colic remains controversial, although in most cases in the first months of life there is a delayed formation of intestinal microbiocenosis, which is in favor of prescribing eubiotics.
Literature
Abdominal bloating (flatulence) is an increased production and accumulation of gas in the intestines, accompanied by various clinical manifestations. It occurs often, is observed at different ages - from infants to schoolchildren. Independent disease is not. This is a symptom, meaning that a lot of gas has accumulated in the intestines, which bulges its walls and causes pain or other discomfort. Most often accompanies the pathology of the intestine or occurs for other reasons not related to disease.
Causes of gas formation

Normally, the process of gas formation in the intestine occurs constantly. This is a physiological phenomenon that does not violate general well-being and proceeds unnoticed. The reasons for it are different:
- swallowing a certain amount of gases in the process of eating;
- digestion of food, which is a chain of biochemical reactions of the breakdown of proteins, fats and carbohydrates with the release of gases;
- diffusion (gas exchange), when oxygen from the vessels of the intestinal wall, which is necessary for the normal functioning of certain bacteria, enters the lumen, and carbon dioxide is removed by venous blood and excreted by the lungs;
- vital activity of the intestinal microflora itself, emitting carbon dioxide in the process of food processing.
Gases formed in a healthy body, improve the process of digestion: increase intestinal motility, help better "digestion" of food and the rapid release of the intestine. But sometimes the mechanism of gas formation fails, and the child appears signs of flatulence.
Causes of flatulence
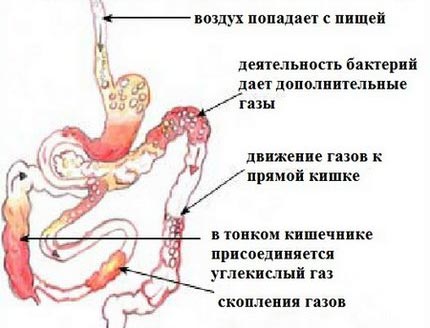
The causes of bloating that cause feeling unwell are different bowel pathologies, which are divided into several groups:
- Diseases of the digestive organs of inflammatory nature (pancreatitis, intestinal inflammation - colitis, etc.).
- Non-inflammatory (dysbacteriosis, enzymatic disorders) - diseases associated with disorders of the digestion process.
- Infectious diseases with intestinal damage - helminth infections, protozoal infections (amebiasis, etc.), acute intestinal infections, in which flatulence is combined with diarrhea.
- Congenital malformations of the colon and its location - its lengthening (dolichosigma) or increased mobility.
Flatulence also develops due to alimentary (food) causes. The most frequent of them are: overeating, breaking the diet, eating large amounts of fat, carbonated drinks, products that increase gas formation (legumes, black bread, beer), an insufficient amount in the diet of plant fibers.
Intestinal colic in children premature and weak, with signs of malnutrition occur much more often than in healthy babies at birth.
Other factors
In addition to the above, there are other factors leading to flatulence in infants. They are related to feeding the nursing mother. Some foods cause gas formation in newborns:
- spicy seasonings and spices;
- whole cow milk;
- legumes, grapes, cabbage;
- black bread;
- drinks with gases, etc.
Flatulence in children who are not breastfed, and artificial feeding, can be caused by:
- unadapted for feeding the child at this age mixtures;
- early feeding;
- violation of the multiplicity and time of the diet;
- psychogenic factors.
The mechanism of the formation of intestinal swelling and pain during gas formation is directly related to overexcitement or stress. The release of adrenaline into the blood leads to a narrowing of blood vessels, which significantly reduces the excretion and absorption of gases. Stress also increases intestinal tone, as a result: peristalsis and food movement slow down, fermentation and decay processes increase, and, therefore, increasing the amount of gases in a child. Bursting, tight stomach, cramps and diarrhea appear.
Manifestations of pathology in children
Strong gas formation in the intestine leads to the appearance of a fetid odor, chronic abdominal pain, uncontrolled discharge of gas (more than 20 times a day).
Increased flatulence is also manifested by an increase in the abdomen, acute paroxysmal or arching abdominal pain, belching, or hiccups.
Children suffer from increased flatulence very often and at any age - this is a common problem. But the most troubles are bloating in newborns. At the age of about 5 months, the child’s body is characterized by an undeveloped digestive system - the absence of normal microflora in the intestine. In addition, infants have an undeveloped enzyme system, which will be improved only by 4–5 months.
It also leads to fermentation in the intestines, resulting in abdominal distension, spastic contraction of some parts of the intestines and relaxation of others, which is manifested by intestinal colic - sharp paroxysmal abdominal pain in an infant. The causes and treatment of this condition are always interrelated, it is necessary to understand their mechanisms in order to know what medicine for flatulence and bloating to give to a child.
Symptoms in newborns

In general, the general condition of a child with increased gas formation is not disturbed: there is no lag in development and growth. Difficulties arise only with small children: a child has a 1 year old and, especially, a newborn, it is impossible to clarify complaints. But you can understand that a stomach ache can be done indirectly by the behavior of the baby:
- the child constantly releases gases;
- constantly screaming, restless, showing increased activity, not sleeping;
- does not take the breast;
- if you manage to feed - quickly saturated.
Due to the strong gas in the intestines, the stomach becomes even more puffy. In relation to intestinal colic, which is the main symptom of flatulence at this age, there is a rule of "three":
- appears in the third month of life;
- lasts up to three hours;
- finally takes place at the age of three months.
Symptoms in preschool children

A child has 2 years of life suffering from bloating, the following reasons come to the fore:
- eating large amounts of easily digestible carbohydrates: grapes, chocolate, muffin, etc .;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- overweight;
- fermentopathy (insufficient production of lactase, splitting milk sugar);
- violation of intestinal microflora.
Similar causes cause belching in a 3-year-old child, in addition to other manifestations of increased gas formation. But at this age, flatulence develops much less frequently than children under one year old.
A child of 4 years of life shows signs of flatulence from the first days of attending kindergarten. This is due to a change in diet, in connection with which the intestine undergoes adaptation processes. A hard belly in a child, burping with air, frequent discharge of gases leads to stress, which in turn, enhances the process of gas formation.
In such cases, a mandatory consultation with a doctor is necessary to establish the causes of this condition and to know how to deal with flatulence and bloating.
In a 6 year old child, the causes and clinical manifestations differ little from those in the previous age group. May play a role:
- expanding the diet when more sweets are eaten and soda, raw vegetables;
- wrong combination of products;
- chewing gum;
- great psychological stress and stress if the child began to attend school.
When a child has a hard stomach and complaints of rumbling, pain, belching after a meal, it is necessary to adjust the diet during gas formation.
First aid and treatment
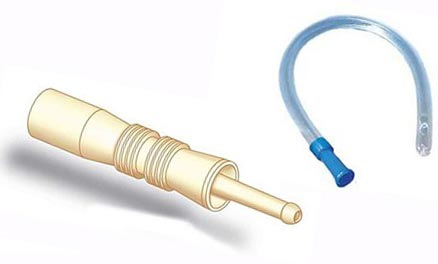
First aid for bloating, which can be given to a child at home, consists of the following measures:
- to massage the abdomen in a clockwise direction;
- give the child from the stomach dill water or Plantex - herbal medicine against flatulence based on fennel;
- in case of inefficiency, simethicone (Espumizan, Infacol, Bobotik, Bebinos), which is a symptomatic means of abdominal distention, which removes gas from the intestine, but does not cure flatulence;
- if the child has constipation, leading to pain when gas is formed, a glycerin suppository can be administered;
- in extreme cases, use a tube to remove gases;
- in older children with constipation leading to flatulence, a cleansing enema is possible.
Important! Treatment of flatulence should take place exclusively under the supervision of a physician. Self-medication is unacceptable, because often the increased gas formation in a child occurs due to the development of serious diseases of the digestive tract (pancreatitis, colitis, dysbacteriosis), in the presence of helminth infections, congenital bowel disease. Medicines to be taken for bloating are prescribed only by a doctor.
Therapeutic measures depend on the age of the child and the causes of pathology. After determining the etiological factor (the cause of meteorism) anti-inflammatory treatment is carried out, if necessary - antibiotic therapy. Preparations are used to restore the normal intestinal microflora, symptomatic therapy (antispasmodics for pain, laxatives, medicines that actively absorb the gases).
Prevention
Watch the video of Dr. Komarovsky - what to do if a child has a stomach ache:
Prevention of flatulence in the intestines, on the advice of Dr. Komarovsky, must be started long before the development of flatulence. Background correction of the event is applied, which allows to avoid the accumulation of gases in the intestine in 15% of children, if you follow certain rules:
- breastfeeding;
- strict adherence to a nursing mother's diet;
- putting a small child on the belly after feeding.
Are you one of those millions of women who are struggling with being overweight?
And all your attempts to lose weight did not succeed?
And have you already thought about radical measures? It is understandable, because a slim figure is an indicator of health and a reason for pride. In addition, it is at least the longevity of man. And the fact that a person losing “extra pounds” looks younger is an axiom that does not require proof.
Older children need regular walks with outdoor games, a favorable psychological environment at home, in kindergarten, at school, with the exception of overeating, dieting. Doing these simple tips will prevent children from experiencing flatulence.
Flatulence - increased flatulence and in the intestines - a phenomenon common in adults and children. It is not a disease, but it may be a symptom of a disease, or a condition caused by another cause. Normally, the formation of gases occurs in adults and in children, but in quantities that do not cause discomfort or pain, this process is imperceptible to a healthy organism. But flatulence in a child is always accompanied by unpleasant symptoms and is a serious problem for parents. Abdominal bloating in a child is of particular concern and requires increased attention and quick identification of the cause of this condition.
Causes of Strong Gas Formation
Especially often flatulence occurs in an infant, although in other age categories it is not uncommon. In children, increased gas formation occurs due to the imperfection of the development and functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Excess amount of gas in the intestine puts pressure on its walls, causing an increase in the abdomen and a sharp pain syndrome - intestinal colic. They disturb the baby up to 3 - 4 months, then often spontaneously stop.
The reasons leading to the development of a child bloating are diverse, but at each age have their own characteristics.
The most common cause of flatulence in children when treatment is not required is not the fully developed digestive and nervous systems.
In a newborn child and up to about 5 months of age, the intestine is sterile: it lacks the normal intestinal microflora, which takes part in the digestive process and creates a balance with conditionally pathogenic flora when dysbiosis occurs or pathogenic microorganisms enter the intestine. The enzyme system is also being adjusted to the same age: the imperfection of the production of enzymes in an infant also causes increased gas formation. All this leads to the fermentation process in the intestines, the tummy of the infant puchitis, there are severe pains due to spastic contractions of some parts of the intestines and stretching others due to flatulence. These mechanisms need to be understood in order to know how to help a child with bloating.
Other reasons
There are other causes of bloating in an infant:
- errors in the mother's diet: spicy seasonings, coarse fiber (black bread), fresh vegetables (cabbage, tomatoes), legumes, whole milk, etc .;
- the use of unadapted mixtures during artificial feeding;
- age-appropriate supplements;
- overeating and eating disorders;
- infectious diseases;
- psychogenic factor: during overexcitation or stress under the influence of adrenaline, vasoconstriction occurs, which inhibits the excretion and absorption of gases. In addition, stress leads to an increase in intestinal tone, slowing the movement of food, and to the processes of its fermentation, decay, and, therefore, to increased gas formation (during fermentation gases with the smell of rotten eggs are formed).
In older children, causes of flatulence are gastritis, pancreatitis, colitis, and various helminth infections. They play a major role neurosis.
Self-medication is unacceptable
In order to know what to do if a newborn has a tummy tummy, an air burp appears, the temperature rises, boils in the stomach, you need to contact a pediatrician.
It is dangerous to treat an infant without knowing the exact causes of this condition - you can miss a serious illness in which flatulence is one of its manifestations (for example, intestinal obstruction, dysbiosis, intestinal infection).
Clinical manifestations
The main clinical manifestations of flatulence in the newborn:
- discomfort and paroxysmal abdominal pain;
- belching, hiccups for no apparent reason;
- feeling of bloating, lack of appetite;
- sometimes - nausea, vomiting, in infants - regurgitation;
- stool disorders - there may be alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- infants become moody, their sleep is disturbed;
- the temperature remains normal.
Features of clinical symptoms in infants
In general, the general condition is not disturbed: the baby grows and develops according to his age, there is no lag in the physical and psychomotor development of the baby. Difficulties arise when they appear that cannot complain about their condition.
The most characteristic symptom of flatulence in infants is intestinal colic. Because of spastic pain, the baby refuses to breast, quickly becomes saturated, if it is possible to feed him, screams, becomes restless, does not sleep.
Regarding colic, there is a “three” rule:
- arise in the third week of life;
- an attack can last up to three hours in a row;
- disappear without a trace after three months.
It is possible to think that this is a manifestation of intestinal colic, and not a serious surgical pathology, if:
- seizures occur every evening or night at about the same time;
- last 30–60 minutes (sometimes up to 3 hours);
- after the discharge of gas, an improvement occurs (after that, the baby’s tummy stops swelling);
- body temperature does not rise;
- from the mouth of the baby, it ceases to smell unpleasant when belching with air and regurgitation.
Diseases leading to increased gas formation
But if the bouts of intestinal colic in a newborn are long and frequent, they can be a manifestation:
- fermentopathy (lactase deficiency);
- intestinal infection;
- congenital abnormalities of the digestive system.
In breast milk there is milk sugar - lactose. He splits a very active enzyme - lactase, which the newborn is produced in large quantities. In some situations (for example, when overfeeding) the infant develops relative lactase deficiency: the child has eaten a large amount of lactose, for the processing of which he lacked lactase. Its clinical manifestation is a bubbling tummy.
In case of an intestinal infection, besides the fact that the baby has a tummy tummy, there is audible boiling in the intestine with no appetite at all - a burping of a rotten egg appears, the temperature rises to high numbers. Against the background of high temperature, all signs of intoxication appear: nausea, vomiting, belching, and loose stools that have a rotten smell.
To treat a child with an intestinal infection should begin immediately, it should be done by experienced specialists, sometimes, depending on the severity of the condition, in the hospital.
Prevention and treatment of problems
To successfully help a child get rid of flatulence, and, therefore, colic, you need to start prevention long before the child's abdominal distention and mom's sleepless nights.
The so-called background correction avoids the accumulation of gas in the intestine in 15% of infants. The background correction is:
- breast-feeding;
- diet with flatulence in a child, which must be followed by a nursing mother;
- lay on the stomach to strengthen the anterior abdominal wall;
- give dill water or Plantex for bloating;
- make a massage of the abdomen in a clockwise direction, if the colic lasts a long time, not allowing the child to calm down and fall asleep.
The second stage of prevention and treatment
If using these simple rules you can not cope with increased gas formation, you can proceed to the second stage of measures for colic:
- Give the child a drug containing simethicone (Bebinos, Espumizan, Infacol). It is a symptomatic remedy that removes gas from the intestines, but does not cure colic.
- If you have problems with bowel movements, you can introduce a glycerin candle to your child to relieve constipation.
- In extreme cases, use the vent tube.
- With strong and painful cramps, you can give a child an antispasmodic - Riabal or Viburcol. But this is only possible after the appointment of a pediatrician.
Proper nutrition is the key to a healthy bowel
Diet with flatulence in infants should be followed by a nursing mother strictly, so as not to aggravate the condition of the baby. It is necessary to exclude fresh vegetables, sour cabbage, legumes, carbonated drinks. But, in addition to diet, mom needs to drink a sufficient amount of liquid - up to 2.5 liters per day. And remember that flatulence is not a disease, but an unpleasant symptom. Nevertheless, it is necessary to fight with him, making it easier for the child. It is necessary to show increased attention and notice any changes in the behavior of the baby. Not in all cases, the baby is capricious, sometimes crying indicates a health problem.
Patience, the correct understanding of the problem will help to avoid common mistakescommitted by parents.
Flatulence in children or abdominal distention is an increased accumulation of gases in the intestines, their passage is difficult. The problem is often found in children up to a year, their body begins to get used to the new conditions of life, nutrition.
Increased flatulence is not a disease, in most cases it is a symptom of a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract. Many pediatricians do not insist on treating flatulence, but parents want to alleviate the condition of the crumbs, quickly get rid of the problem.
Causes

There are a lot of negative factors affecting the appearance of increased gas formation in children. Flatulence is observed in absolutely healthy children and having gastrointestinal diseases. The main causes of intestinal flatulence:
- due to the immaturity of the children's digestive system. Weak nerve endings, immature muscle tissue in the abdominal area leads to the appearance of colic. Over time, with the proper development of the crumbs, the problem goes away by itself. Increased flatulence is most common in premature babies or in multiple pregnancies;
- ingestion of large amounts of air during feeding or crying. Infants poorly control reflexes, only learn to eat properly. Sometimes the cause of this situation is improper attachment to the breast or feeding from the bottle; (From you can learn about the anti-wheeled baby bottles);
- congenital insufficient production of digestive enzymes causes the occurrence of flatulence;
- overeating or overfeeding a child leads to problems with the digestive system;
- inappropriate age food. Prikorm it is recommended to carry out at that moment when recommended by the pediatrician; (Read more about the rules of introduction of complementary foods, read the address);
- the appearance of colic is affected by an unbalanced diet (the use of soda, fast food, fatty, sweet foods negatively affects the health of the baby);
- the occurrence of colic in a child contributes to the consumption of the following products (bread, spinach, radish, cabbage, all types of legumes, dairy products, if the baby has lactose intolerance);
- frequent constipation provokes the process of fermentation, as a result of which gas formation increases several times, the body does not have time to get rid of them;
- improper feeding formula for babies. (Read the rules on feeding newborns; look at the review of infant formulas; find out the benefits of mixtures without palm oil; see Nan for infant formula; read the Similac mixture; we have an article).
Flatulence in children can signal the course of such diseases:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (, and others);
- acute intestinal infections;
- helminth infection; (About helminthiasis in children read the address);
- the course of inflammatory processes in the intestine;
- neurosis, sometimes the stomach reacts sharply to emotional shocks.
Important! In the first year of life, flatulence in the crumbs is a completely normal process, requiring the use of folk drugs or special preparations. If the problem persists, accompanies the child at an older age, or appears suddenly, consult a doctor. Pathology may indicate a course of serious diseases. The sooner you identify the cause of flatulence, the greater the chances for a speedy recovery of the crumbs.
Symptoms and diagnosis
First you need to find out whether colic is not related to the symptoms of another disease. At the doctor's office, the doctor, with the help of palpation, probes, taps on the child's abdomen, the sound can determine if there is a problem in a particular area. If pathology is detected, additional diagnostic measures are assigned (abdominal ultrasound, x-rays, and others).
When flatulence is observed abundant discharge of gases (involuntary, arbitrary). Doctors identify several additional clinical signs of the presence of the disease in children:
- discomfort in the abdomen or intestines;
- belching, hiccups, appearing for no apparent reason;
- feeling of bloating (fullness), lack of appetite;
- the stomach is visually puffed up; hard to palpation;
- nausea is sometimes noted, in infants - frequent;
- violation of the chair (sometimes two states replace each other);
- asphyxia or shortness of breath (most often seen in premature babies);
- the baby is often naughty, there are problems with sleep.
Infants cannot tell their parents where it hurts, that is why they become capricious, often crying for no reason. Be careful to notice any changes in the behavior of the child. Not in all cases the crumb is capricious, sometimes crying indicates a health problem.
Methods of treatment with medications
How to treat flatulence in children? Independent treatment is not recommended. In any case, visit the doctor, the pediatrician will identify the cause of the problem, prescribe the appropriate treatment. The elimination of colic occurs in several stages:
- corrected diet. Nutrition plays a major role in the occurrence of flatulence. For starters, products that promote increased gas formation are excluded (described above). Meals should be regular, frequent, small portions. The digestive system will get used to the regime, enzymes will quickly be able to split food, the surplus will go out in time;
- elimination of adverse factors, diseases that caused colic in a child. Treatment is prescribed after accurate diagnosis of the problem. This category includes intestinal infections, gastrointestinal ailments, intestinal obstruction, dysbacteriosis;
- using special means of flatulence, they restore the motility of the gastrointestinal tract, normalize the process of digestion (Motilium, Zerukal);
- probiotics, prebiotics restore the natural microflora, promote the growth of positive bacteria (good medicines for flatulence, Lactrofilter);
- the use of enterosorbents, aimed at splitting gases, excretion of accumulated toxins (Smekta, Activated carbon, Polysorb).
How to get rid of flatulence? Additionally, children are prescribed active rest, hardening, and general strengthening of the body. Babies up to two years old are prescribed medication only after consulting with a pediatrician. The following non-specific remedies will help relieve colic of a baby:

- many parents relieve the condition of the baby by warming the abdominal area with a heating pad. Before carrying out manipulations consult with the doctor;
- pediatricians recommend using gas outlet tube (the device is inserted into the anus, helps out the accumulated gases); (For details on how to use the vapor pipe, see the page);
- stroking the tummy clockwise helps some little ones.
Scraps up to the sixth month of life are forbidden to give pills for flatulence, but it is mandatory to give pills. The drug is sold in pharmacies, but it can be made at home: for a glass of boiling water, take a tablespoon of finely chopped dill. Insist the remedy for two hours, give the baby a teaspoon a day, mix with breast milk or regular water.
Dill water has a positive effect on intestinal motility, relaxes the smooth muscles of the intestine, facilitates the process of feces, has a beneficial effect on digestion. Means drink nursing mothers to improve lactation.
Folk remedies and recipes
- pour a glass of boiled water a tablespoon of dry chamomile pharmacy, leave for several hours. Cool the finished product, strain, give the baby a teaspoonful every 4–5 hours;
- mix in equal proportions of dried codling, St. John's wort, yarrow. Fill the mixture with boiling water in the ratio of 1:10, leave for four hours. Children from the age of five are allowed to drink 3-4 cups per day;
- infusion of cumin seeds. A tablespoon of raw materials pour 250 ml hot waterinsist 30 minutes. Ready means give to the kid on the table spoon each time before a meal. The course of treatment is not more than 10 days;
- tincture of parsley. Per 100 ml of water, take a tablespoon of finely chopped parsley, simmer on low heat for 10 minutes. Strain the finished drug, cool, give the child a teaspoon before eating. It is useful to use fresh parsley, it prevents the development of flatulence in children and adults;
- herbal collection of dill seeds (35g), mountain ash (50g), chamomile (35g), valerian root (35g). Mix all the ingredients, pour a glass of boiling water with a spoonful of the mixture, leave for two hours. It is best to prepare the tool in a thermos. After cooling, give the baby a third of a glass before eating. Every time you prepare a new medicine, it is undesirable to store the product in the refrigerator;
- clover infusion. Finely chop the grass, pour a teaspoon of raw materials with 250 ml of boiling water, leave for four hours. Give the baby a quarter cup a few times a day before meals;
- babies are shown taking warm baths several times a week with the addition of chamomile, calendula and anise broth. Medical procedures have a beneficial effect not only on the digestive process, but also prevent the appearance of dermatitis, soothe the baby before bedtime;
- warm tea with mint is an excellent remedy for flatulence for children. In a regular long leaf tea, put a few peppermint leaves. A child up to a year - about a teaspoon three times a day, for children under five years old - about a quarter cup twice a day, older children can drink healthy tea without restrictions.
Children for up to three months pediatricians do not recommend giving any drugs. Sometimes the problem lies in the mother's diet, any inappropriate product adversely affects the baby's digestion (if the baby is breastfed). Young mother should review the diet, exclude foods that cause flatulence.
An important role is played by the process of breastfeeding. Many babies in this moment swallow air, which leads to colic. Make sure that the crumb swallows only a small part of the halo, after feeding, hold the baby in an upright position for half an hour. Avoid strong agitation of the contents of the bottle, air bubbles can get there, which increases the chances of flatulence in the crumbs.
Preventive measures

Prevent the appearance of colic in infants quite easily, to cope with the problem at an older age is possible only if you observe a healthy diet, diet, strengthen the children's body. The following tips will help to prevent flatulence in a newborn:
- hold the baby correctly, immediately after feeding, do not put the baby in a vertical position;
- exclude from your diet chocolate, legumes, sweets, other foods that increase gas formation;
- if the trouble does not go away with time, contact your pediatrician.
The meteorism at the baby does not represent threat for his life, it is necessary to pay attention to the phenomenon, but you should not panic. Consult a doctor, use useful tipsdescribed above.
More interesting details about flatulence in the following video:
Often, the human body fails. In this case, a variety of phenomena may occur, representing inconveniences for its owner. In this article I would like to consider the causes of bloating and gas formation.
Terminology
At the very beginning it is necessary to understand the terms that will be actively used in this article. So, in medical practice, this phenomenon is most often called "flatulence" or "flatulence." People simply say “gas formation”. This is a special condition of the body, when in the intestine due to a number of reasons a lot of gases accumulate. They can cause not just discomfort, but also pain.
Symptomatology
What kind of symptoms can a person observe with bloating? Flatulence may be accompanied by the following conditions:
- Feeling of "inflating" the abdomen.
- Heaviness in the stomach.
- The discharge of gases. Often with unpleasant sounds.
- Belching.
- Unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- Reduced or complete lack of appetite.
- Irritability, weakness, general malaise.
About the reasons
So, what are the most basic causes of bloating and gas formation? First of all, I would like to say that they are formed due to bacteria, which in the large intestine actively ferment carbohydrates (previously not "processed" in the small intestine). Therefore, we can make a simple conclusion that the main cause of gas formation is precisely the intake of certain foods.
Reason 1. Food
So, we consider the main causes of bloating and gas formation. As mentioned above, the first one is nutrition. After all, some food can be a provocateur for such an unpleasant state. This is especially true of foods that are rich in fiber. But they cannot be completely abandoned, because along with the fact that they can cause active formation of gases in the intestines, they still play the most important role in the process of digesting food and the work of the gastrointestinal tract. What are these products?
- Legumes
- Fresh vegetables.
- Fresh fruits.
- Whole grains.
Various types of dietary supplements, which include fiber (including flea plantain), can also lead to increased gas formation. This will be especially noticeable if such preparations are introduced too rapidly in the diet. In addition, abdominal distension and gas formation can be “obtained” if you eat food that is called “fast food”.
Reason 2. Power Mode
Causes of bloating after eating are hidden in a variety of errors in human nutrition. What, then, should be known and remembered?
- Legumes can up to 10 times.
- If you want to avoid flatulence and bloating, it is better to abandon the excessive and too frequent consumption of such foods as cabbage, sorrel, grapes, spinach, raspberries, gooseberries, sweet apples, dates, raisins, beer, kvass, black bread.
- Raw vegetables should be eaten in small quantities. It is best to boil or steam.
- Similarly, it is necessary to cook also meat and poultry. Too greasy and fried foods can also contribute to excessive gas formation and bloating of the intestines.
- You need to eat only in a calm state of the body. This should be done while sitting. Food must be chewed thoroughly, slowly. Also, doctors do not recommend drinking water with water.
Reason 3. Water
- If you drink soda too often.
- If you dramatically change the water familiar to the body (this happens when a person moves for a certain time to a new region of residence - to visit, to rest, etc.).
- If a person likes to drink food with water.
Reason 4. Air ingestion
What are the causes of frequent abdominal distention? So, it may be a habit of too much and often swallow air. It is worth saying that each person daily swallows a certain amount of it. This happens at the time of eating, drinking, talking. This is normal. But in some cases, you can capture too much air, which will lead to its large accumulation in the intestines. Part of it will come out with a belching, part of it will have to leave the body in another natural way. When can a person swallow too much air too much (which leads to bloating and excessive gas formation)?
- Often this happens in those people who love to chew gum.
- Increased gas formation threatens those who like to talk while eating.
- Also, excess air enters the body if a person drinks water through a straw.
- Doctors say that you do not need to wash down food with water. It also leads to gas formation.
- Those people who like to eat “on the go” also suffer from this problem.
Reason 5. Stress and poor lifestyle.
What else are the causes of frequent abdominal distention? So, it can be the most common stress. In this case, the body fails. It can be almost anything. Including To a similar phenomenon also leads to a wrong lifestyle. What does this mean?
- Hypodynamia. Those. when a person leads an inactive, sedentary lifestyle. Scientists say that in such a case, constipation is most often slowed down, which are accompanied by fermentation and decay processes in its lower parts (which leads to active gas formation).
- With an incorrect lifestyle, a person is often diagnosed with a “lazy bowel,” which is also accompanied by increased gas formation.
- It is also necessary to say that for the body to work properly, a person should have enough time to rest. Very important in this case is a full sleep. Only in this way can the intestine "relax" and prepare for work.
Reason 6. Age
What else are the causes of severe abdominal distention? So, this phenomenon is often observed in the elderly. This occurs due to age-related changes in the body. Over time, the musculature of the intestine weakens, which causes flatulence. In medical practice, this condition is called "age atony."
Reason 7. Profession
It should also be said that the causes of bloating in men (as well as women) may be associated with professional activity. So, experts say that climbers often suffer from increased gas formation. This phenomenon is called “high altitude mountaineering”. Everything happens due to the change in pressure during the ascent to a certain height.
Reason 8. Medication intake.
What are the causes of upper abdominal distention? So, intake of certain medications can lead to a similar phenomenon.
- Antibiotics. During their reception the intestinal microflora is often destroyed, which causes increased flatulence.
- Laxatives. If a person abuses their intake, it can lead to increased gas formation, bloating. A similar phenomenon affects women who want to lose weight, cleansing your body with the help of such medical facilities.
Reason 9. Diseases
Some diseases are also the main causes of bloating and nausea. If the diet and the intake of certain products should not cause a similar condition, it is necessary to check with a gastroenterologist. After all, the culprits may be certain diseases. Thus, the abdomen may indicate that a person has diverticulitis, ulcerative colitis, colon cancer, Crohn's disease, or another disease.
Reason 10. Constipation
There are still causes of bloating after eating. So, it can be the most common constipation. In this case, a person has an accumulation of fecal masses, which prevents the normal periodic discharge of gases. They accumulate in the body, which causes bloating, discomfort and other unpleasant sensations.
Reason 11. Food intolerance
What else are the causes of upper abdominal distention? So, if a person, after consuming certain foods, observes a similar condition, one should seek medical help. After all, it may be that the body simply can not or can not process the carbohydrates that are contained in this food product. For example, it can be when a person cannot eat cereals. When consumed, and there is excessive gas formation, bloating.
Women
Separately, I would like to consider the causes of bloating in a woman. After all, quite often the representatives of the fair sex can also have this phenomenon independently of all the reasons listed above.
- Menopause. Abdominal distension is often disturbed by women during this period in life (age from 45 to 60 years). All the fault in this case are hormones that affect the work of the whole organism, including the intestines.
- Premenstrual period. Often bloating is observed in women in the period before menstruation. Again, in this case, everything happens due to changes in hormonal levels.
- Pregnancy. Also during pregnancy, a woman has excessive bloating. If this happens in the first trimester, the hormones are again to blame. If in the last months, this may be due to the fact that the enlarged uterus puts pressure on the intestines, which prevents its normal operation.
Of all the above reasons, we can conclude that any hormonal changes in a woman’s body can cause a variety of problems and unforeseen situations, including strength and bloating.
Children
What are the causes of bloating in a child? If we talk about newborns, then it is to blame for the tuning of the baby’s gastrointestinal tract. The bodies of the crumbs are still not working in the same way as in an adult, they are only being developed, adjusted. In addition, they are still too weak to fully digest even the food that enters the body - mother's milk or a mixture. Often this leads to colic, which affects almost all children under the age of three months. Most often, after the expiration of this period, the gastrointestinal tract is adjusted to work, it is already getting used to new conditions, and this phenomenon disappears by itself. The causes of bloating in the lower abdomen in an older child are most often in the wrong diet or consumption of those foods that contribute to increased gas formation. If the parents and this is excluded, it is necessary to seek help from a doctor. After all, this phenomenon may be a symptom of a disease.
What to do?
Having considered all the possible causes of bloating in a woman, a man and a child, I would like to say a few words about how to cope with this problem. First of all, it is necessary to determine the reason why this is happening. And only then begin to act. You can use the following medications:
- The drug "Motilium". Produced by a Belgian company. This is a remedy for increased gas. Available in three types: tablets (including lingual), as well as in suspension. An important point: the medicine does not need to be drunk, it quickly dissolves in the tongue, immediately starting its work in the intestines.
- The drug "Bobotik". These are drops of the Polish manufacturer, which are mainly prescribed to children (including newborns). However, the drug can also be used by adults. Often, doctors prescribe it to women during pregnancy and lactation.
- The drug "Motilak." Russian remedy, where the active active element is a synthetically created domperidone. The drug is designed to improve intestinal motility, "relieve" bloating, relieve the feeling of overeating, belching and heartburn.
- The drug "Unienzyme". Indian origin. It is an enzymatic digestive remedy containing components that reduce flatulence.
- Drug "Enterosgel". This is an absorbent drug of a new generation. Its main component, polymethylsiloxane polyhydrate, resembles a silicon sponge, which absorbs substances harmful to the body. Available in the form of paste or suspension. It has no side effects and can safely be taken together with other drugs.






